In the following table, select the amount of each good that each country exports and imports in the boxes across the row marked "Trade Action," and enter each country's final consumption of each good on the line marked "Consumption." When the two countries did not specialize, the total production of jeans was 23 million pairs per week, and the total production of corn was 68 million bushels per week. Because of specialization, the total production of jeans has increased by million pairs per week, and the total production of corn has increased by million bushels per week. Because the two countries produce more jeans and more corn under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade. Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption").
In the following table, select the amount of each good that each country exports and imports in the boxes across the row marked "Trade Action," and enter each country's final consumption of each good on the line marked "Consumption." When the two countries did not specialize, the total production of jeans was 23 million pairs per week, and the total production of corn was 68 million bushels per week. Because of specialization, the total production of jeans has increased by million pairs per week, and the total production of corn has increased by million bushels per week. Because the two countries produce more jeans and more corn under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade. Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption").
Micro Economics For Today
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337613064
Author:Tucker, Irvin B.
Publisher:Tucker, Irvin B.
Chapter2: Productions Possibilities, Opportunity Costs, And Economic Growth
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13SQ
Related questions
Question
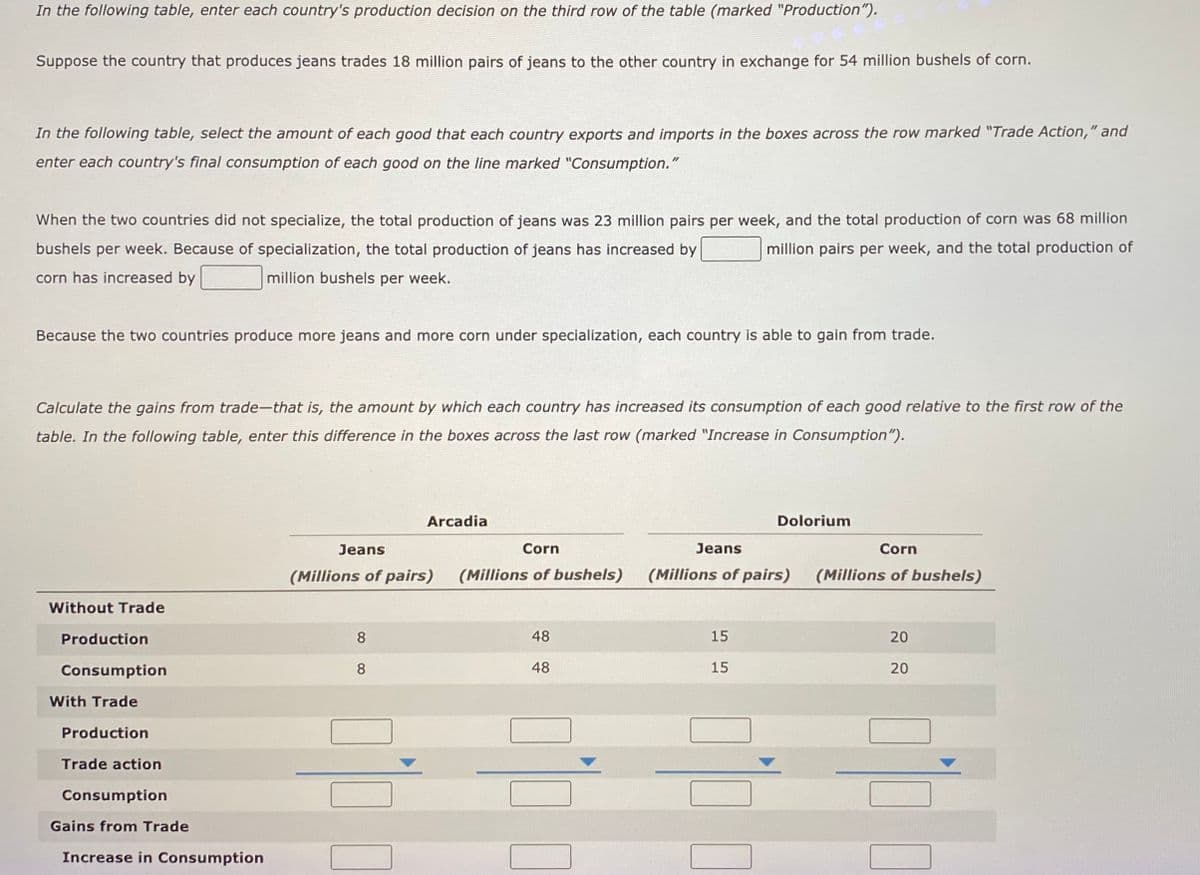
Transcribed Image Text:In the following table, enter each country's production decision on the third row of the table (marked "Production").
Suppose the country that produces jeans trades 18 million pairs of jeans to the other country in exchange for 54 million bushels of corn.
In the following table, select the amount of each good that each country exports and imports in the boxes across the row marked "Trade Action," and
enter each country's final consumption of each good on the line marked "Consumption."
When the two countries did not specialize, the total production of jeans was 23 million pairs per week, and the total production of corn was 68 million
bushels per week. Because of specialization, the total production of jeans has increased by
million pairs per week, and the total production of
corn has increased by
million bushels per week.
Because the two countries produce more jeans and more corn under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade.
Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the
table. In the following table,
this difference in the boxes
cross the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption").
Arcadia
Dolorium
Jeans
Corn
Jeans
Corn
(Millions of pairs)
(Millions of bushels)
(Millions of pairs)
(Millions of bushels)
Without Trade
Production
8
48
15
20
Consumption
48
15
20
With Trade
Production
Trade action
Consumption
Gains from Trade
Increase in Consumption
Expert Solution
Step 1
In international economics, according to Ricardian theory of comparative (CA) advantage, a country that can manufacture a commodity at lower cost that its competitor will specialize in its production and export to its competitor in exchange for another commodity.
The following table contains details about the production of two goods – (jeans & corn) in each country.
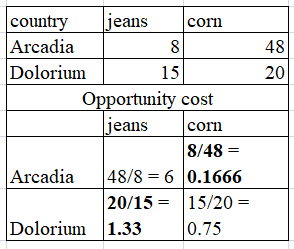
The table shows that Arcadia has comparative (CA) advantage in the manufacture of corn. So it must produce corn and export it to Dolorium. However, the latter has comparative (CA) advantage in the manufacture of jeans. So it must produce jeans and export it to Arcadia.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you








Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc