Block m, of mass 15 kg moving with velocity v = 33 m/s on a frictionless plane collides block mą which is connected to b m3 by a long, massless spring with spring constant k = 7000 N/m: see the figure. Each of blocks mą and mg has a mass Before the collision, blocks mą and mg are stationary and the spring is relaxed. m, m2 my Frictionless- For parts A. B and C assume that the collision of blocks m, and m2 is completely inelastic. (Because the spring is re before the collision, block mg does not move at the instant of impact, therefore (m1 +m2) must move through a finite displacement before any force acts on mg and cause it to move.) For parts D and E assume that the collision of blocks m, and mą is elastic. (Because the spring is relaxed before the collision. block mg does not move at the instant of impact therefore mą must move through a finite displacement befor force acts on mg and cause it to move.)
Block m, of mass 15 kg moving with velocity v = 33 m/s on a frictionless plane collides block mą which is connected to b m3 by a long, massless spring with spring constant k = 7000 N/m: see the figure. Each of blocks mą and mg has a mass Before the collision, blocks mą and mg are stationary and the spring is relaxed. m, m2 my Frictionless- For parts A. B and C assume that the collision of blocks m, and m2 is completely inelastic. (Because the spring is re before the collision, block mg does not move at the instant of impact, therefore (m1 +m2) must move through a finite displacement before any force acts on mg and cause it to move.) For parts D and E assume that the collision of blocks m, and mą is elastic. (Because the spring is relaxed before the collision. block mg does not move at the instant of impact therefore mą must move through a finite displacement befor force acts on mg and cause it to move.)
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter9: Momentum And Its Conservation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 70A
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
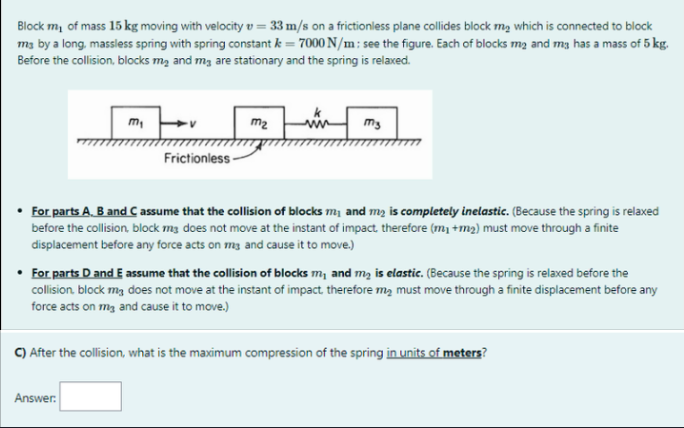
Transcribed Image Text:Block m, of mass 15 kg moving with velocity v = 33 m/s on a frictionless plane collides block m, which is connected to block
m3 by a long, massless spring with spring constant k = 7000 N/m: see the figure. Each of blocks mą and mg has a mass of 5 kg.
Before the collision, blocks mą and mg are stationary and the spring is relaxed.
m,
m2
my
Frictionless-
For parts A. B and C assume that the collision of blocks m, and m2 is completely inelastic. (Because the spring is relaxed
before the collision, block m3 does not move at the instant of impact. therefore (m, +m2) must move through a finite
displacement before any force acts on mg and cause it to move.)
• For parts D and E assume that the collision of blocks m, and mą is elastic. (Because the spring is relaxed before the
collision. block mg does not move at the instant of impact therefore mą must move through a finite displacement before any
force acts on mg and cause it to move.)
C) After the collision, what is the maximum compression of the spring in units of meters?
Answer:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning