At 700 K the equilibrium constant for the reaction CCl4 (g) C(s) + 2Cl₂(g) is Kp = 0.76. A flask is charged with 1.60 atm of CC14, which then reaches equilibrium at 700 K. Part C What is the partial pressure of C1₂ at equilibrium? Express your answer using two significant figures. [5] ΑΣΦ P= 0.58 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining atm
At 700 K the equilibrium constant for the reaction CCl4 (g) C(s) + 2Cl₂(g) is Kp = 0.76. A flask is charged with 1.60 atm of CC14, which then reaches equilibrium at 700 K. Part C What is the partial pressure of C1₂ at equilibrium? Express your answer using two significant figures. [5] ΑΣΦ P= 0.58 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining atm
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section12.5: Using Equilibrium Constants
Problem 12.7CE
Related questions
Question
Please explain- thanks!
Background and question:
Please provide only typed answer solution no handwritten solution needed allowed
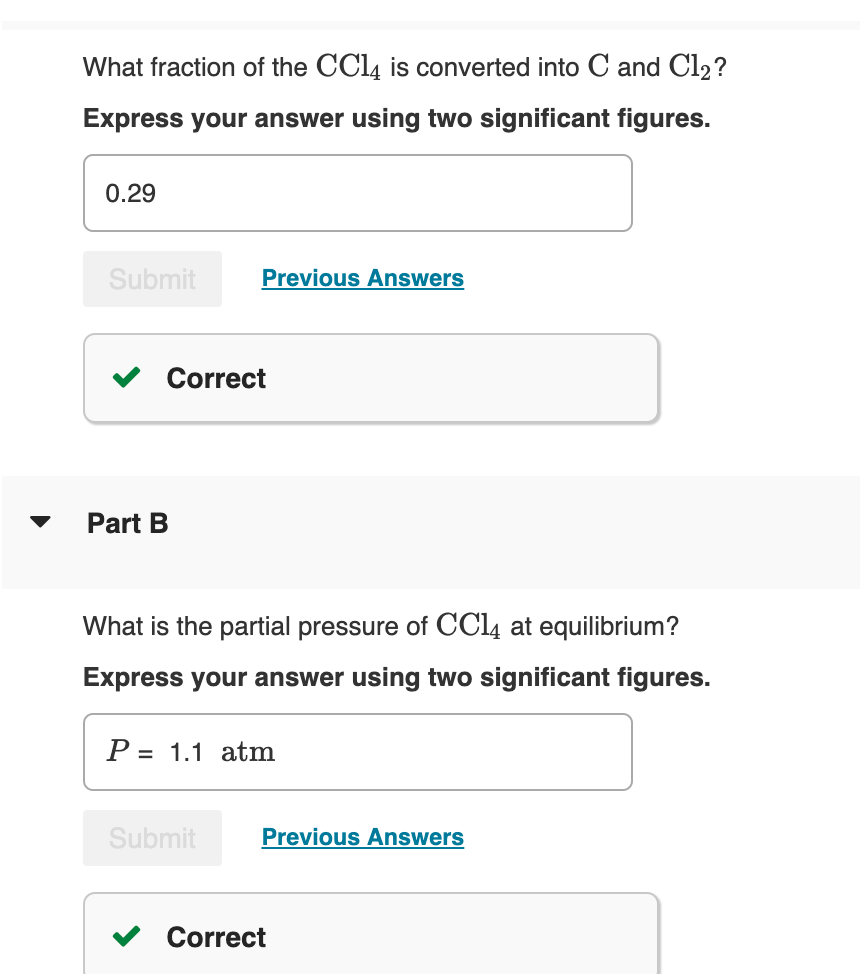
Transcribed Image Text:What fraction of the CCl4 is converted into C and Cl₂?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
0.29
Submit
Correct
Part B
Previous Answers
What is the partial pressure of CC14 at equilibrium?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
P= 1.1 atm
Submit
Previous Answers
Correct
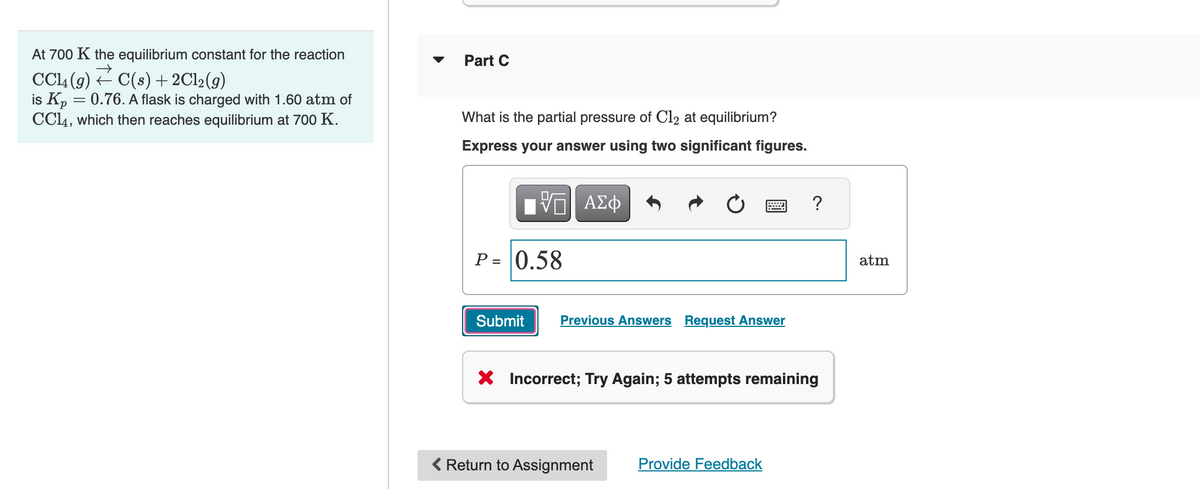
Transcribed Image Text:At 700 K the equilibrium constant for the reaction
→
CC₁4 (9) C(s) + 2Cl₂(g)
is Kp = 0.76. A flask is charged with 1.60 atm of
CC14, which then reaches equilibrium at 700 K.
Part C
What is the partial pressure of C12 at equilibrium?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
VE ΑΣΦ
P = 0.58
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
Return to Assignment
?
Provide Feedback
atm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax