Consider the titration of a 25.0mL sample of 0.195M acetic acid (CH3COOH) with 0.300M NaOH. Determine the pH after 5.0mL of NaOH is added. The Ka of acetic acid is 1.8x10-5.
Consider the titration of a 25.0mL sample of 0.195M acetic acid (CH3COOH) with 0.300M NaOH. Determine the pH after 5.0mL of NaOH is added.
The Ka of acetic acid is 1.8x10-5.
Buffers find variety of uses in chemical reactions requiring constant pH. They are prepared by adding of weak acid in strong base or its conjugate salt. They have a special property (buffer action) that enables them to resist any pH change.
Given:
The dissociation constant of acetic acid is .
The volume of acetic acid is 25 mL.
The concentration of acetic acid is 0.195 M.
The concentration of NaOH is 0.300 M.
The volume of NaOH is 5.0 mL.
Reaction between acetic acid and NaOH is shown below.
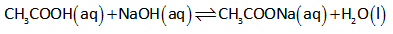
When 5 mL of NaOH is added, the number of moles of acetic acid is calculated as follows,
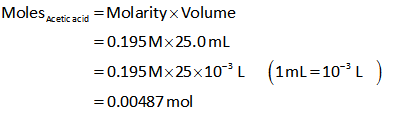
Similarly, the number of moles of NaOH is calculated as follows,
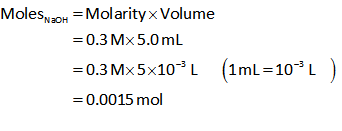
It is clear that moles of NaOH is less than that of acetic acid therefore, NaOH will get completely consumed in the reaction.
Thus, the ICE table is thus shown below.
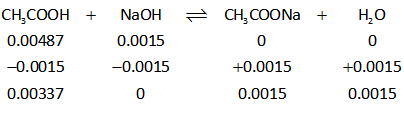
The solution contains only acetic acid and sodium acetate. Therefore, it is a buffer solution.
The pH of buffer solution is calculated by the formula shown below.
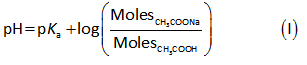
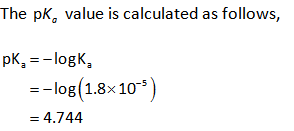
Plug in all values in equation (I).
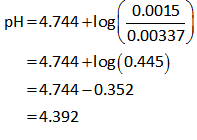
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 7 images









