"Photosynthesis is a process in which light energy is captured and stored by an organism, and the stored energy is used to drive cellular processes," (Blankenship, p. 1). Photosynthesis doesn't just happen in green plants; it can occur in bacteria, as well. It occurs when light- harvesting molecules absorb energy in the form of light and transfer it to a reaction center, where light energy is converted to chemical energy. Most of us know about chlorophyll as the light-harvesting molecule, but there are many forms of chlorophyll found in different organisms. However, they all have similar properties when interacting with light. PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS 1.6 C 0.7 1.4 0.6 1.2- Soret 0.5 A 0.4 0.8 H COOCH, phytyl bacteriochlorophyll a 0.3 0.6 0.2 0.4 0.1 0.2 01 700 750 800 850 900 300 400 500 600 700 800 2 (nm) 2 (nm) Figure 4.7 Absorption (left) and fluorescence (right) spectra of bacteriochlorophyll a in diethyl ether. 5. Look at this figure from Blankenship's book, Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis. You can see the structure for bacteriochlorophyll a, along with its absorption spectrum. a. What is the molecular shape around the labeled carbon atom? b. What is the hybridization around that same carbon? c. Based on this structure, would you exnect this molecule to absorb light in the visible spectrum? Why or why not Absorbance Fluorescence (Arbitrary units)
"Photosynthesis is a process in which light energy is captured and stored by an organism, and the stored energy is used to drive cellular processes," (Blankenship, p. 1). Photosynthesis doesn't just happen in green plants; it can occur in bacteria, as well. It occurs when light- harvesting molecules absorb energy in the form of light and transfer it to a reaction center, where light energy is converted to chemical energy. Most of us know about chlorophyll as the light-harvesting molecule, but there are many forms of chlorophyll found in different organisms. However, they all have similar properties when interacting with light. PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS 1.6 C 0.7 1.4 0.6 1.2- Soret 0.5 A 0.4 0.8 H COOCH, phytyl bacteriochlorophyll a 0.3 0.6 0.2 0.4 0.1 0.2 01 700 750 800 850 900 300 400 500 600 700 800 2 (nm) 2 (nm) Figure 4.7 Absorption (left) and fluorescence (right) spectra of bacteriochlorophyll a in diethyl ether. 5. Look at this figure from Blankenship's book, Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis. You can see the structure for bacteriochlorophyll a, along with its absorption spectrum. a. What is the molecular shape around the labeled carbon atom? b. What is the hybridization around that same carbon? c. Based on this structure, would you exnect this molecule to absorb light in the visible spectrum? Why or why not Absorbance Fluorescence (Arbitrary units)
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter7: Quantum Theory Of The Atom
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.100QP: Ozone in the stratosphere absorbs ultraviolet light of wavelengths shorter than 320 nm, thus...
Related questions
Question
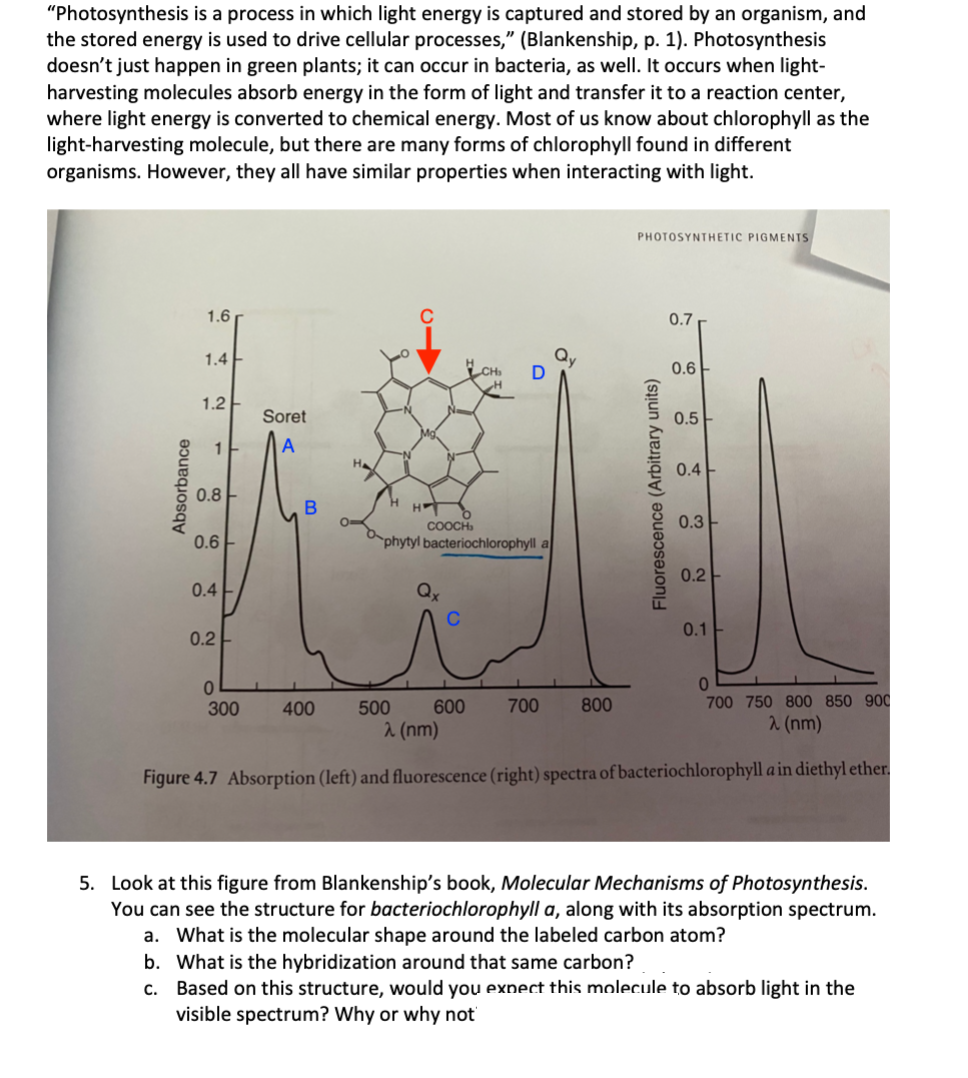
Transcribed Image Text:"Photosynthesis is a process in which light energy is captured and stored by an organism, and
the stored energy is used to drive cellular processes," (Blankenship, p. 1). Photosynthesis
doesn't just happen in green plants; it can occur in bacteria, as well. It occurs when light-
harvesting molecules absorb energy in the form of light and transfer it to a reaction center,
where light energy is converted to chemical energy. Most of us know about chlorophyll as the
light-harvesting molecule, but there are many forms of chlorophyll found in different
organisms. However, they all have similar properties when interacting with light.
PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS
1.6
C
0.7
1.4
0.6
1.2-
Soret
0.5
A
0.4
0.8
H
COOCH,
phytyl bacteriochlorophyll a
0.3
0.6
0.2
0.4
0.1
0.2
01
700 750 800 850 900
300
400
500
600
700
800
2 (nm)
2 (nm)
Figure 4.7 Absorption (left) and fluorescence (right) spectra of bacteriochlorophyll a in diethyl ether.
5. Look at this figure from Blankenship's book, Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis.
You can see the structure for bacteriochlorophyll a, along with its absorption spectrum.
a. What is the molecular shape around the labeled carbon atom?
b. What is the hybridization around that same carbon?
c. Based on this structure, would you exnect this molecule to absorb light in the
visible spectrum? Why or why not
Absorbance
Fluorescence (Arbitrary units)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning