By accident, a large plate is dropped and breaks into three pieces. The pieces fly apart parallel to the floor. As the plate falls, its momentum has only a vertical component, and no component parallel to the floor. After the collision, the component of the total momentum parallel to the floor must remain zero, since the net external force acting on the plate has no component parallel to the floor. Using the data shown in the drawing find (a) the mass of piece 1 and (b) the mass of piece 2. 3.00 m/s (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Units 25.0 1 2 3=1.30 kg 3.07 m/s + 1.79 m/s 45.0°
By accident, a large plate is dropped and breaks into three pieces. The pieces fly apart parallel to the floor. As the plate falls, its momentum has only a vertical component, and no component parallel to the floor. After the collision, the component of the total momentum parallel to the floor must remain zero, since the net external force acting on the plate has no component parallel to the floor. Using the data shown in the drawing find (a) the mass of piece 1 and (b) the mass of piece 2. 3.00 m/s (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Units 25.0 1 2 3=1.30 kg 3.07 m/s + 1.79 m/s 45.0°
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter12: Static Equilibrium And Elasticity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 37P: To get up on the roof, a person (mass 70.0 kg) places 6.00-m aluminum ladder (mass 10.0 kg) against...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
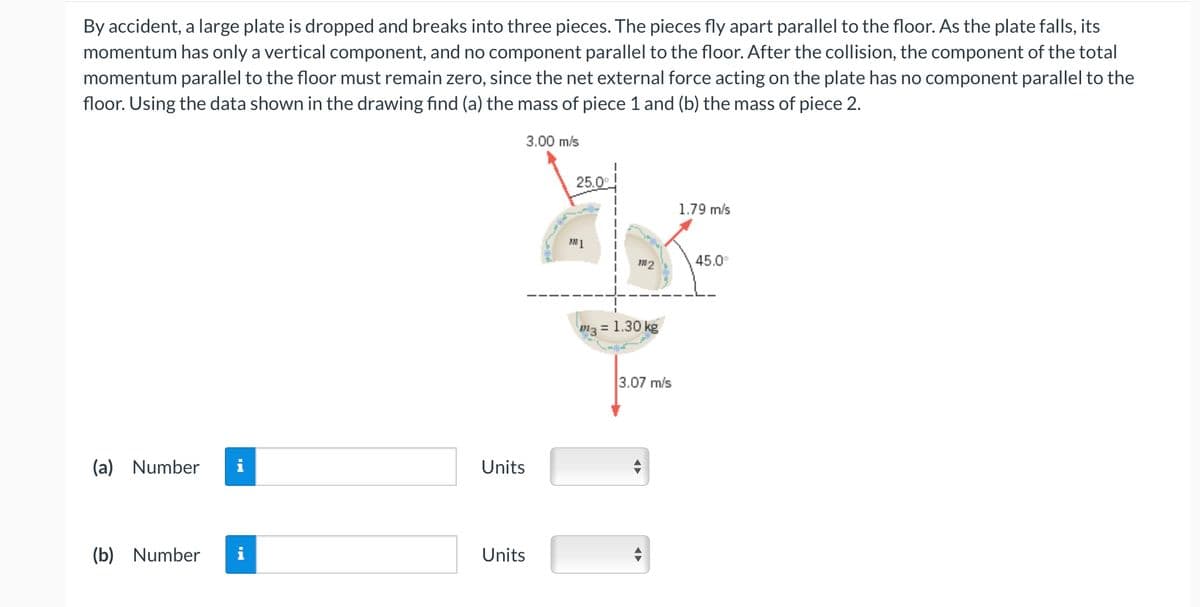
Transcribed Image Text:By accident, a large plate is dropped and breaks into three pieces. The pieces fly apart parallel to the floor. As the plate falls, its
momentum has only a vertical component, and no component parallel to the floor. After the collision, the component of the total
momentum parallel to the floor must remain zero, since the net external force acting on the plate has no component parallel to the
floor. Using the data shown in the drawing find (a) the mass of piece 1 and (b) the mass of piece 2.
3.00 m/s
(a) Number
(b) Number
Units
Units
25.0°
m1
m3
m2
= 1.30 kg
3.07 m/s
1.79 m/s
45.0°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning