Because the two countries produce more jeans and more rye under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade. Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption"). Contente Dolorium Jeans Rye Jeans Rye (Millions of pairs) (Millions of bushels) (Millions of pairs) (Millions of bushels) Without Trade Production 8 48 15 20 Consumption 8 48 15 20 With Trade Production 32 80 Trade action Exports 18 ▼ Imports 54 ▼ Imports 18 Exports 54 ▼ Consumption 14 54 18 26 Gains from Trade Increase in Consumption
Because the two countries produce more jeans and more rye under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade. Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption"). Contente Dolorium Jeans Rye Jeans Rye (Millions of pairs) (Millions of bushels) (Millions of pairs) (Millions of bushels) Without Trade Production 8 48 15 20 Consumption 8 48 15 20 With Trade Production 32 80 Trade action Exports 18 ▼ Imports 54 ▼ Imports 18 Exports 54 ▼ Consumption 14 54 18 26 Gains from Trade Increase in Consumption
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter33: International Trade
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2SCQ: Brazil can produce 100 pounds of beef or 10 autos. In contrast the United States can produce 40...
Related questions
Question
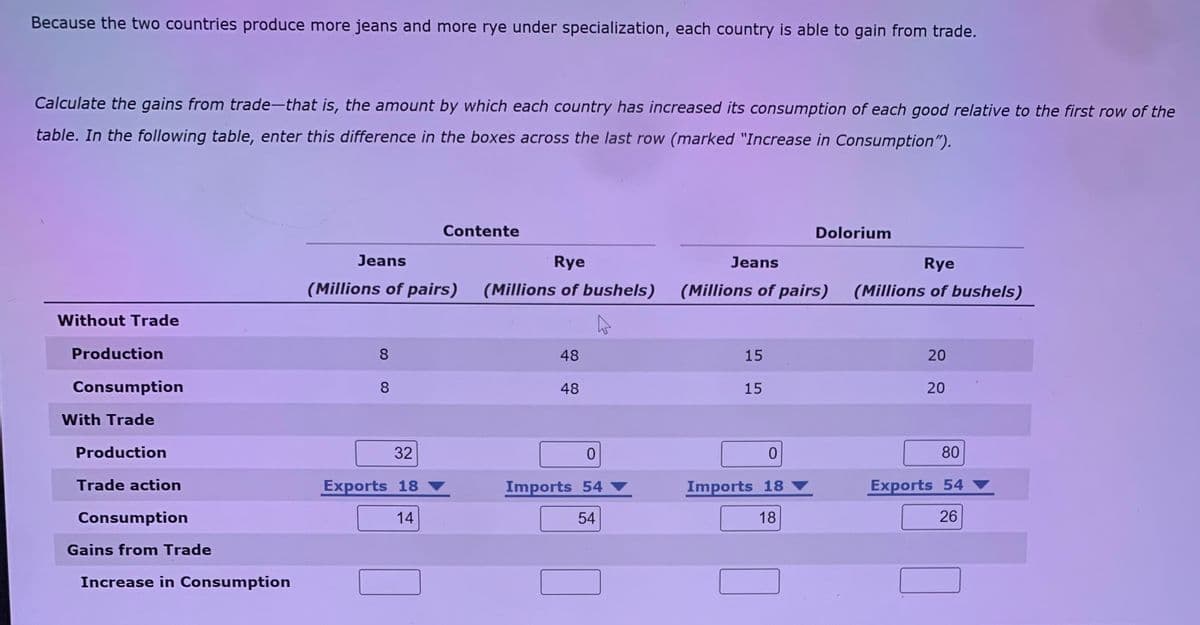
Transcribed Image Text:Because the two countries produce more jeans and more rye under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade.
Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the
table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption").
Contente
Dolorium
Jeans
Rye
Jeans
Rye
(Millions of pairs)
(Millions of bushels)
(Millions of pairs)
(Millions of bushels)
Without Trade
Production
8.
48
15
20
Consumption
8.
48
15
20
With Trade
Production
32
80
Trade action
Exports 18
Imports 54
Imports 18
Exports 54
Consumption
14
54
18
26
Gains from Trade
Increase in Consumption
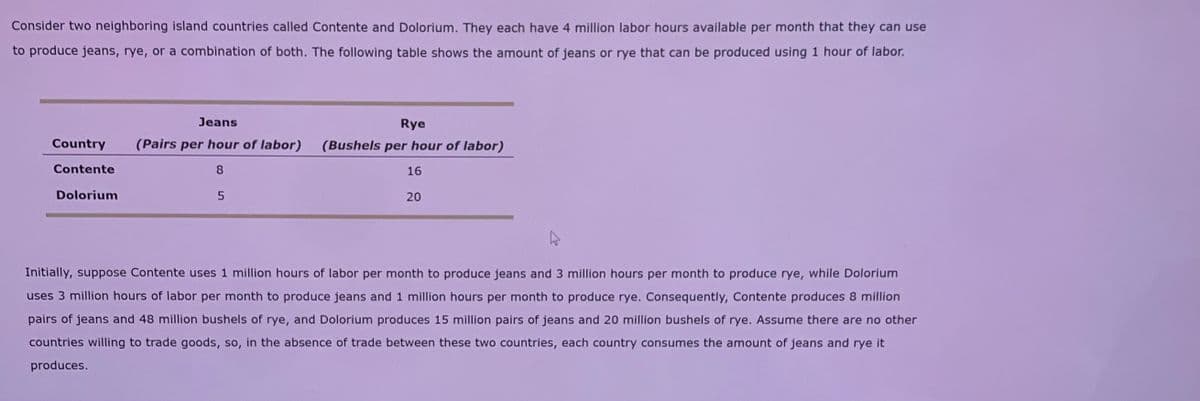
Transcribed Image Text:Consider two neighboring island countries called Contente and Dolorium. They each have 4 million labor hours available per month that they can use
to produce jeans, rye, or a combination of both. The following table shows the amount of jeans or rye that can be produced using 1 hour of labor.
Jeans
Rye
Country
(Pairs per hour of labor)
(Bushels per hour of labor)
Contente
8
16
Dolorium
5.
20
Initially, suppose Contente uses 1 million hours of labor per month to produce jeans and 3 million hours per month to produce rye, while Dolorium
uses 3 million hours of labor per month to produce jeans and 1 million hours per month to produce rye. Consequently, Contente produces 8 million
pairs of jeans and 48 million bushels of rye, and Dolorium produces 15 million pairs of jeans and 20 million bushels of rye. Assume there are no other
countries willing to trade goods, so, in the absence of trade between these two countries, each country consumes the amount of jeans and rye it
produces.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Since you have asked multiple questions, we will answer the first question for you. If you require the solution of the other questions, please post it separately.
International trade refers to the exchange of goods and services between two or more nations for money. The main reason behind the international trade is the comparative advantage experienced by some nations in production of certain goods.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax





Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning