Beginning inventory, 9/1/2021 7,500 units @ $10.00 Purchases: 9/7 9/25 Sales: 4,500 units @ $10.40 12,000 units @ $11.75 9/10 9/29 14,000 units were on hand at the end of September. 4,000 units 6,000 units Required: 1. Assuming that CNB uses a periodic inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory. 2. Assuming that CNB uses a perpetual inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory.
Beginning inventory, 9/1/2021 7,500 units @ $10.00 Purchases: 9/7 9/25 Sales: 4,500 units @ $10.40 12,000 units @ $11.75 9/10 9/29 14,000 units were on hand at the end of September. 4,000 units 6,000 units Required: 1. Assuming that CNB uses a periodic inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory. 2. Assuming that CNB uses a perpetual inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory.
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337690881
Author:Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Chapter6: Cost Of Goods Sold And Inventory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 51E: Inventory Costing Methods On June 1, Welding Products Company had a beginning inventory of 210 cases...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
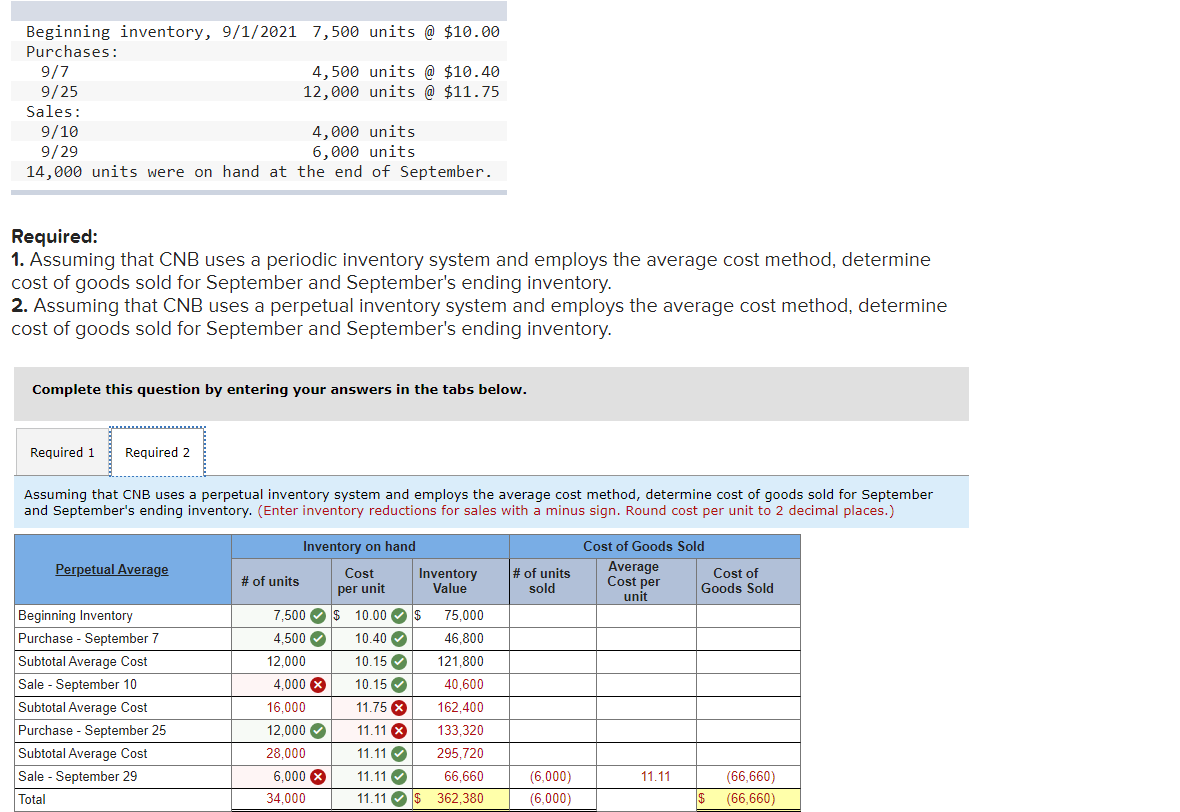
Transcribed Image Text:Beginning inventory, 9/1/2021 7,500 units @ $10.00
Purchases:
9/7
4,500 units @ $10.40
12,000 units @ $11.75
9/25
Sales:
9/10
9/29
14,000 units were on hand at the end of September.
4,000 units
6,000 units
Required:
1. Assuming that CNB uses a periodic inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine
cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory.
2. Assuming that CNB uses a perpetual inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine
cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1
Required 2
Assuming that CNB uses a perpetual inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine cost of goods sold for September
and September's ending inventory. (Enter inventory reductions for sales with a minus sign. Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.)
Inventory on hand
Cost of Goods Sold
Perpetual Average
Average
Çost per
unit
# of units
Inventory
Value
Cost of
Goods Sold
Cost
# of units
per unit
sold
Beginning Inventory
7,500 O $ 10.00 O $
75,000
Purchase - September 7
4,500 O
10.40 O
46,800
Subtotal Average Cost
12,000
10.15 O
121,800
Sale - September 10
4,000 8
10.15 O
40,600
Subtotal Average Cost
16,000
11.75 X
162,400
Purchase - September 25
12,000 O
11.11 8
133,320
Subtotal Average Cost
28,000
11.11 O
295,720
Sale - September 29
6,000 X
11.11 O
66,660
(6,000)
11.11
(66,660)
Total
34,000
11.11 O $
362,380
(6,000)
$ (66,660)
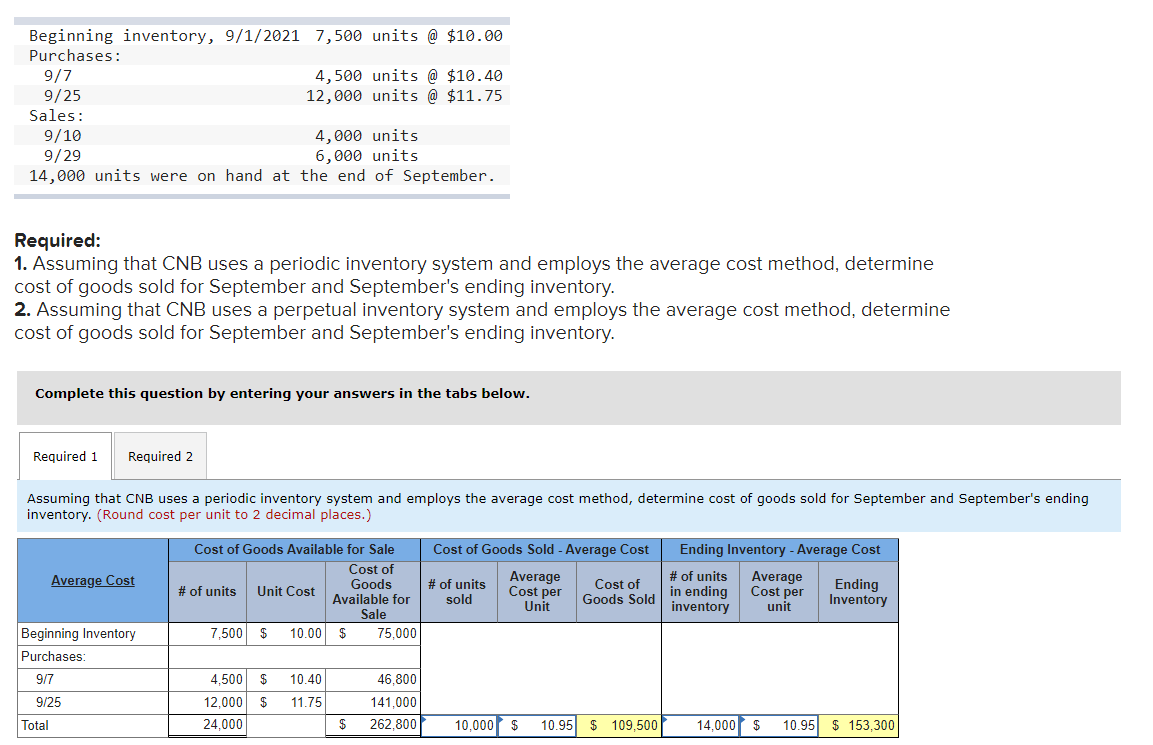
Transcribed Image Text:Beginning inventory, 9/1/2021 7,500 units @ $10.00
Purchases:
9/7
9/25
Sales:
9/10
9/29
14,000 units were on hand at the end of September.
4,500 units @ $10.40
12,000 units @ $11.75
4,000 units
6,000 units
Required:
1. Assuming that CNB uses a periodic inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine
cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory.
2. Assuming that CNB uses a perpetual inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine
cost of goods sold for September and September's ending inventory.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1
Required 2
Assuming that CNB uses a periodic inventory system and employs the average cost method, determine cost of goods sold for September and September's ending
inventory. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.)
Cost of Goods Available for Sale
Cost of Goods Sold - Average Cost
Ending Inventory - Average Cost
Cost of
Goods
Available for
Sale
Average
Cost per
Unit
# of units
in ending
inventory
Average
Cost per
unit
Average Cost
Ending
Inventory
# of units
Cost of
# of units
Unit Cost
sold
Goods Sold
Beginning Inventory
7,500 $
10.00
$
75.000|
Purchases:
9/7
4,500 $
10.40
46,800
9/25
12,000 $
11.75
141,000
Total
24,000
$
262,800
10,000 $
10.95 $ 109,500
14,000 $
10.95 $ 153,300
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,
