Below 4 equations for calculation of wages in Latvia (ALGA, EUR) are given, depending on productivity (PRODUKTIVITATE, thsd EUR), price level (CENA), unemployment rate (BEZDARBS, %) and ratio of GDP of Latvia and the EU (IKP_ATTIECIBA). Which equation would you use, why (for justification use all the indicators known from the lectures)? (t-stat0,05:14 = 2,14; t-stat0,05:15 = 2,13; t-stat 0,05:16 F-stat 0.05:3:13 = 3,29; F-stat = 3,63; F-stat0,05;2:14 2,12; 0,05;2:14 = 3,59) Dependent Vanabe: LOG(ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 17 after adjustments Coefficient Varabe LOG(CENA) LOG PRODUKTIVITATE) BEZDARBS C R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat Variable LOG(CENA) LOG(IKP ATTIECIBA) Dependent Variable: LOG(ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 18 after adjustments С 1.733446 0.316520 -0.011502 7.202105 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat Std. Error 0.143014 0.181278 0.003949 0.314418 0.995794 Mean dependent var 0.994823 S.D. dependentvar 0.040174 Akake into criterion 0.020981 Schwarz oferin 32.80553 F-statistic 1.840821 Pobstatistic) Coefficient 1.588128 0.073034 0.718542 0.119047 7,940545 0.087802 Std. Emor t-Statistic +-Statistic Prob *0,05;2:13 Dependent Varable: LOG (ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 17 after adjustments 12.12084 0.0000 LOG (CENA) 1.682538 1.746049 0.1044 LOG(KP_ATTIECIBA) 0.613199 -2.912980 0.0121 BEZDARBS -0.003104 22.90614 0.0000 C 7.906579 0.994508 Mean dependent var 0.993776 S.D. dependent var 0.048459 Akake into criterion 0.032377 Schwarz criterion 31.34517 F-statistic 1.965028 Prob(F-statisto) Variable 7.959451 R-squared 0.558335 Adjusted R-squared -3.388885 S.E. of regression -3.192835 Sum squared resid 1025.827 Log Ikelihood 0.000000 Duroin-Watson stat Prob. 21.71778 0.0000 6.035777 0.0000 117.4808 0.0000 Variable Coefficient LOG(CENA) BEZDARBS C 7.904990 R-squared 0.588888 Adjusted R-squared -3.149484 S.E. of regression -3.001088 Sum squared resid 1358.142 Log likelihood 0.000000 Durbin-Watson stat Std. Error Dependent Variable: LOG(ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 17 after adjustments Coefficient 1.974777 0.039330 -0.016842 0.002674 0.037767 7.747829 0.122338 0.246822 13.75320 2.484378 0.005984 -0.518692 0.071659 110.3366 t-Statistic 0.996479 Mean dependent var 0.995666 S.D. dependent var 0.036756 Akake into criterion 0.017563 Schwarz criterion 34.31709 Ftatistic 1.765948 Prob(F-statistic) Std. Emor 0.994807 Mean dependent var 0.994085 S.D. dependent var 0.043013 Akake into criterion 0.025901 Schwarz criterion 31.01477 F-statistic 1.929371 Prob(F-statsto) Prob 0.0000 0.0274 0.6127 0.0000 +-Statistic 50.21103 -8.297883 205.1410 7.959451 0.558335 -3.566716 -3.370666 1226.321 0.000000 Prob. 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 7.959451 0.558335 -3.295855 -3.148817 1340.984 0.000000 =
Below 4 equations for calculation of wages in Latvia (ALGA, EUR) are given, depending on productivity (PRODUKTIVITATE, thsd EUR), price level (CENA), unemployment rate (BEZDARBS, %) and ratio of GDP of Latvia and the EU (IKP_ATTIECIBA). Which equation would you use, why (for justification use all the indicators known from the lectures)? (t-stat0,05:14 = 2,14; t-stat0,05:15 = 2,13; t-stat 0,05:16 F-stat 0.05:3:13 = 3,29; F-stat = 3,63; F-stat0,05;2:14 2,12; 0,05;2:14 = 3,59) Dependent Vanabe: LOG(ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 17 after adjustments Coefficient Varabe LOG(CENA) LOG PRODUKTIVITATE) BEZDARBS C R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat Variable LOG(CENA) LOG(IKP ATTIECIBA) Dependent Variable: LOG(ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 18 after adjustments С 1.733446 0.316520 -0.011502 7.202105 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat Std. Error 0.143014 0.181278 0.003949 0.314418 0.995794 Mean dependent var 0.994823 S.D. dependentvar 0.040174 Akake into criterion 0.020981 Schwarz oferin 32.80553 F-statistic 1.840821 Pobstatistic) Coefficient 1.588128 0.073034 0.718542 0.119047 7,940545 0.087802 Std. Emor t-Statistic +-Statistic Prob *0,05;2:13 Dependent Varable: LOG (ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 17 after adjustments 12.12084 0.0000 LOG (CENA) 1.682538 1.746049 0.1044 LOG(KP_ATTIECIBA) 0.613199 -2.912980 0.0121 BEZDARBS -0.003104 22.90614 0.0000 C 7.906579 0.994508 Mean dependent var 0.993776 S.D. dependent var 0.048459 Akake into criterion 0.032377 Schwarz criterion 31.34517 F-statistic 1.965028 Prob(F-statisto) Variable 7.959451 R-squared 0.558335 Adjusted R-squared -3.388885 S.E. of regression -3.192835 Sum squared resid 1025.827 Log Ikelihood 0.000000 Duroin-Watson stat Prob. 21.71778 0.0000 6.035777 0.0000 117.4808 0.0000 Variable Coefficient LOG(CENA) BEZDARBS C 7.904990 R-squared 0.588888 Adjusted R-squared -3.149484 S.E. of regression -3.001088 Sum squared resid 1358.142 Log likelihood 0.000000 Durbin-Watson stat Std. Error Dependent Variable: LOG(ALGA) Method: Least Squares Included observations: 17 after adjustments Coefficient 1.974777 0.039330 -0.016842 0.002674 0.037767 7.747829 0.122338 0.246822 13.75320 2.484378 0.005984 -0.518692 0.071659 110.3366 t-Statistic 0.996479 Mean dependent var 0.995666 S.D. dependent var 0.036756 Akake into criterion 0.017563 Schwarz criterion 34.31709 Ftatistic 1.765948 Prob(F-statistic) Std. Emor 0.994807 Mean dependent var 0.994085 S.D. dependent var 0.043013 Akake into criterion 0.025901 Schwarz criterion 31.01477 F-statistic 1.929371 Prob(F-statsto) Prob 0.0000 0.0274 0.6127 0.0000 +-Statistic 50.21103 -8.297883 205.1410 7.959451 0.558335 -3.566716 -3.370666 1226.321 0.000000 Prob. 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 7.959451 0.558335 -3.295855 -3.148817 1340.984 0.000000 =
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Econometrics
Below 4 equations for calculation of wages in Latvia (ALGA, EUR) are given, depending on productivity (PRODUKTIVITATE, thsd EUR), price level (CENA), unemployment rate (BEZDARBS, %) and ratio of GDP of Latvia and the EU (IKP_ATTIECIBA). Which equation would you use, why (for justification use all the indicators known from the lectures)? (t-stat0,05;14 = 2,14; t-stat0,05;15 = 2,13; t-stat0,05;16 = 2,12; F-stat0,05;3;13 = 3,29; F-stat0,05;2;13 = 3,63; F-stat0,05;2;14 = 3,59)
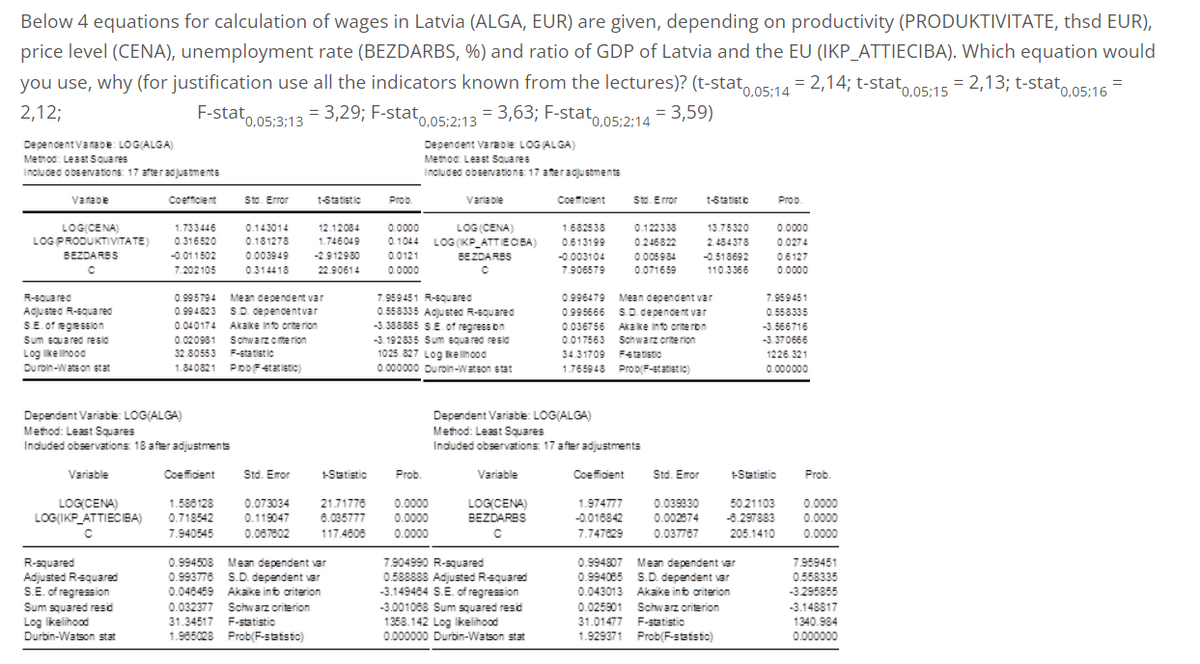
Transcribed Image Text:Below 4 equations for calculation of wages in Latvia (ALGA, EUR) are given, depending on productivity (PRODUKTIVITATE, thsd EUR),
price level (CENA), unemployment rate (BEZDARBS, %) and ratio of GDP of Latvia and the EU (IKP_ATTIECIBA). Which equation would
you use, why (for justification use all the indicators known from the lectures)? (t-stat0,05;14
= 2,14; t-stat 0.05:15
= 2,13; t-stat 0,05:16
= 3,29; F-stat0,05;2:13 = 3,63; F-stat
¹0,05;2:14 = 3,59)
2,12;
F-stat0,05:3:13
Dependent Vanabe: LOG(ALGA)
Method: Least Squares
Included observations: 17 after adjustments
Varable
LOG(CENA)
LOG PRODUKTIVITATE)
BEZDARBS
C
R-squared
Adjusted R-squared
S.E. of regression
Sum squared resid
Log Ikelhood
Durbin-Watson stat
Variable
LOG(CENA)
LOG(IKP_ATTIECIBA)
C
Coefficient
R-squared
Adjusted R-squared
S.E. of regression
Sum squared resid
Log likelihood
Durbin-Watson stat
Dependent Variable: LOG(ALGA)
Method: Least Squares
Included observations: 18 after adjustments
1.733446
0.143014
0.316520 0.181278
-0.011502 0.003949
7.202105 0.314418
Std. Error
Coefficient
0.995794 Mean dependent var
0.994823 S.D. dependentvar
0.040174 Akake into criterion
0.020981 Schwarz omerion
32.80553
1.840821 Pobstatistic)
1.588128
0.718542
7.940545
Std. Emor
t-Statistic
0.073034
0.119047
0.087802
12.12084
1.746049
-2.912980
22.90614
+-Statistic
Prob
0.994508 Mean dependent var
0.993776 S.D. dependent var
0.048459 Akake into criterion
0.032377 Schwarz criterion
31.34517 F-statistic
1.965028 Prob(F-statistic)
Dependent Varable: LOG (ALGA)
Method: Least Squares
Included observations: 17 after adjustments
Prob.
21.71778 0.0000
8.035777 0.0000
117.4808 0.0000
Variable
0.0000
LOG (CENA)
0.1044 LOG(KP_ATTIECIBA)
0.0121
0.0000
BEZDARBS
C
7.959451 R-squared
0.558335 Adjusted R-squared
-3.388885 S.E. of regression
-3.192835 Sum squared resid
1025.827 Log Ikelihood
0.000000 Durpin-Watson stat
Variable
LOG(CENA)
BEZDARBS
C
Coefficient
7.904990 R-squared
0.588888 Adjusted R-squared
-3.149484 S.E. of regression
-3.001088 Sum squared resid
1358.142 Log likelihood
0.000000 Durbin-Watson stat
1.682538
0.613199
-0.003104
7.906579
Dependent Variable: LOG(ALGA)
Method: Least Squares
Included observations: 17 after adjustments
Std. Error
0.122338
0.246822
0.005984
0.071659
Coefficient
Mean dependent var
S.D. dependent var
0.996479
0.995666
0.036756 Akalke info criterion
0.017563 Schwarz criterion
34.31709
F-statistic
1.765948 Prob(F-statistic)
1.974777
-0.016842
7.747829
t-Statistic
Std. Emor
0.039330
0.002874
0.037767
13.75320 0.0000
2.484378
0.0274
-0.518692 0.6127
110.3366
0.0000
+-Statistic
Prob
7.959451
0.558335
-3.566716
-3.370666
1226.321
0.000000
50.21103
-8.297883
205.1410
0.994807 Mean dependent var
0.994065 S.D. dependent var
0.043013 Akake into criterion
0.025901 Schwarz criterion
31.01477 F-statistic
1.929371 Prob(F-statsto)
Prob.
0.0000
0.0000
0.0000
7.959451
0.558335
-3.295855
-3.148817
1340.984
0.000000
=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman