Consider Case #2 from Table 1: Table 1: Case numbers and their respective Pg and V2 Initial pressure (P1) Volume in state 2 (V2) Case # (kPa) (m³) 1 900 0.306 2 1000 0.270 1200 0.216 4 1400 0.186 5 1000 0.234 a) Find the temperature when the piston just touched the stopper (T2) in °C. b) Find the final pressure (P3) in kPa. c) Find the total heat transfer from state 1 to state 3. d) Draw a T-v in reference to the saturation line showing the constant pressure lines and all the states.
Consider Case #2 from Table 1: Table 1: Case numbers and their respective Pg and V2 Initial pressure (P1) Volume in state 2 (V2) Case # (kPa) (m³) 1 900 0.306 2 1000 0.270 1200 0.216 4 1400 0.186 5 1000 0.234 a) Find the temperature when the piston just touched the stopper (T2) in °C. b) Find the final pressure (P3) in kPa. c) Find the total heat transfer from state 1 to state 3. d) Draw a T-v in reference to the saturation line showing the constant pressure lines and all the states.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Please solve this problem
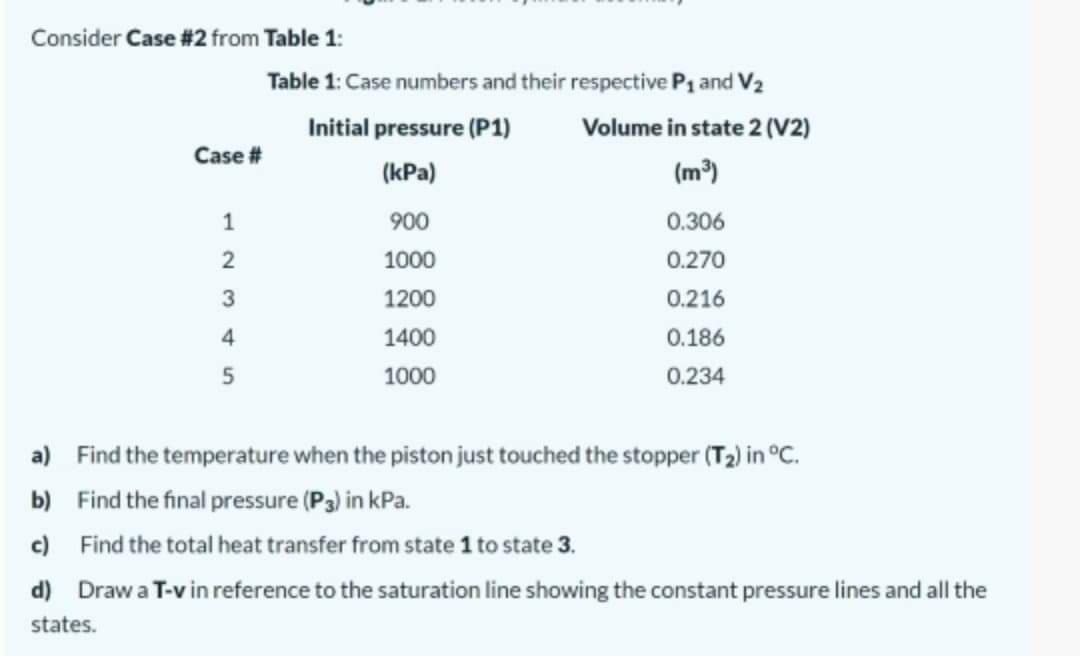
Transcribed Image Text:Consider Case #2 from Table 1:
Table 1: Case numbers and their respective P1 and V2
Initial pressure (P1)
Volume in state 2 (V2)
Case #
(kPa)
(m)
1
900
0.306
1000
0.270
1200
0.216
4
1400
0.186
5
1000
0.234
a) Find the temperature when the piston just touched the stopper (T2) in °C.
b) Find the final pressure (P3) in kPa.
c) Find the total heat transfer from state 1 to state 3.
d)
Draw a T-v in reference to the saturation line showing the constant pressure lines and all the
states.
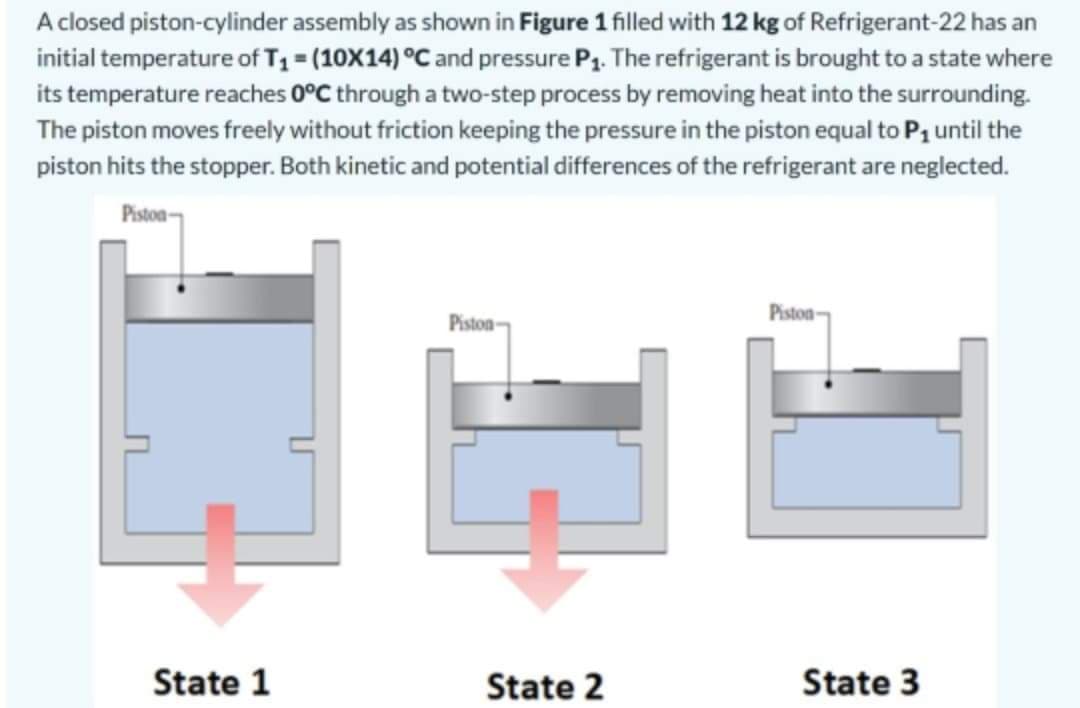
Transcribed Image Text:A closed piston-cylinder assembly as shown in Figure 1 filled with 12 kg of Refrigerant-22 has an
initial temperature of T1 = (10X14) °C and pressure P1. The refrigerant is brought to a state where
its temperature reaches 0°C through a two-step process by removing heat into the surrounding.
The piston moves freely without friction keeping the pressure in the piston equal to P1 until the
piston hits the stopper. Both kinetic and potential differences of the refrigerant are neglected.
Piston-
Piston-
Piston
State 1
State 2
State 3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY