Calculate AG at 298 K if the partial pressures of NO₂ and N₂O4 are 0.36 atm and 1.64 atm, respectively. Express the free energy in kilojoules to two decimal places. 96 AF
Calculate AG at 298 K if the partial pressures of NO₂ and N₂O4 are 0.36 atm and 1.64 atm, respectively. Express the free energy in kilojoules to two decimal places. 96 AF
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.50PAE: For the reaction NO(g)+NO2(g)N2O3(g) , use tabulated thermodynamic data to calculate H and S. Then...
Related questions
Question
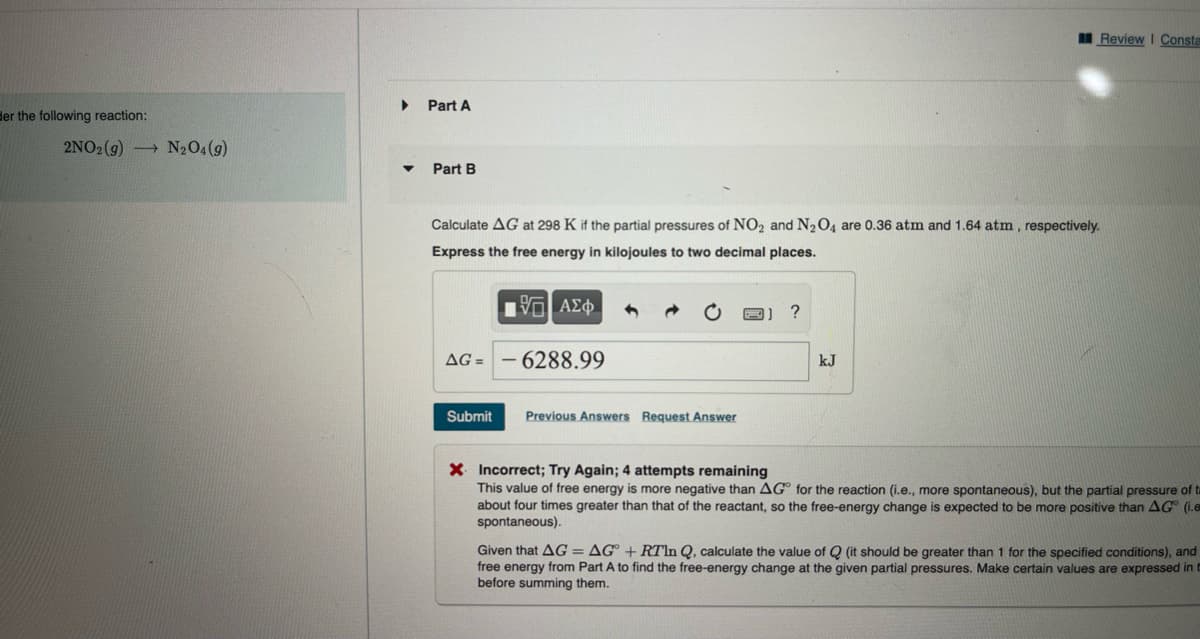
Transcribed Image Text:der the following reaction:
2NO2(g) N₂O4 (9)
Part A
Part B
Calculate AG at 298 K if the partial pressures of NO₂ and N₂O4 are 0.36 atm and 1.64 atm, respectively.
Express the free energy in kilojoules to two decimal places.
|ΨΕΙ ΑΣΦ
AG= -6288.99
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
?
Review I Consta
kJ
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
This value of free energy is more negative than AG for the reaction (i.e., more spontaneous), but the partial pressure of ta
about four times greater than that of the reactant, so the free-energy change is expected to be more positive than AG (i.e
spontaneous).
Given that AG = AG + RTln Q, calculate the value of Q (it should be greater than 1 for the specified conditions), and
free energy from Part A to find the free-energy change at the given partial pressures. Make certain values are expressed in
before summing them.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
