Can you help me this question Explain the short-run impact upon net exports and GDP of the following in the multiplier model, using Table 28-1 where possible: An increase in investment (I ) of $100 billion A decrease in government purchases (G) of $50 billion An increase in foreign output which increased exports by $10 billion A depreciation of the exchange rate that raised exports by $30 billion and lowered imports by $20 billion at every level of GDP
Can you help me this question Explain the short-run impact upon net exports and GDP of the following in the multiplier model, using Table 28-1 where possible: An increase in investment (I ) of $100 billion A decrease in government purchases (G) of $50 billion An increase in foreign output which increased exports by $10 billion A depreciation of the exchange rate that raised exports by $30 billion and lowered imports by $20 billion at every level of GDP
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
100%
Can you help me this question
Explain the short-run impact upon net exports and
An increase in investment (I ) of $100 billion
A decrease in government purchases (G) of $50 billion
An increase in foreign output which increased exports by $10 billion
A
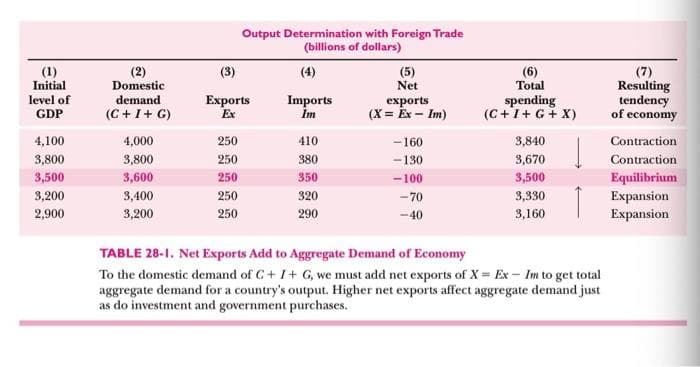
Transcribed Image Text:(1)
Initial
level of
GDP
4,100
3,800
3,500
3,200
2,900
(2)
Domestic
demand
(C+I+ G)
4,000
3,800
3,600
3,400
3,200
Output Determination with Foreign Trade
(billions of dollars)
(3)
Exports
Ex
250
250
250
250
250
Imports
Im
410
380
350
320
290
(5)
Net
exports
(X= Ex - Im)
-160
-130
-100
-70
-40
(6)
Total
spending
(C+I+G + X)
3,840
3,670
3,500
3,330
3,160
TABLE 28-1. Net Exports Add to Aggregate Demand of Economy
To the domestic demand of C+I+ G, we must add net exports of X= Ex- Im to get total
aggregate demand for a country's output. Higher net exports affect aggregate demand just
as do investment and government purchases.
(7)
Resulting
tendency
of economy
Contraction
Contraction
Equilibrium
Expansion
Expansion
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education