Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter15: Acid–base Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 99AP
Related questions
Question
Compute for the weight of NaCl needed to prepare 250 mL of 0.05 M NaCl solution.
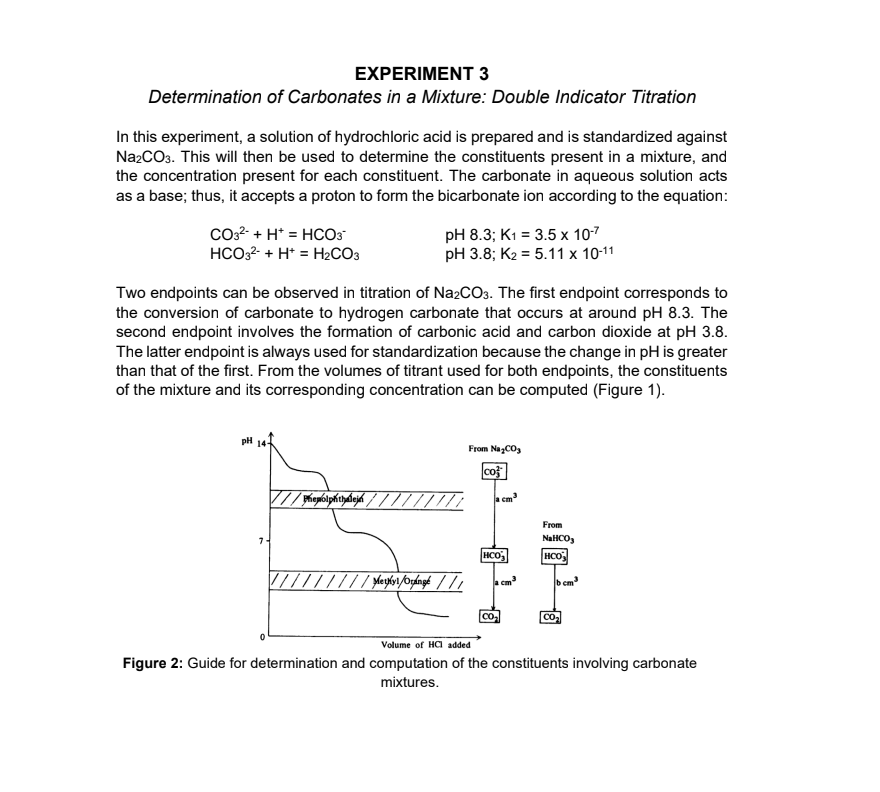
Transcribed Image Text:EXPERIMENT 3
Determination of Carbonates in a Mixture: Double Indicator Titration
In this experiment, a solution of hydrochloric acid is prepared and is standardized against
N22CO3. This will then be used to determine the constituents present in a mixture, and
the concentration present for each constituent. The carbonate in aqueous solution acts
as a base; thus, it accepts a proton to form the bicarbonate ion according to the equation:
pH 8.3; K1 = 3.5 x 10-7
рH 3.8; Кг %3D 5.11 х 10-11
CO32- + H* = HCO3
%3D
HCO32- + H* = H2CO3
Two endpoints can be observed in titration of Na2CO3. The first endpoint corresponds to
the conversion of carbonate to hydrogen carbonate that occurs at around pH 8.3. The
second endpoint involves the formation of carbonic acid and carbon dioxide at pH 3.8.
The latter endpoint is always used for standardization because the change in pH is greater
than that of the first. From the volumes of titrant used for both endpoints, the constituents
of the mixture and its corresponding concentration can be computed (Figure 1).
pH 14-
From NazCO,
cos
cm
From
NaHCO,
HCO
HCO
cm
b cm
CO2
Volume of HCI added
Figure 2: Guide for determination and computation of the constituents involving carbonate
mixtures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
