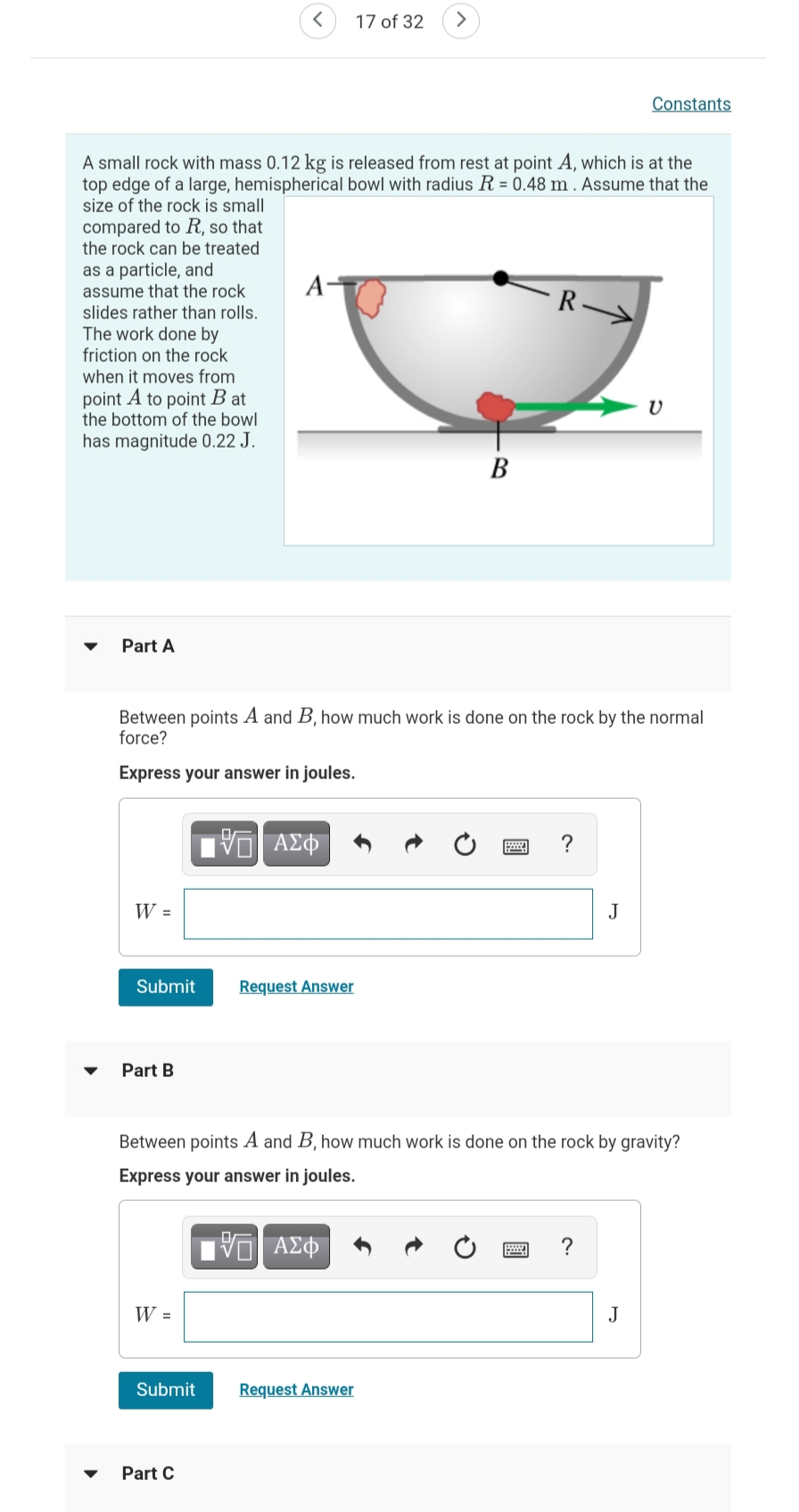
Constants A small rock with mass 0.12 kg is released from rest at point A, which is at the top edge of a large, hemispherical bowl with radius R = 0.48 m. Assume that the size of the rock is small compared to R, so that the rock can be treated as a particle, and assume that the rock slides rather than rolls. A- R- The work done by friction on the rock when it moves from point A to point B at the bottom of the bowl has magnitude 0.22 J. B Part A Between points A and B, how much work is done on the rock by the normal force? Express your answer in joules. ΑΦ ? W = J Submit Request Answer Part B Between points A and B, how much work is done on the rock by gravity? Express your answer in joules. ΑΣΦ W = J Submit Request Answer
Constants A small rock with mass 0.12 kg is released from rest at point A, which is at the top edge of a large, hemispherical bowl with radius R = 0.48 m. Assume that the size of the rock is small compared to R, so that the rock can be treated as a particle, and assume that the rock slides rather than rolls. A- R- The work done by friction on the rock when it moves from point A to point B at the bottom of the bowl has magnitude 0.22 J. B Part A Between points A and B, how much work is done on the rock by the normal force? Express your answer in joules. ΑΦ ? W = J Submit Request Answer Part B Between points A and B, how much work is done on the rock by gravity? Express your answer in joules. ΑΣΦ W = J Submit Request Answer
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter11: Gravity, Planetary Orbits, And The Hydrogen Atom
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 60P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
What's the answer for part A, B, C, D and E?
Transcribed Image Text:17 of 32
>
Constants
A small rock with mass 0.12 kg is released from rest at point A, which is at the
top edge of a large, hemispherical bowl with radius R = 0.48 m . Assume that the
size of the rock is small
compared to R, so that
the rock can be treated
as a particle, and
assume that the rock
slides rather than rolls.
The work done by
friction on the rock
when it moves from
A-
R
point A to point B at
the bottom of the bowl
has magnitude 0.22 J.
В
Part A
Between points A and B, how much work is done on the rock by the normal
force?
Express your answer in joules.
W =
J
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Between points A and B, how much work is done on the rock by gravity?
Express your answer in joules.
ΑΣΦ
W =
J
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
Transcribed Image Text:Part C
What is the speed of the rock as it reaches point B?
Express your answer in meters per second.
ΑΣΦ
?
V =
m/s
Submit
Request Answer
Part D
Of the three forces acting on the rock as it slides down the bowl, which (if any)
are constant?
Check all that apply.
None of the forces.
Frictional force.
Normal force.
Force due to gravity.
Submit
Request Answer
Part E
Just as the rock reaches point B, what is the normal force on it due to the
bottom of the bowl?
Express your answer in newtons.
ΑΣΦ
n =
N
Submit
Request Answer
O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University