The reaction below was carried out in a 1.00 L container. At equilibrium it is found that there are 0.0227 mole S(s), 0.00220 mole H₂O(g), 0.406 mol H₂S(g) and 0.512 mol SO₂(g). What is the value of Kc? 3 S(s) + 2 H₂O(g) = 2 H₂S(g) + SO₂(g) 1.49 x 10⁹ O 6.71 x 10-10 O 5.73 x 10-5 5.66 x 10-11 O 1.74 x 104 The reaction below has a rate constant of 2.6 x 10-3 L²mol-2.5-¹. If the rate of disappearance of O₂ is 0.066 mol/L-min, what is the rate of appearance of NO₂? 4 NH3(g) +7 O2(g) 4 NO2(g) + 6 H₂O(g) Enter your answer without units using decimal notation (but give an answer that has units of mol/L-min). Answer with 2 significant figures..
The reaction below was carried out in a 1.00 L container. At equilibrium it is found that there are 0.0227 mole S(s), 0.00220 mole H₂O(g), 0.406 mol H₂S(g) and 0.512 mol SO₂(g). What is the value of Kc? 3 S(s) + 2 H₂O(g) = 2 H₂S(g) + SO₂(g) 1.49 x 10⁹ O 6.71 x 10-10 O 5.73 x 10-5 5.66 x 10-11 O 1.74 x 104 The reaction below has a rate constant of 2.6 x 10-3 L²mol-2.5-¹. If the rate of disappearance of O₂ is 0.066 mol/L-min, what is the rate of appearance of NO₂? 4 NH3(g) +7 O2(g) 4 NO2(g) + 6 H₂O(g) Enter your answer without units using decimal notation (but give an answer that has units of mol/L-min). Answer with 2 significant figures..
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter14: Chemical Kinetics: The Rates Of Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12PS: The reaction 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) was studied at 904 C, and the data in the table...
Related questions
Question
100%
(a) and (b) questions?
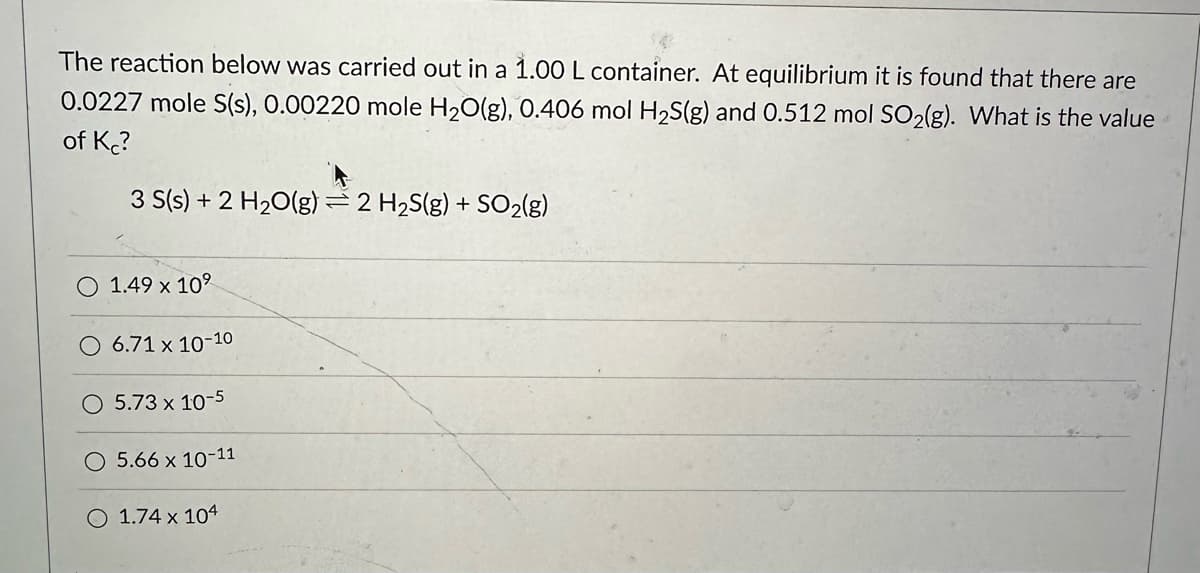
Transcribed Image Text:The reaction below was carried out in a 1.00 L container. At equilibrium it is found that there are
0.0227 mole S(s), 0.00220 mole H₂O(g), 0.406 mol H₂S(g) and 0.512 mol SO₂(g). What is the value
of Kc?
3 S(s) + 2 H₂O(g) = 2 H₂S(g) + SO₂(g)
1.49 x 10⁹
O 6.71 x 10-10
O 5.73 x 10-5
5.66 x 10-11
O 1.74 x 104

Transcribed Image Text:The reaction below has a rate constant of 2.6 x 10-3 L²mol-2.5-¹. If the rate of disappearance of O₂
is 0.066 mol/L-min, what is the rate of appearance of NO₂?
4 NH3(g) +7 O2(g) 4 NO2(g) + 6 H₂O(g)
Enter your answer without units using decimal notation (but give an answer that has units of
mol/L-min). Answer with 2 significant figures..
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning