Consider a Solow-Swan economy with a Cobb-Douglas production function with a constant savings rate. Imagine that the population growth rate "n" is a decreasing function of capital and it has the following functional form: for low values of k it's constant at some high level. For intermediate levels of k, it decreases rapidly. And for high values of k the population growth rate is constant again. In other words, the population growth rate looks like : a. Why may the population growth rate look like this? (make sure you discuss its three components and how each of them may be a function of k in the real world) b. Does a steady state necessarily exist?
Consider a Solow-Swan economy with a Cobb-Douglas production function with a constant savings rate. Imagine that the population growth rate "n" is a decreasing function of capital and it has the following functional form: for low values of k it's constant at some high level. For intermediate levels of k, it decreases rapidly. And for high values of k the population growth rate is constant again. In other words, the population growth rate looks like : a. Why may the population growth rate look like this? (make sure you discuss its three components and how each of them may be a function of k in the real world) b. Does a steady state necessarily exist?
Chapter20: Economic Growth In The Global Economy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5P
Related questions
Question
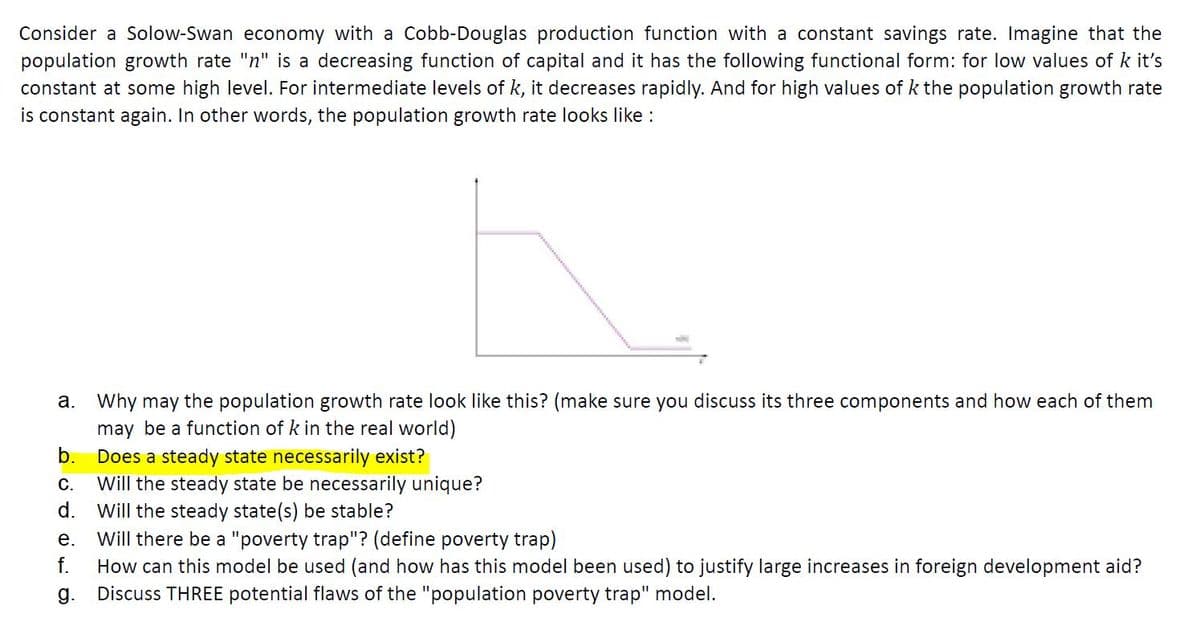
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a Solow-Swan economy with a Cobb-Douglas production function with a constant savings rate. Imagine that the
population growth rate "n" is a decreasing function of capital and it has the following functional form: for low values of k it's
constant at some high level. For intermediate levels of k, it decreases rapidly. And for high values of k the population growth rate
is constant again. In other words, the population growth rate looks like :
a. Why may the population growth rate look like this? (make sure you discuss its three components and how each of them
may be a function of k in the real world)
b.
Does a steady state necessarily exist?
Will the steady state be necessarily unique?
Will the steady state(s) be stable?
Will there be a "poverty trap"? (define poverty trap)
How can this model be used (and how has this model been used) to justify large increases in foreign development aid?
Discuss THREE potential flaws of the "population poverty trap" model.
C.
d.
е.
f.
g.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc