Case 7: A spring with a spring constant of 225 N/m is mounted vertically on the floor. A 1.22 kg ball is placed on the spring, which is compressed to point A, a distance of 1.51 meters from the spring's equilibrium position. The ball is released and pushed upward by the spring. Point B is 2.2 meters above point A. Point C is where the ball attains its maximum height. There is no rotation of the ball and no wind resistance. Point T B Gravitational Potential Energy Elastic Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy Lost to Friction Total Mechanical Energy
Case 7: A spring with a spring constant of 225 N/m is mounted vertically on the floor. A 1.22 kg ball is placed on the spring, which is compressed to point A, a distance of 1.51 meters from the spring's equilibrium position. The ball is released and pushed upward by the spring. Point B is 2.2 meters above point A. Point C is where the ball attains its maximum height. There is no rotation of the ball and no wind resistance. Point T B Gravitational Potential Energy Elastic Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy Lost to Friction Total Mechanical Energy
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter7: Rotational Motion And The Law Of Gravity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 76AP: A massless spring of constant k = 78.4 N/m is fixed on the left side of a level track. A block of...
Related questions
Question
100%
Very important and needed to be completed, Thank you very much
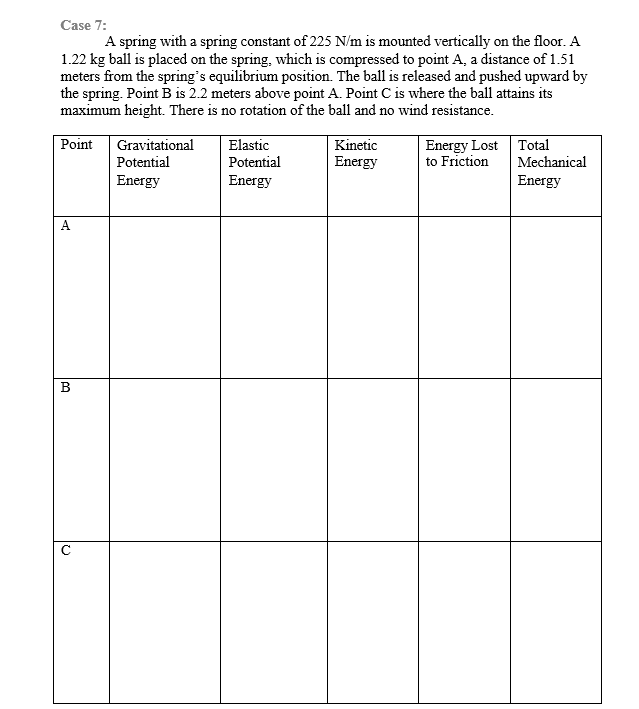
Transcribed Image Text:Case 7:
A spring with a spring constant of 225 N/m is mounted vertically on the floor. A
1.22 kg ball is placed on the spring, which is compressed to point A, a distance of 1.51
meters from the spring's equilibrium position. The ball is released and pushed upward by
the spring. Point B is 2.2 meters above point A. Point C is where the ball attains its
maximum height. There is no rotation of the ball and no wind resistance.
Point
A
B
с
Gravitational
Potential
Energy
Elastic
Potential
Energy
Kinetic
Energy
Energy Lost
to Friction
Total
Mechanical
Energy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning