Consider the insoluble compound silver hydroxide , AgOH . The silver ion also forms a complex with cyanide ions . Write a balanced net ionic equation to show why the solubility of AgOH (s) increases in the presence of cyanide ions and calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction. For Ag(CN)," , Kę=5.6×1018 . Use the pull-down boxes to specify states such as (aq) or (s). K=
Consider the insoluble compound silver hydroxide , AgOH . The silver ion also forms a complex with cyanide ions . Write a balanced net ionic equation to show why the solubility of AgOH (s) increases in the presence of cyanide ions and calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction. For Ag(CN)," , Kę=5.6×1018 . Use the pull-down boxes to specify states such as (aq) or (s). K=
Chapter10: Effect Of Electrolytes On Chemical Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.16QAP
Related questions
Question
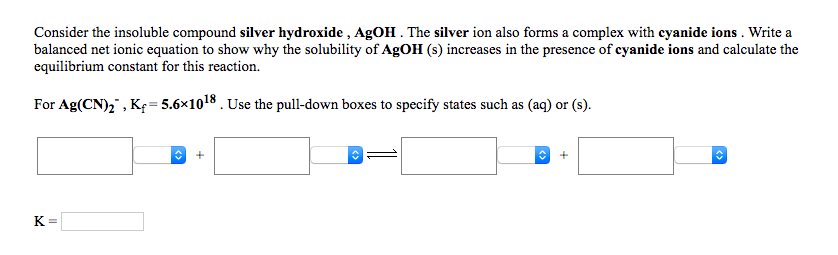
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the insoluble compound silver hydroxide , AgOH . The silver ion also forms a complex with cyanide ions . Write a
balanced net ionic equation to show why the solubility of AgOH (s) increases in the presence of cyanide ions and calculate the
equilibrium constant for this reaction.
For Ag(CN)," , Kę=5.6×1018 . Use the pull-down boxes to specify states such as (aq) or (s).
K=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

