Assume that a consumer spends all of her income (B) on good X and good Y, her budget constraint can be expressed as: PxX + PyY = B Where Px is the price of good X, X is the quantity of good X consumed, Py is the price of good Y, Y is the quantity of good Y consumed, and B is the consumer's total income. Rearranging the above equation to get the budget line expressed as Y in terms of X, we have: B Y == Py Py Now, suppose the consumer has an income of $120 to spend on goods X and Y whose prices are $3 and $5 respectively Px -X
Assume that a consumer spends all of her income (B) on good X and good Y, her budget constraint can be expressed as: PxX + PyY = B Where Px is the price of good X, X is the quantity of good X consumed, Py is the price of good Y, Y is the quantity of good Y consumed, and B is the consumer's total income. Rearranging the above equation to get the budget line expressed as Y in terms of X, we have: B Y == Py Py Now, suppose the consumer has an income of $120 to spend on goods X and Y whose prices are $3 and $5 respectively Px -X
Micro Economics For Today
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337613064
Author:Tucker, Irvin B.
Publisher:Tucker, Irvin B.
Chapter6: Consumer Choice Theory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19SQ
Related questions
Question
Graph the budget line showing all the different combinations of good ? (drawn on the horizontal
axis) and good ? (drawn on the vertical axis) that can be bought given the consumer’s total income.
In the graph, indicate the y-intercept and x-intercept of the budget line.
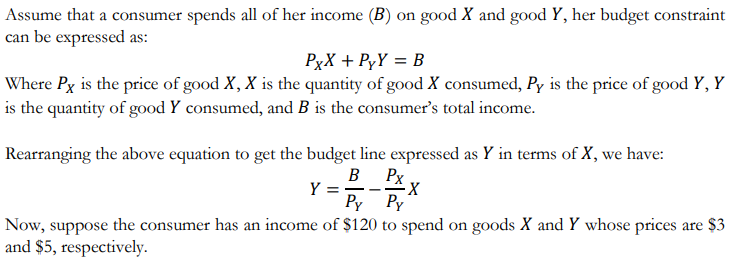
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that a consumer spends all of her income (B) on good X and good Y, her budget constraint
can be expressed as:
PxX + PyY = B
Where Px is the price of good X, X is the quantity of good X consumed, Py is the price of good Y, Y
is the quantity of good Y consumed, and B is the consumer's total income.
Rearranging the above equation to get the budget line expressed as Y in terms of X, we have:
B
Y ==
Py Py
Px
-X
Now, suppose the consumer has an income of $120 to spend on goods X and Y whose prices are $3
and $5, respectively.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you







Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning