Consider a population P(t) satisfying the logistic equation dP = aP – bP2 where B = aP is dt - the time rate at which births occur and D = bP² is the rate at which deaths occur. If initial population is P(0) = Po and B, biths per month and Do deaths per month are occuring at BoPo time t = 0, show that the limiting population is M = Do %3D
Consider a population P(t) satisfying the logistic equation dP = aP – bP2 where B = aP is dt - the time rate at which births occur and D = bP² is the rate at which deaths occur. If initial population is P(0) = Po and B, biths per month and Do deaths per month are occuring at BoPo time t = 0, show that the limiting population is M = Do %3D
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
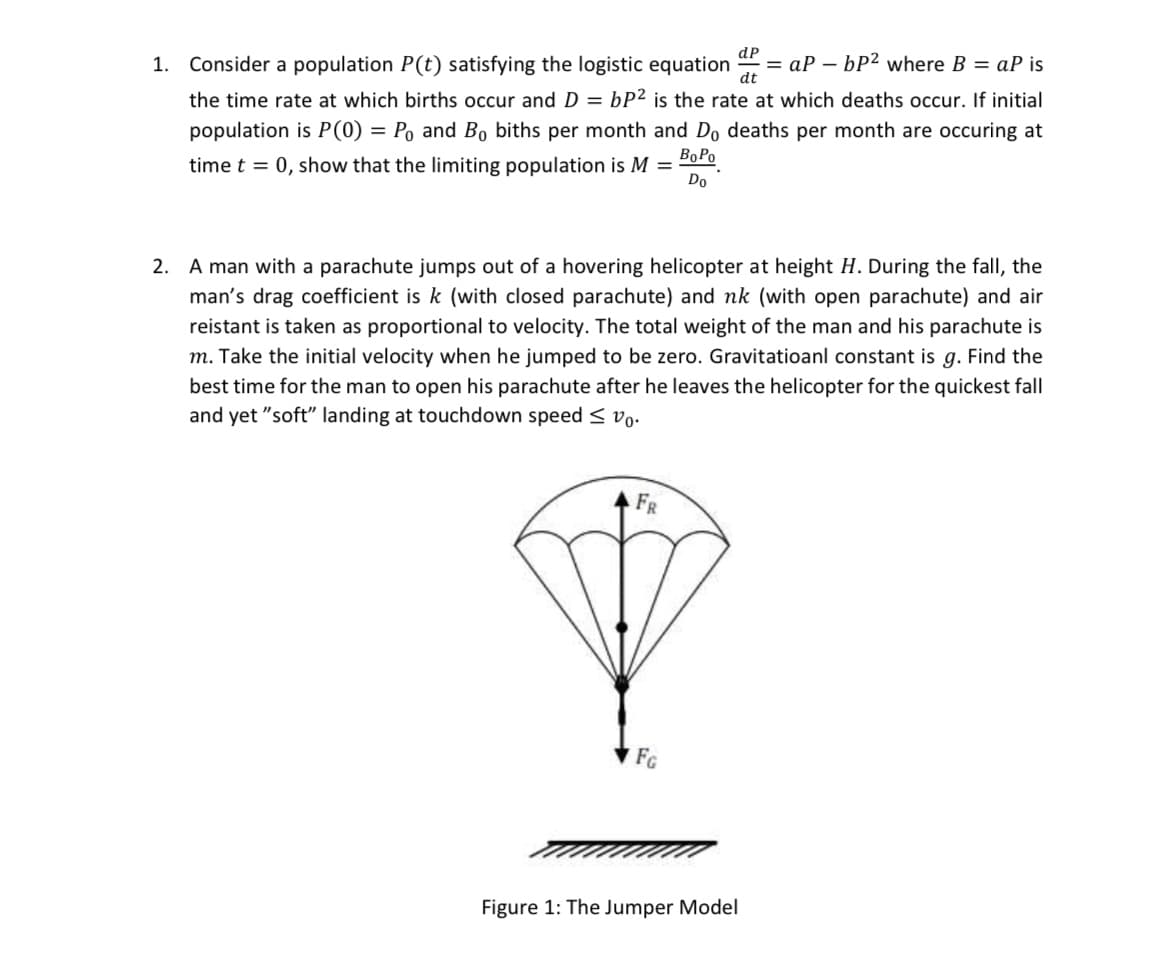
Transcribed Image Text:1. Consider a population P(t) satisfying the logistic equation
dP
= aP – bP2 where B = aP is
dt
the time rate at which births occur and D = bP2 is the rate at which deaths occur. If initial
population is P(0) = Po and Bọ biths per month and Do deaths per month are occuring at
BoPo
time t = 0, show that the limiting population is M =
Do
2. A man with a parachute jumps out of a hovering helicopter at height H. During the fall, the
man's drag coefficient is k (with closed parachute) and nk (with open parachute) and air
reistant is taken as proportional to velocity. The total weight of the man and his parachute is
m. Take the initial velocity when he jumped to be zero. Gravitatioanl constant is g. Find the
best time for the man to open his parachute after he leaves the helicopter for the quickest fall
and yet "soft" landing at touchdown speed < vo.
FR
FG
Figure 1: The Jumper Model
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

