Consider the DE d'y + 16- + 64y = I dz2 dr hich is linear with constant coefficients. irst we will work on solving the corresponding homogeneous equation. The auxiliary equation (using m as your variable) is = 0 which has root Because this is a repeated root, we don't have much choice but to use the exponential function corresponding to this root to do reduction of order. 8z 2 = ue Then (using the prime notation for the derivatives) So, plugging Y2 into the left side of the differential equation, and reducing, we get
Consider the DE d'y + 16- + 64y = I dz2 dr hich is linear with constant coefficients. irst we will work on solving the corresponding homogeneous equation. The auxiliary equation (using m as your variable) is = 0 which has root Because this is a repeated root, we don't have much choice but to use the exponential function corresponding to this root to do reduction of order. 8z 2 = ue Then (using the prime notation for the derivatives) So, plugging Y2 into the left side of the differential equation, and reducing, we get
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
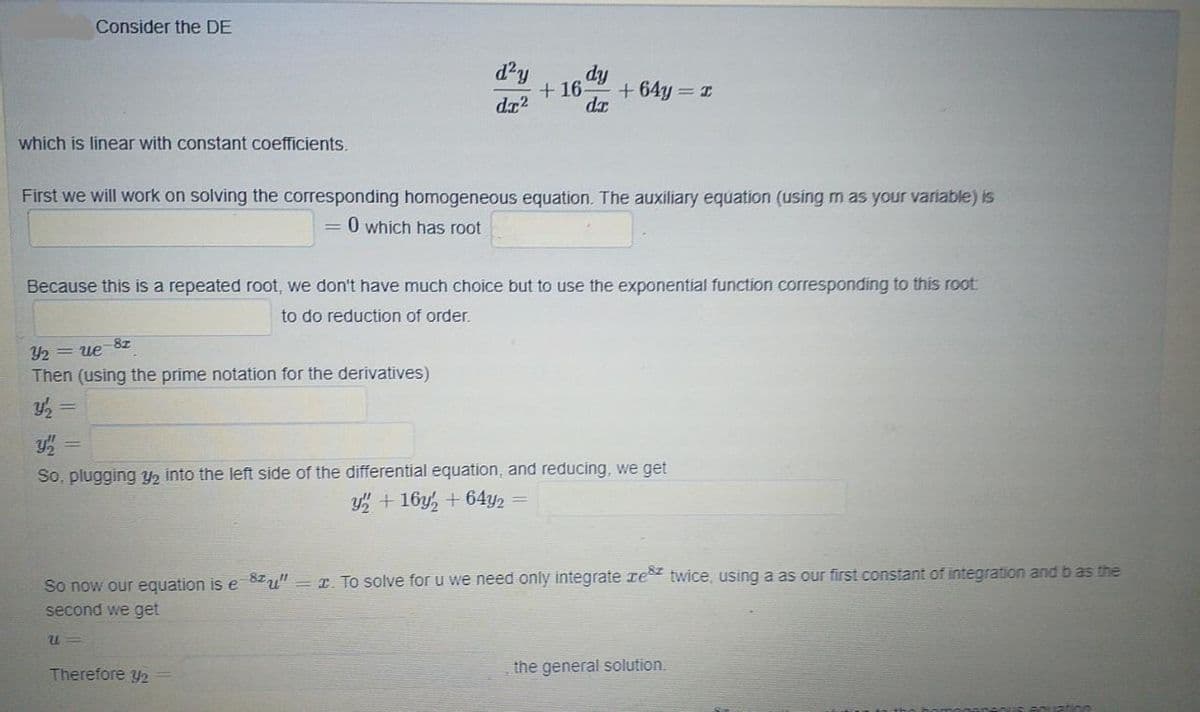
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the DE
d'y
fip
+ 16-
+ 64y = I
dz2
da
which is linear with constant coefficients.
First we will work on solving the corresponding homogeneous equation. The auxiliary equation (using m as your variable) is
O which has root
Because this is a repeated root, we don't have much choice but to use the exponential function corresponding to this root
to do reduction of order.
Y2 = ue
Then (using the prime notation for the derivatives)
So, plugging Y2 into the left side of the differential equation, and reducing, we get
y + 16y, + 64y2 =
So now our equation is e 8Iu" = r. To solve for u we need only integrate re twice, using a as our first constant of integration and b as the
second we get
Therefore y2
the general solution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

