Consider the following version or the linear Cournot duopoly model. The market price, P is determined by (inverse) market demand: P =1- Q if Q<1, P = 0 otherwise Each firm decides on the quantity to sell (market share): q1 and q2. Q = q1 + q2 total market demand. Both firms seek to maximize profits. There are no fixed costs. The marginal cost of producing each unit of the good: c1 and c2. c1 is common knowledge and equal to , however c2 is known only by firm 2. Firm 1 believes that c2 is 'high" c = } with probability and 'low' c = 0 with probability . Firm l’s belief about firm 2's cost is common knowledge Find the pure strategy Bayes Nash Equilibrium and compare it to the situation in which the cost of firm 2 is common knowledge. Does firm 2 have an incentive to reveal her cost when it is low? When it is high? What do you conclude?
Consider the following version or the linear Cournot duopoly model. The market price, P is determined by (inverse) market demand: P =1- Q if Q<1, P = 0 otherwise Each firm decides on the quantity to sell (market share): q1 and q2. Q = q1 + q2 total market demand. Both firms seek to maximize profits. There are no fixed costs. The marginal cost of producing each unit of the good: c1 and c2. c1 is common knowledge and equal to , however c2 is known only by firm 2. Firm 1 believes that c2 is 'high" c = } with probability and 'low' c = 0 with probability . Firm l’s belief about firm 2's cost is common knowledge Find the pure strategy Bayes Nash Equilibrium and compare it to the situation in which the cost of firm 2 is common knowledge. Does firm 2 have an incentive to reveal her cost when it is low? When it is high? What do you conclude?
Chapter26: Monopolistic Competition And Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13E
Related questions
Question
Cournot competition with incomplete information -
Thank you!
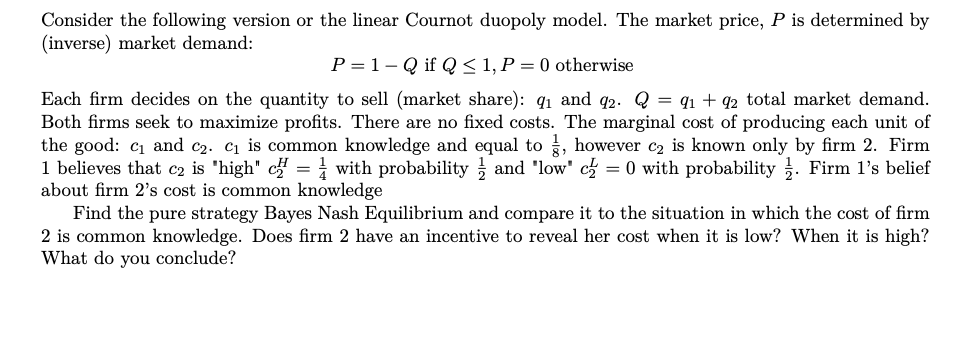
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following version or the linear Cournot duopoly model. The market price, P is determined by
(inverse) market demand:
P = 1- Q if Q< 1, P = 0 otherwise
Each firm decides on the quantity to sell (market share): q1 and q2. Q = q1 + q2 total market demand.
Both firms seek to maximize profits. There are no fixed costs. The marginal cost of producing each unit of
the good: c1 and c2. c1 is common knowledge and equal to , however c2 is known only by firm 2. Firm
1 believes that c2 is 'high" c = i with probability and 'low' c = 0 with probability . Firm l's belief
about firm 2's cost is common knowledge
Find the pure strategy Bayes Nash Equilibrium and compare it to the situation in which the cost of firm
2 is common knowledge. Does firm 2 have an incentive to reveal her cost when it is low? When it is high?
What do you conclude?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



