Consider the following data from a repeated-measures design. You want to use a repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H.: HD = 0 (the null hypothesis states that the mean difference for the general population is zero). The data consist of five observations, each with two measurements, A and B, taken before and after a treatment. Assume the population of the differences in these measurements are normally distributed. Complete the following table by calculating the differences and the squared differences:
Consider the following data from a repeated-measures design. You want to use a repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H.: HD = 0 (the null hypothesis states that the mean difference for the general population is zero). The data consist of five observations, each with two measurements, A and B, taken before and after a treatment. Assume the population of the differences in these measurements are normally distributed. Complete the following table by calculating the differences and the squared differences:
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:SMD
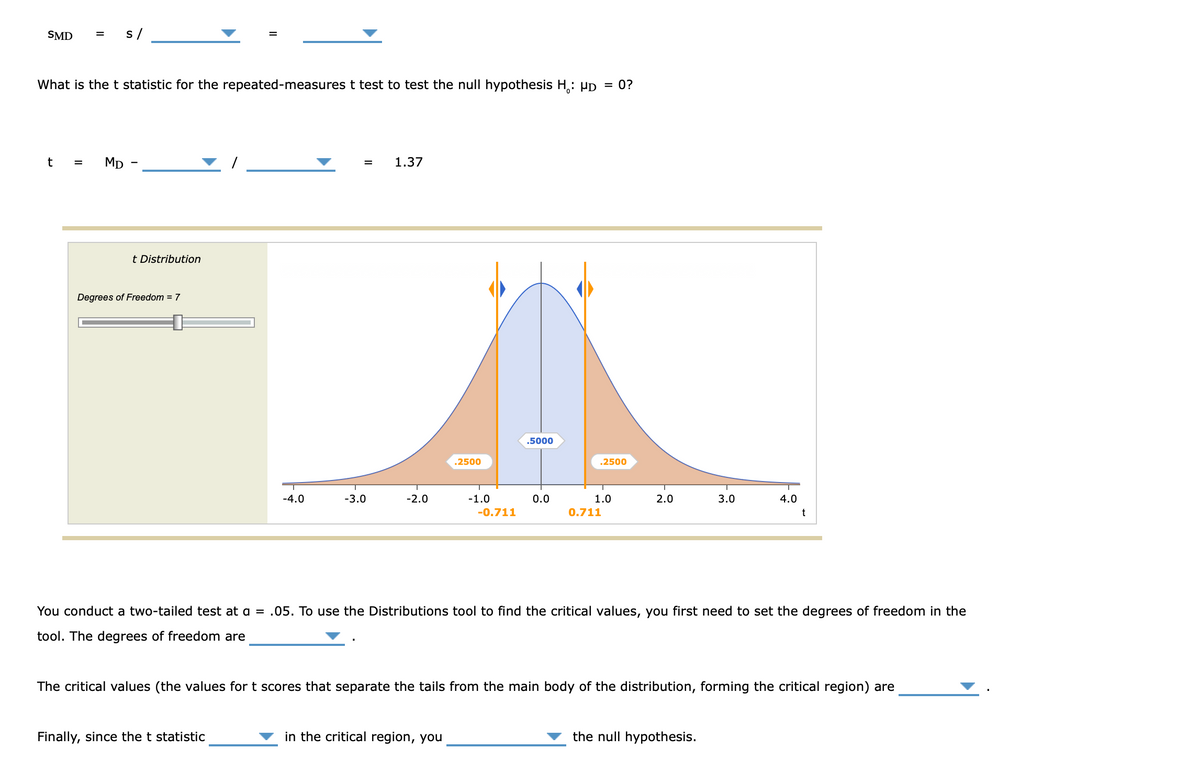
S/
What is the t statistic for the repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H₂: µd = 0?
t
= MD -
=
1.37
t Distribution
Degrees of Freedom = 7
T
T
T
-4.0
-3.0
-2.0
2.0
3.0
-0.711
0.711
t
You conduct a two-tailed test at a = .05. To use the Distributions tool to find the critical values, you first need to set the degrees of freedom in the
tool. The degrees of freedom are
The critical values (the values for t scores that separate the tails from the main body of the distribution, forming the critical region) are
Finally, since the t statistic
in the critical region, you
the null hypothesis.
.2500
-1.0
.5000
0.0
.2500
T
1.0
4.0

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following data from a repeated-measures design. You want to use a repeated-measures t test to test the null hypothesis H₁: HD = 0 (the
null hypothesis states that the mean difference for the general population is zero). The data consist of five observations, each with two measurements,
A and B, taken before and after a treatment. Assume the population of the differences in these measurements are normally distributed.
Complete the following table by calculating the differences and the squared differences:
Difference Score
Squared Difference Score
(D²)
Observation A B
(D = B - A)
1
1
2
2
3
3
3
4 6
4
6
5
5
6 8
The mean difference score is Mp
For a repeated-measures t test, you need to calculate the t statistic, which requires you to calculates and SMD.
What is the estimated standard deviation of the difference scores?
S =
= V
6.80 /
What is the estimated standard error of the mean difference scores? (Note: For best results, retain at least six decimal places from your calculation of
s.)
SMD
s /
||
LO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill