(b) Considering g(x), determine P(0.5 < x < 1.0) and P(x >= 2.O)
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter8: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 11E: An ordinary die is rolled. Find the probability of each event. Rolling a number greater than 1 but...
Related questions
Question
Please answer letter B
Transcribed Image Text:ucture.com/courses/29733/quizzes/414373/take
Question 5
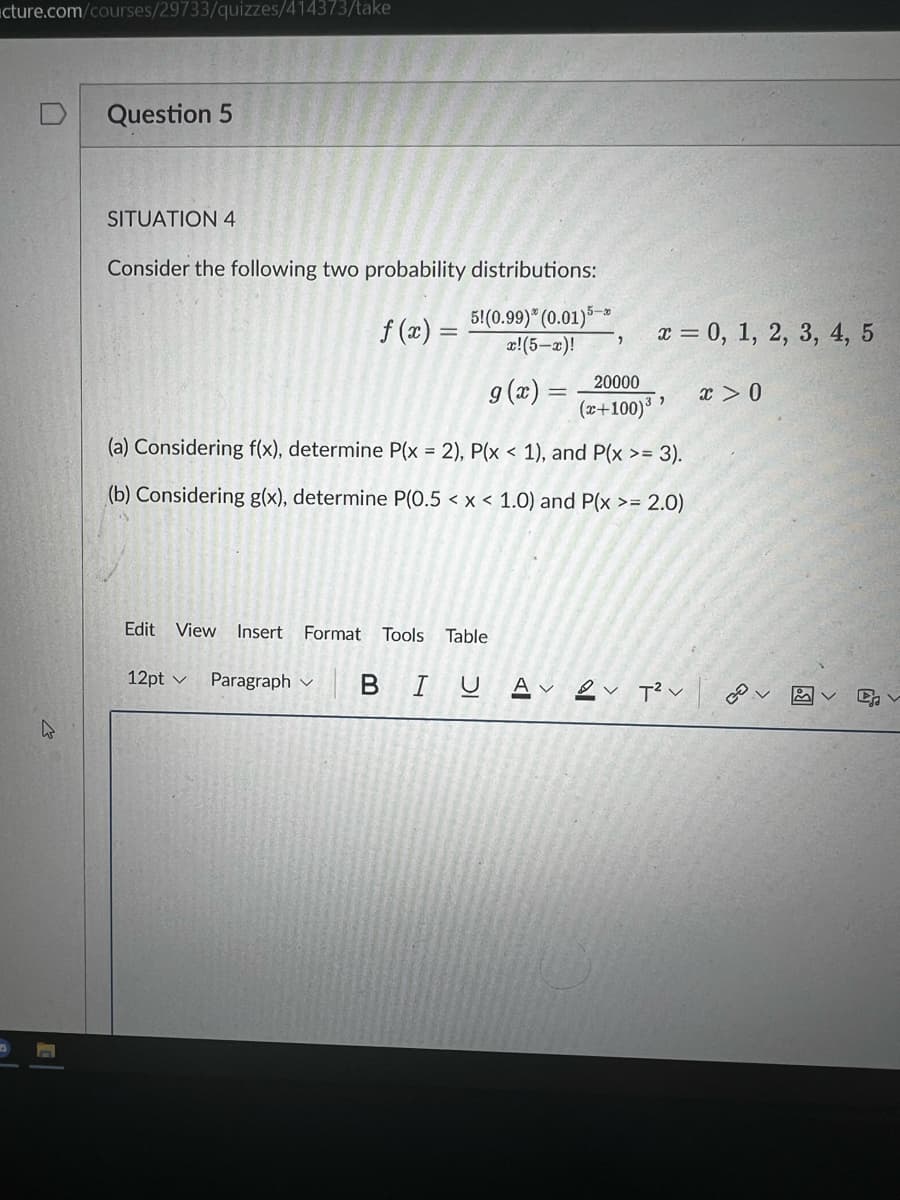
SITUATION 4
Consider the following two probability distributions:
5!(0.99)" (0.01)5-
x!(5-x)!
0
f (x) =
a = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
9 (x) = _20000
(x+100)³ '
x > 0
(a) Considering f(x), determine P(x = 2), P(x < 1), and P(x >= 3).
(b) Considering g(x), determine P(0.5 < x < 1.0) and P(x >= 2.0)
Edit View Insert Format Tools Table
12pt v
Paragraph v
U Av ev T?v
网
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning