As shown below, a metal rod of length L = 10 cm is being pulled along horizontal, frictionless, conducting rails at a constant velocity v with v = 5.0m/s T В The rails are connected at one end with a metal strip. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B 1.2 T, directed out of the page, fills the region in which the rod moves. The resistance of the rod is R 0.40 2, and assume that the resistance of the rails and metal strip is negligibly small (d) Find the magnitude of the external force on the rod that is needed to maintain the constant velocity (e) This set up is similar to the rail gun we may have looked previously, but this time the current is induced by the motion rather than provided by an external power source. When the current in the rail gun is due to an external source and is constant, and we ignore the effects of Faraday's law, we find that the rod has a constant acceleration. What happens to the acceleration of the rod if we now do include the effects of both an external source and Faraday's (and Lenz's) law, as compared to just the external source? Assume that the source of the current is a battery or similar source that contributes to the total EMF
As shown below, a metal rod of length L = 10 cm is being pulled along horizontal, frictionless, conducting rails at a constant velocity v with v = 5.0m/s T В The rails are connected at one end with a metal strip. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B 1.2 T, directed out of the page, fills the region in which the rod moves. The resistance of the rod is R 0.40 2, and assume that the resistance of the rails and metal strip is negligibly small (d) Find the magnitude of the external force on the rod that is needed to maintain the constant velocity (e) This set up is similar to the rail gun we may have looked previously, but this time the current is induced by the motion rather than provided by an external power source. When the current in the rail gun is due to an external source and is constant, and we ignore the effects of Faraday's law, we find that the rod has a constant acceleration. What happens to the acceleration of the rod if we now do include the effects of both an external source and Faraday's (and Lenz's) law, as compared to just the external source? Assume that the source of the current is a battery or similar source that contributes to the total EMF
Chapter12: Sources Of Magnetic Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 88AP: Two long coaxial copper tubes, each of length L, are connected to a battery of voltage V. The inner...
Related questions
Question
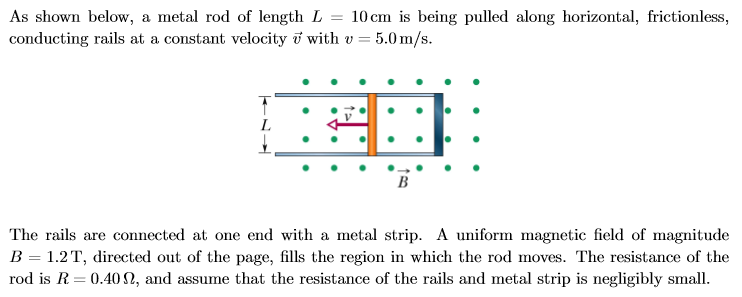
Transcribed Image Text:As shown below, a metal rod of length L = 10 cm is being pulled along horizontal, frictionless,
conducting rails at a constant velocity v with v = 5.0m/s
T
В
The rails are connected at one end with a metal strip. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude
B 1.2 T, directed out of the page, fills the region in which the rod moves. The resistance of the
rod is R 0.40 2, and assume that the resistance of the rails and metal strip is negligibly small

Transcribed Image Text:(d) Find the magnitude of the external force on the rod that is needed to maintain the constant
velocity
(e) This set up is similar to the rail gun we may have looked previously, but this time the current is
induced by the motion rather than provided by an external power source. When the current in
the rail gun is due to an external source and is constant, and we ignore the effects of Faraday's
law, we find that the rod has a constant acceleration. What happens to the acceleration of the
rod if we now do include the effects of both an external source and Faraday's (and Lenz's) law,
as compared to just the external source? Assume that the source of the current is a battery or
similar source that contributes to the total EMF
Expert Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps with 10 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning