Consider the following region R and the vector field F. a. Compute the two-dimensional divergence of the vector field. b. Evaluate both integrals in the flux form of Green's Theorem and check for consistency. c. State whether the vector field is source free. F= (8xy,9x? - 4y?); R is the region bounded by y = x(5 – x) and y = 0. a. The two-dimensional divergence is b. Set up the integral over the region. Set up the line integral for the y = x(5 - x) boundary. jo. dt Set up the line integral for the y = 0 boundary. 5 dt Evaluate these integrals and check for consistency. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes to complete your choice. O A. The integrals are not consistent because the integral over R evaluates to while the line integrals evaluate to O B. The integrals are consistent because they all evaluate to c. Is the vector field source-free? O A. No, because the two-dimensional divergence is not zero everywhere. O B. Yes, because the two-dimensional divergence is zero everywhere. OC. Yes, because the flux is zero for the given region. O D. No, because the flux is zero only for the given region.
Consider the following region R and the vector field F. a. Compute the two-dimensional divergence of the vector field. b. Evaluate both integrals in the flux form of Green's Theorem and check for consistency. c. State whether the vector field is source free. F= (8xy,9x? - 4y?); R is the region bounded by y = x(5 – x) and y = 0. a. The two-dimensional divergence is b. Set up the integral over the region. Set up the line integral for the y = x(5 - x) boundary. jo. dt Set up the line integral for the y = 0 boundary. 5 dt Evaluate these integrals and check for consistency. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes to complete your choice. O A. The integrals are not consistent because the integral over R evaluates to while the line integrals evaluate to O B. The integrals are consistent because they all evaluate to c. Is the vector field source-free? O A. No, because the two-dimensional divergence is not zero everywhere. O B. Yes, because the two-dimensional divergence is zero everywhere. OC. Yes, because the flux is zero for the given region. O D. No, because the flux is zero only for the given region.
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
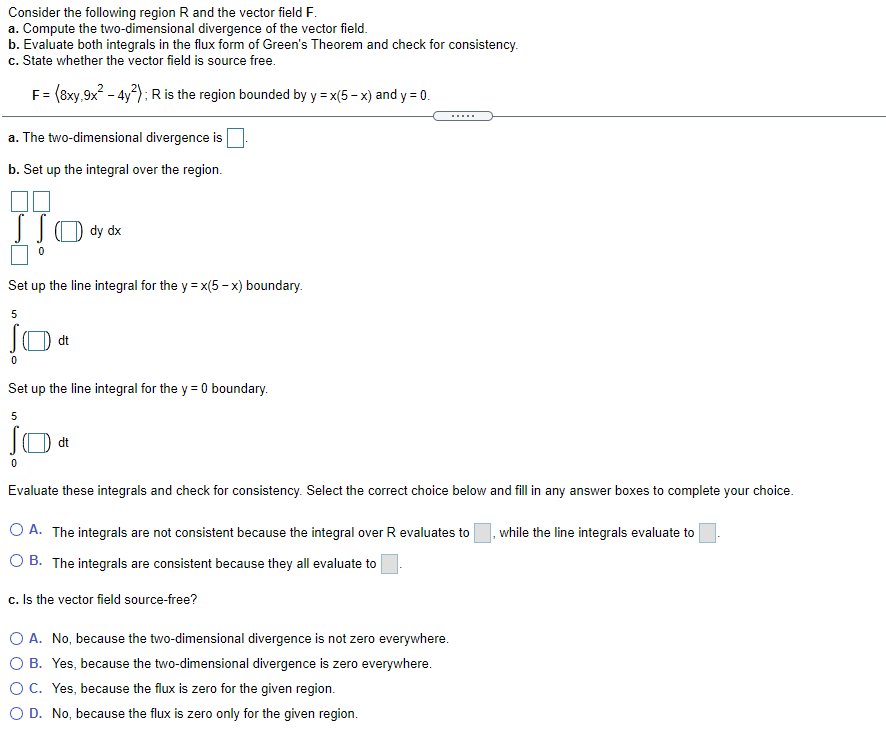
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following region R and the vector field F.
a. Compute the two-dimensional divergence of the vector field.
b. Evaluate both integrals in the flux form of Green's Theorem and check for consistency.
c. State whether the vector field is source free.
F= (8xy,9x? - 4y?); R is the region bounded by y = x(5 - x) and y = 0.
a. The two-dimensional divergence is
b. Set up the integral over the region.
dy dx
Set up the line integral for the y = x(5 - x) boundary.
5
dt
Set up the line integral for the y = 0 boundary.
5
dt
Evaluate these integrals and check for consistency. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes to complete your choice.
O A. The integrals are not consistent because the integral over R evaluates to|
, while the line integrals evaluate to
B. The integrals are consistent because they all evaluate to
c. Is the vector field source-free?
O A. No, because the two-dimensional divergence is not zero everywhere.
O B. Yes, because the two-dimensional divergence is zero everywhere.
OC. Yes, because the flux is zero for the given region.
O D. No, because the flux is zero only for the given region.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

