(b) Find the probability that a fisherman selected at random fishing from shore catches one or more fish in a 6-hour period. The fisherman catches one or more fish if he catches exactly one fish, or exactly two fish, or exactly three fish, or if he catches 4 or more fish. However, there is only one event in which a fisherman does not catch one or more fish. A fisherman does not catch one or more fish when exactly fish are caught. Step 4 Recall that the complement rule gives the probability that an event will not happen. So the probability that a fisherman catches one or more fish is the same as the complement of the probability that a fisherman catches zero fish. We see there are two clear paths for calculating P(1 or more fish). We can calculate P(1 fish or 2 fish or 3 fish or 4 or more fish) or we can make use of the complement and calculate 1 - P(0 fish). Making use of the complement requires less calculation, so we will use it here. P(1 or more fish) = 1 - P(0 fish) We previously determined the probabilities associated with each x. 3 4 or more х PX) 0.46 0.33 0.17 0.03 0.01 Substitute the probability that a fisherman catches zero fish into the equation and simplify the result. P(1 or more fish) = 1 - P(0 fish) = 1- 10.46 0.46 0.54 0.54 Step 5 (c) Find the probability that a fisherman selected at random fishing from shore catches two or more fish in a 6-hour period. There are three events in which a fisherman catches two or more fish: the fisherman could catch exactly 2 fish, exactly x fish, or 4 or more fish. Enter an exact number. Recall the addition rule for probability for mutually exclusive events, and it is clear that we can use the following formula. P(2 or more fish) = P(2 fish) + P fish) + P(4 or more fish) Hi I need help withe the last 2 please.
(b) Find the probability that a fisherman selected at random fishing from shore catches one or more fish in a 6-hour period. The fisherman catches one or more fish if he catches exactly one fish, or exactly two fish, or exactly three fish, or if he catches 4 or more fish. However, there is only one event in which a fisherman does not catch one or more fish. A fisherman does not catch one or more fish when exactly fish are caught. Step 4 Recall that the complement rule gives the probability that an event will not happen. So the probability that a fisherman catches one or more fish is the same as the complement of the probability that a fisherman catches zero fish. We see there are two clear paths for calculating P(1 or more fish). We can calculate P(1 fish or 2 fish or 3 fish or 4 or more fish) or we can make use of the complement and calculate 1 - P(0 fish). Making use of the complement requires less calculation, so we will use it here. P(1 or more fish) = 1 - P(0 fish) We previously determined the probabilities associated with each x. 3 4 or more х PX) 0.46 0.33 0.17 0.03 0.01 Substitute the probability that a fisherman catches zero fish into the equation and simplify the result. P(1 or more fish) = 1 - P(0 fish) = 1- 10.46 0.46 0.54 0.54 Step 5 (c) Find the probability that a fisherman selected at random fishing from shore catches two or more fish in a 6-hour period. There are three events in which a fisherman catches two or more fish: the fisherman could catch exactly 2 fish, exactly x fish, or 4 or more fish. Enter an exact number. Recall the addition rule for probability for mutually exclusive events, and it is clear that we can use the following formula. P(2 or more fish) = P(2 fish) + P fish) + P(4 or more fish) Hi I need help withe the last 2 please.
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter8: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 42E
Related questions
Question
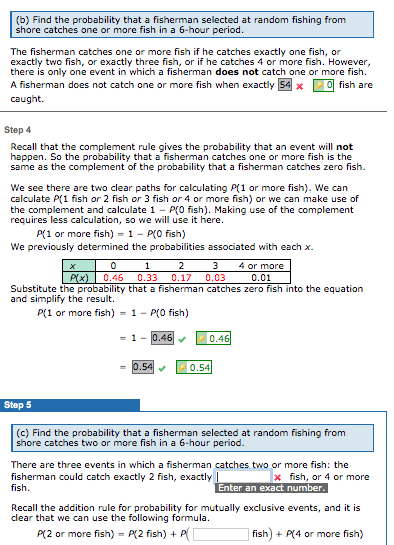
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Find the probability that a fisherman selected at random fishing from
shore catches one or more fish in a 6-hour period.
The fisherman catches one or more fish if he catches exactly one fish, or
exactly two fish, or exactly three fish, or if he catches 4 or more fish. However,
there is only one event in which a fisherman does not catch one or more fish.
A fisherman does not catch one or more fish when exactly
fish are
caught.
Step 4
Recall that the complement rule gives the probability that an event will not
happen. So the probability that a fisherman catches one or more fish is the
same as the complement of the probability that a fisherman catches zero fish.
We see there are two clear paths for calculating P(1 or more fish). We can
calculate P(1 fish or 2 fish or 3 fish or 4 or more fish) or we can make use of
the complement and calculate 1 - P(0 fish). Making use of the complement
requires less calculation, so we will use it here.
P(1 or more fish) = 1 - P(0 fish)
We previously determined the probabilities associated with each x.
3
4 or more
х
PX)
0.46 0.33
0.17 0.03
0.01
Substitute the probability that a fisherman catches zero fish into the equation
and simplify the result.
P(1 or more fish) = 1 - P(0 fish)
= 1- 10.46
0.46
0.54
0.54
Step 5
(c) Find the probability that a fisherman selected at random fishing from
shore catches two or more fish in a 6-hour period.
There are three events in which a fisherman catches two or more fish: the
fisherman could catch exactly 2 fish, exactly
x fish, or 4 or more
fish.
Enter an exact number.
Recall the addition rule for probability for mutually exclusive events, and it is
clear that we can use the following formula.
P(2 or more fish) = P(2 fish) + P
fish) + P(4 or more fish)

Transcribed Image Text:Hi I need help withe the last 2 please.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning