Calculate the following problem and box your final answer 1. The vapor pressure of pure water at 115°C is 1085 torr. A solution of ethylene glycol and water has a vapor pressure of 1.30 atm at the same temperature. What is the mole fraction of ethylene glycol in the solution?
Calculate the following problem and box your final answer 1. The vapor pressure of pure water at 115°C is 1085 torr. A solution of ethylene glycol and water has a vapor pressure of 1.30 atm at the same temperature. What is the mole fraction of ethylene glycol in the solution?
Chapter84: Fractional Distillation, Azeotropes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2P
Related questions
Question
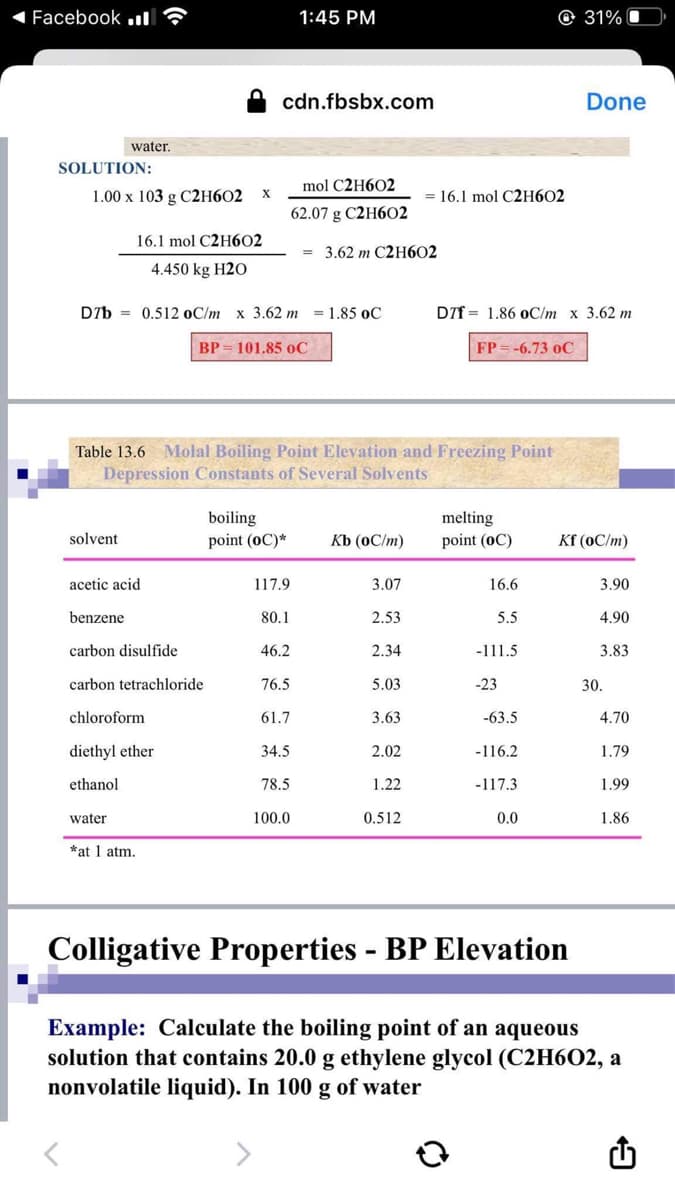
Please based boiling point and kb to the given table below. Thank you

Transcribed Image Text:.Globe
10:37 PM
X Colligative Properties Activity...
ล
53%
Name:
Activity Sheet
Colligative Properties of Solution
Calculate the following problem and box your final answer
1. The vapor pressure of pure water at 115°C is 1085 torr. A
solution of ethylene glycol and water has a vapor pressure of
1.30 atm at the same temperature. What is the mole fraction of
ethylene glycol in the solution?
2. What is the molality of a solution dissolved in chloroform that
boils at 62.8 °C? Boiling point of chloroform is 62.2 °C? Kb
chloroform 3.63 °c/m?
3. Calculate the vapor pressure lowering, DP, when 10.0 mL of
glycerol (C,H,O) is added to 500. mL of water at 50. °C. At this
temperature, the vapor pressure of pure water is 92.5 torr and its
density is 0.988 g/mL. The density of glycerol is 1.26 g/mL.
4. You add 1.00 kg of ethylene glycol antifreeze (CHO) to your
car radiator, which contains 4450 g of water. What are the
boiling and freezing points of the resulting solution?
5. A solution of propylene glycol (antifreeze) in the cars radiator
has a freezing point of -20°C. What is the molarity of the
solution?
0
Transcribed Image Text:Facebook l
SOLUTION:
water.
1.00 x 103 g C2H602 X
solvent
16.1 mol C2H602
4.450 kg H20
D7b 0.512 oC/m x 3.62 m = 1.85 oC
BP = 101.85 oC
acetic acid
benzene
carbon disulfide
carbon tetrachloride
chloroform
water
Table 13.6 Molal Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point
Depression Constants of Several Solvents
diethyl ether
ethanol
*at 1 atm.
cdn.fbsbx.com
boiling
point (OC)*
mol C2H602
62.07 g C2H602
= 3.62 m C2H602
117.9
80.1
46.2
1:45 PM
76.5
61.7
34.5
78.5
100.0
Kb (oC/m)
3.07
2.53
2.34
5.03
3.63
2.02
1.22
= 16.1 mol C2H602
0.512
DTf 1.86 oC/m x 3.62 m
FP = -6.73 OC
melting
point (OC)
16.6
5.5
-111.5
-23
-63.5
-116.2
-117.3
31%
0.0
Done
Kf (oC/m)
3.90
4.90
3.83
30.
4.70
1.79
1.99
1.86
Colligative Properties - BP Elevation
Example: Calculate the boiling point of an aqueous
solution that contains 20.0 g ethylene glycol (C2H6O2, a
nonvolatile liquid). In 100 g of water
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning