Consider two firms that are choosing the price of competing products. The choices are contained in the payoff table. Each firm can raise price, lower price, or maintain their price. Suppose the game is played once each period forever. If both players play the strategy "always lower price" is this a Nash equilibrium? Let b = discount rate, 0 < b<1. Raise price Maintain price Lower price Firm B |Raise price Maintain price Lower price 6. 4 8. 8 1. 1 5, 5 4, 6 2, 7 7.2 1. 1 _3, 3 Firm A O No, because it is dominated by raising the price. O No, because it is dominated by both firms raising the price. O No, because it is dominated by maintaining the price. Yes.
Consider two firms that are choosing the price of competing products. The choices are contained in the payoff table. Each firm can raise price, lower price, or maintain their price. Suppose the game is played once each period forever. If both players play the strategy "always lower price" is this a Nash equilibrium? Let b = discount rate, 0 < b<1. Raise price Maintain price Lower price Firm B |Raise price Maintain price Lower price 6. 4 8. 8 1. 1 5, 5 4, 6 2, 7 7.2 1. 1 _3, 3 Firm A O No, because it is dominated by raising the price. O No, because it is dominated by both firms raising the price. O No, because it is dominated by maintaining the price. Yes.
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter15: Strategic Games
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9MC
Related questions
Question
8
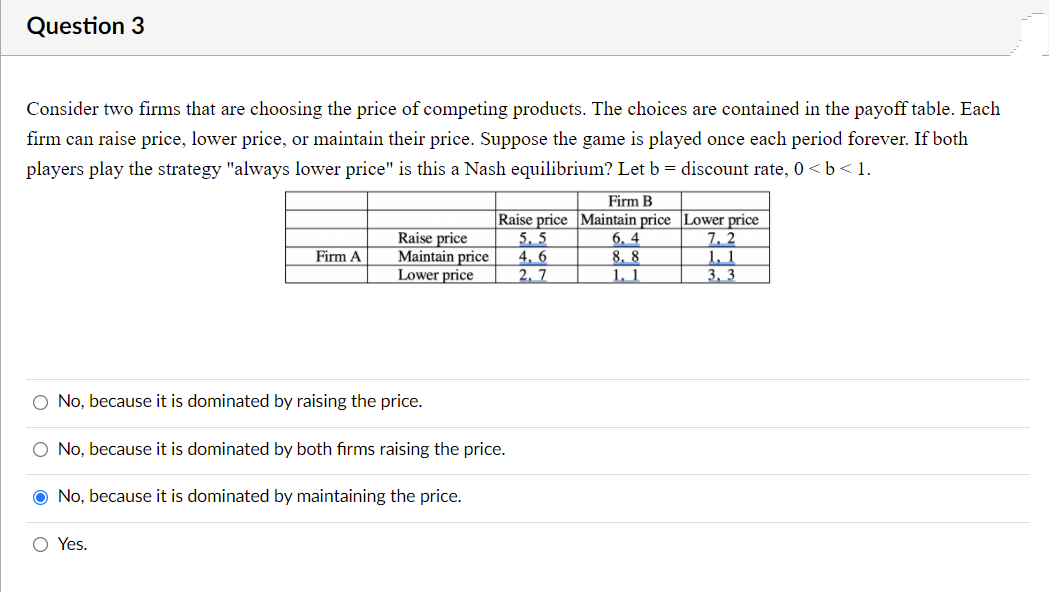
Transcribed Image Text:Question 3
Consider two firms that are choosing the price of competing products. The choices are contained in the payoff table. Each
firm can raise price, lower price, or maintain their price. Suppose the game is played once each period forever. If both
players play the strategy "always lower price" is this a Nash equilibrium? Let b = discount rate, 0 < b < 1.
Firm B
Raise price
Maintain price
Lower price
Raise price Maintain price Lower price
6, 4
8. 8
1, 1
5, 5
4, 6
2, 7
7, 2
1. 1
3, 3
Firm A
O No, because it is dominated by raising the price.
O No, because it is dominated by both firms raising the price.
O No, because it is dominated by maintaining the price.
O Yes.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
