B (a) A movie theater is interested in seeing if female or males, on average, attend the movies a different amount. What is the hypothesis test to be done? (Use u, - H,, where u, is males and u, is females.) O Ho: Hq = Hz O Ho: H, = 0.25 H1: H, = 0.75 O Ho: Hq = H2 O Ho: Hq> Hz B (b) Assume the population variances for the two samples are equal (then df = n1 + n2 - 2). Find the t-statistic, critical value, and the p-value associated with the hypothesis test at the 90% confidence level. (Round your t-statistic and p-value to four decimal places. Round your critical value to three decimal places.) (Use 4, - Hz, where 4, is males and #z is females.) t-statistic critical value p-value B (c) At a 90% confidence level, should the null hypothesis be accepted or rejected? Fill in the blanks. The null hypothesis should -Select--- . The number of times, on average, that females and males attend the movies each year ---Select-- V statistically different. O (d) Assume the population (all people) standard deviation is known to be four movies per year each for males and females. What are the new test statistic and critical value for a 90% confidence level? (Round your answers to three decimal places.) test statistic critical value You may need to use the appropriate table in the Appendix of Tables to answer this question.
B (a) A movie theater is interested in seeing if female or males, on average, attend the movies a different amount. What is the hypothesis test to be done? (Use u, - H,, where u, is males and u, is females.) O Ho: Hq = Hz O Ho: H, = 0.25 H1: H, = 0.75 O Ho: Hq = H2 O Ho: Hq> Hz B (b) Assume the population variances for the two samples are equal (then df = n1 + n2 - 2). Find the t-statistic, critical value, and the p-value associated with the hypothesis test at the 90% confidence level. (Round your t-statistic and p-value to four decimal places. Round your critical value to three decimal places.) (Use 4, - Hz, where 4, is males and #z is females.) t-statistic critical value p-value B (c) At a 90% confidence level, should the null hypothesis be accepted or rejected? Fill in the blanks. The null hypothesis should -Select--- . The number of times, on average, that females and males attend the movies each year ---Select-- V statistically different. O (d) Assume the population (all people) standard deviation is known to be four movies per year each for males and females. What are the new test statistic and critical value for a 90% confidence level? (Round your answers to three decimal places.) test statistic critical value You may need to use the appropriate table in the Appendix of Tables to answer this question.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Report
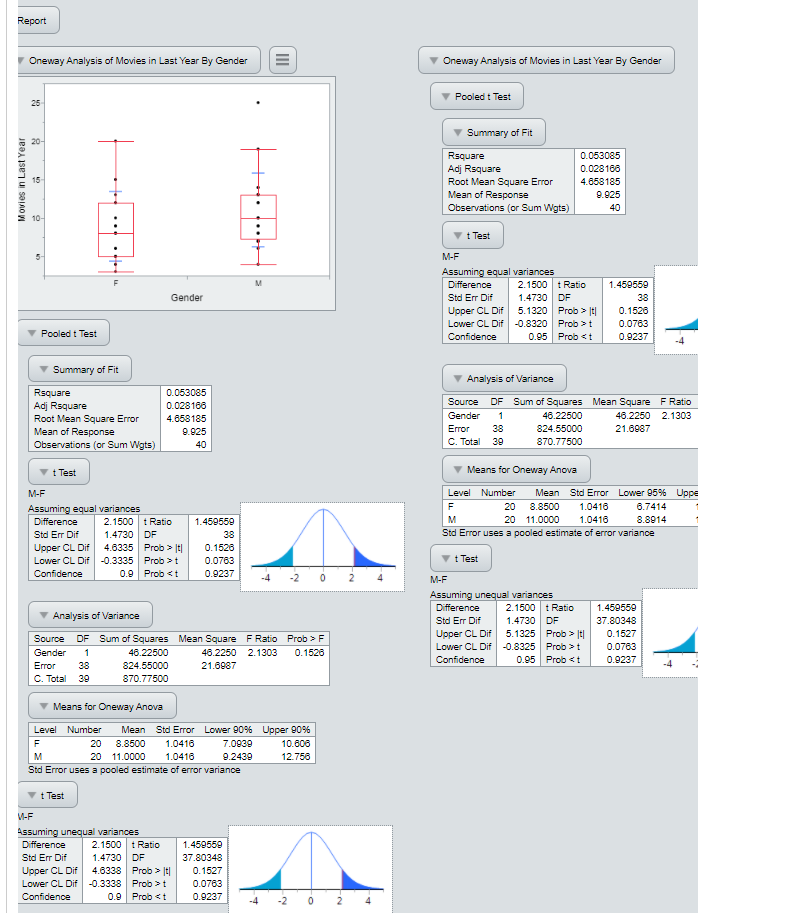
Oneway Analysis of Movies in Last Year By Gender
Oneway Analysis of Movies in Last Year By Gender
Pooled t Test
25
Summary of Fit
Rsquare
0.053085
Adj Rsquare
Root Mean Square Error
Mean of Response
Observations (or Sum Wgts)
0.028188
4.658185
9.025
40
10-
t Test
M-F
Assuming equal variances
M
Difference
2.1500 t Ratio
1.459559
Gender
Std Err Dif
1.4730
DF
38
Upper CL Dif
5.1320 Prob > |E|
0.1526
Lower CL Dif -0.8320 Prob > t
0.0763
Pooled t Test
Confidence
0.95 Prob <t
0.9237
Summary of Fit
Analysis of Variance
Rsquare
0.053085
Source DF Sum of Squares Mean Square F Ratio
Adj Rsquare
Root Mean Square Error
Mean of Response
Observations (or Sum Wgts)
0.028188
4.658185
Gender
1
46.22500
46.2250 2.1303
9.025
Error
38
824.55000
21.6987
40
C. Total 39
870.77500
t Test
Means for Oneway Anova
M-F
Level Number
Mean Std Error Lower 95% Uppe
Assuming equal variances
20
8.8500
1.0416
6.7414
M
20 11.0000
1.0418
8.8014
2.1500 t Ratio
1.4730 DF
4.6335 Prob > |t|
Difference
1.459559
Std Err Dif
38
Std Error uses a pooled estimate of error variance
Upper CL Dif
0.1526
Lower CL Dif -0.3335 Prob >t
0.0763
t Test
Confidence
0.9 Prob <t
0.9237
-2
M-F
Assuming unequal variances
2.1500 t Ratio
1.4730 DF
5.1325 Prob > |E|
Difference
1.459550
Analysis of Variance
Std Err Dif
37.80348
Upper CL Dif
0.1527
Source
DF Sum of Squares Mean Square FRatio Prob >F
Lower CL Dif -0.8325 Prob > t
0.0763
Gender
1
46.22500
46.2250 2.1303
0.1526
Confidence
0.95 Prob <t
0.9237
Error
38
824.55000
21.6987
C. Total
39
870.77500
Means for Oneway Anova
Level Number
Mean Std Eror Lower 90% Upper 90%
20
8.8500
1.0416
7.0939
10.608
M
20 11.0000
1.0416
9.2439
12.750
Std Error uses a pooled estimate of error variance
t Test
M-F
Assuming unequal variances
2.1500 t Ratio
1.4730 DF
4.6338 Prob > |t|
Lower CL Dif -0.3338 Prob >t
0.9 Prob <t
1.459550
37.80348
Difference
Std Err Dif
Upper CL Dif
0.1527
0.0763
Confidence
0.9237
-2 0
II
..
Movies in Last Year
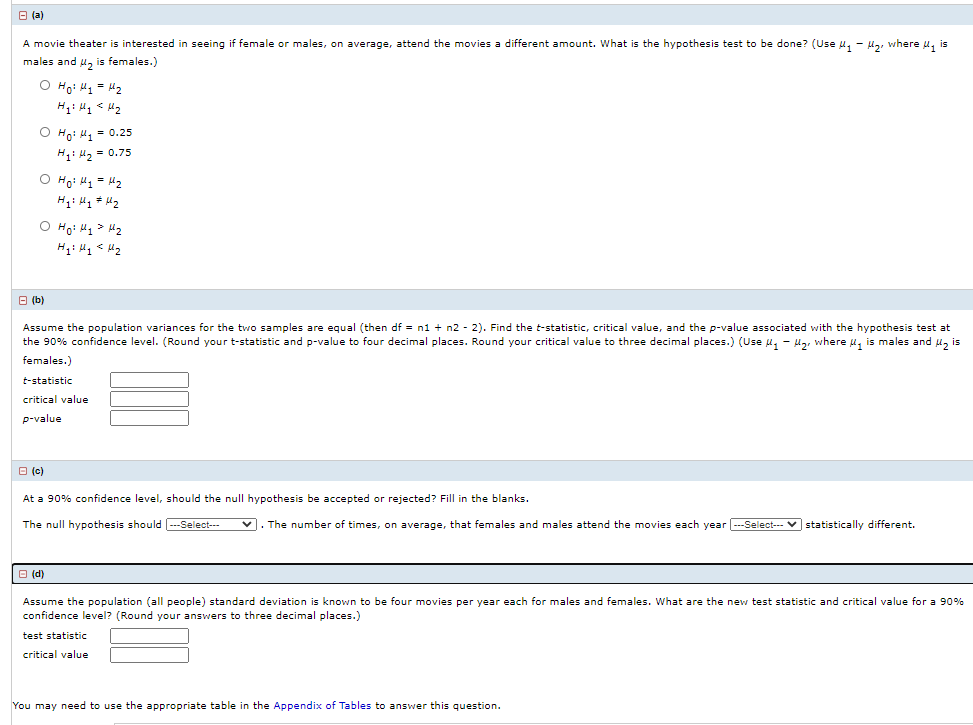
Transcribed Image Text:O (a)
A movie theater is interested in seeing if female or males, on average, attend the movies a different amount. What is the hypothesis test to be done? (Use u, - Hg, where u, is
males and u, is females.)
O Ho: H1 = H2
O Ho: H, = 0.25
H1 42 = 0.75
O Ho: H1 = H2
O Ho: H1> H2
O (b)
Assume the population variances for the two samples are equal (then df = n1 + n2 - 2). Find the t-statistic, critical value, and the p-value associated with the hypothesis test at
the 90% confidence level. (Round your t-statistic and p-value to four decimal places. Round your critical value to three decimal places.) (Use u, - lg, where u, is males and u, is
females.)
t-statistic
critical value
p-value
O (c)
At a 90% confidence level, should the null hypothesis be accepted or rejected? Fill in the blanks.
The null hypothesis should ---Select--
. The number of times, on average, that females and males attend the movies each year ---Select-- v statistically different.
(d)
Assume the population (all people) standard deviation is known to be four movies per year each for males and females. What are the new test statistic and critical value for a 90%
confidence level? (Round your answers to three decimal places.)
test statistic
critical value
You may need to use the appropriate table in the Appendix of Tables to answer this question.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman