Consider I =E∫x32dx1dx2dx3 , where x12 + x22 ≤ x32 , 0 ≤ x3 ≤ 1 ,that is, E is the solid bounded by the cone x12 + x22 = x32 , the plane x3=0, and the plane x3=1 (a)Sketch the solid E' in spherical coordinates that will correspond to E. (b)In the application of Fubini's theorem to the E′ solution of the question (a) above, with the orderof integration ∫∫∫ρ4cos2(ϕ)sen(ϕ)dρdϕdθ explain, illustrating in the sketch of solid E', how we find the lower and upper ends of the iterated integrals (c)Use spherical coordinates to calculate I.
Consider I =E∫x32dx1dx2dx3 , where x12 + x22 ≤ x32 , 0 ≤ x3 ≤ 1 ,that is, E is the solid bounded by the cone x12 + x22 = x32 , the plane x3=0, and the plane x3=1
(a)Sketch the solid E' in spherical coordinates that will correspond to E.
(b)In the application of Fubini's theorem to the E′ solution of the question (a) above, with the orderof
(c)Use spherical coordinates to calculate I.
Some data may be needed (see image below): In the formulas below E, S and l always denote a solid, a surface, and a line, respectively. While n(x) denotes the normal unitary exterior of S in x, and T(x) denotes the unitary tangent of l in x.
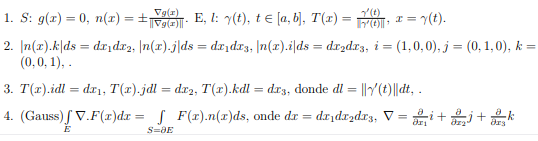
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









