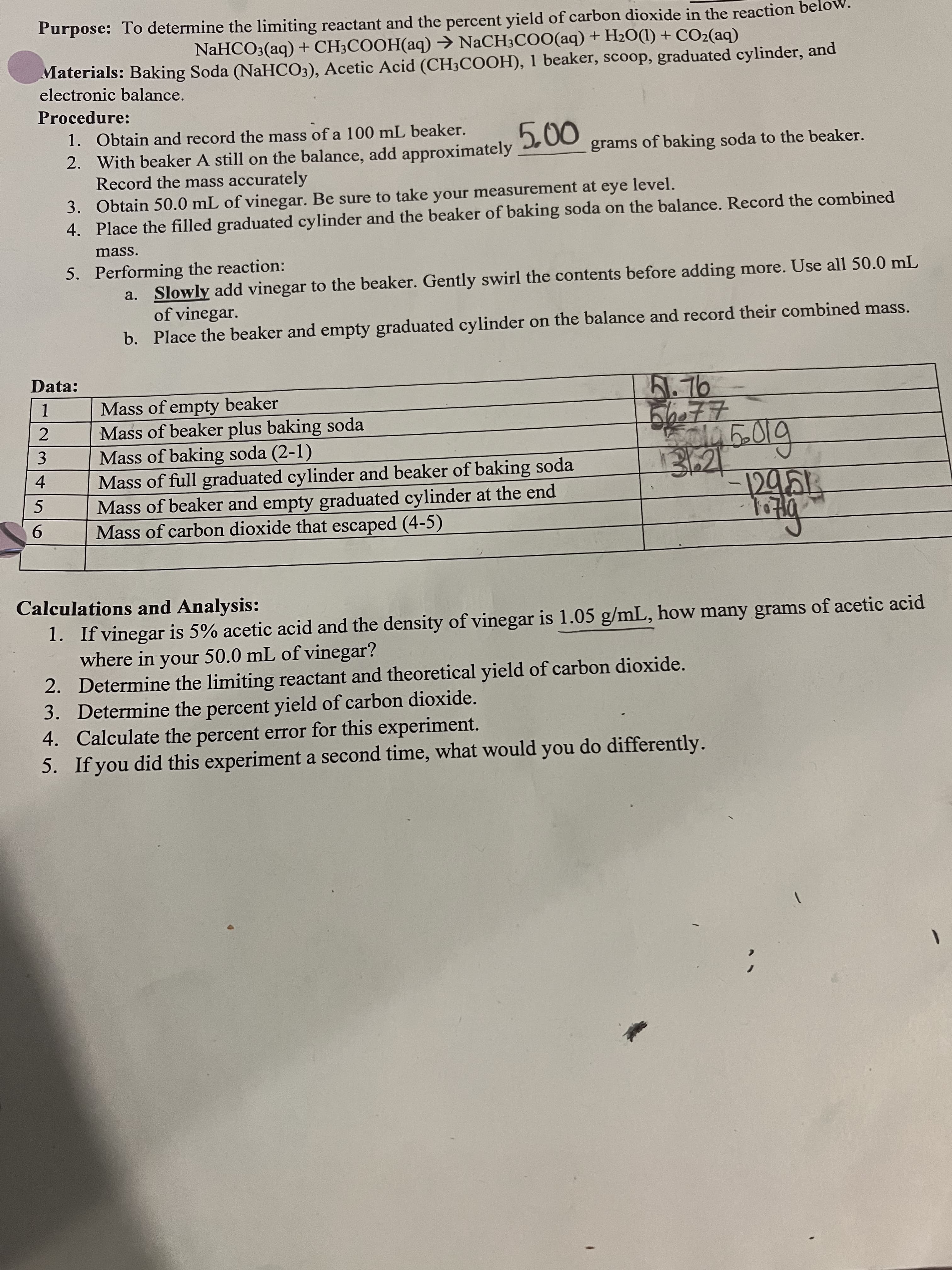
234 Purpose: To determine the limiting reactant and the percent yield of carbon dioxide in the reaction bel NaHCO3(aq) + CH3COOH(aq) → NACH3CO0(aq) + H2O(1) + CO2(aq) Materials: Baking Soda (NaHCO3), Acetic Acid (CH3COOH), 1 beaker, scoop, graduated cylinder, and electronic balance. Procedure: 000 grams of baking soda to the beaker. 1. Obtain and record the mass of a 100 mL beaker. 2. With beaker A still on the balance, add approximately Record the mass accurately 3. Obtain 50.0 mL of vinegar. Be sure to take your measurement at eye level. 4. Place the filled graduated cylinder and the beaker of baking soda on the balance. Record the combined mass. 5. Performing the reaction: a. Slowly add vinegar to the beaker. Gently swirl the contents before adding more. Use all 50.0 mL of vinegar. b. Place the beaker and empty graduated cylinder on the balance and record their combined mass. Data: B.76 Mass of empty beaker 1. Mass of beaker plus baking soda Mass of baking soda (2-1) Mass of full graduated cylinder and beaker of baking soda Mass of beaker and empty graduated cylinder at the end Mass of carbon dioxide that escaped (4-5) 9. पिछा Calculations and Analysis: 1. If vinegar is 5% acetic acid and the density of vinegar is 1.05 g/mL, how many grams of acetic acid where in your 50.0 mL of vinegar? 2. Determine the limiting reactant and theoretical yield of carbon dioxide. 3. Determine the percent yield of carbon dioxide. 4. Calculate the percent error for this experiment. 5. If you did this experiment a second time, what would you do differently. 1.
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.
I need help with questions 2-5 with guided steps.... I only got help with the first one which I understood.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps






