Coulomb constant, k=8.987×109N⋅m2/C2. Vacuum permitivity, ϵ0=8.854×10−12F/m. Magnitude of the Charge of one electron, e=−1.60217662×10−19C. Mass of one electron, me=9.10938356×10−31kg. Mass of one proton, mp=1.6726219×10−27kg, Charge of one proton, ep=1.60217662×10−19C Unless specified otherwise, each symbol carries their usual meaning. For example, μC means microcoulomb . PartI Suppose, We have a dipole where 3 charges q1=3e,q2=2e,q3=−5e are placed on the vertices of the square as shown in the figure given above. Side length of the square is 2nm. a) Calculate the dipole moment of this dipole. X component of the dipole: Y component of the dipole: b) Calculate the electric potential at point P due to this dipole. PartII Now suppose, we have a continuous charge distribution D for which potential at any point (x,y) in the xy plane is given by, V(x,y)=3xy(mx+n), where V is in volt, coordinates x, y are in meter, m, n both are constant and m=1N/Cm2, n=1N/Cm. c) Calculate the potential at point P due to continuous charge distribution D only. Potential at P
Coulomb constant, k=8.987×109N⋅m2/C2. Vacuum permitivity, ϵ0=8.854×10−12F/m. Magnitude of the Charge of one electron, e=−1.60217662×10−19C. Mass of one electron, me=9.10938356×10−31kg. Mass of one proton, mp=1.6726219×10−27kg, Charge of one proton, ep=1.60217662×10−19C Unless specified otherwise, each symbol carries their usual meaning. For example, μC means microcoulomb .
PartI
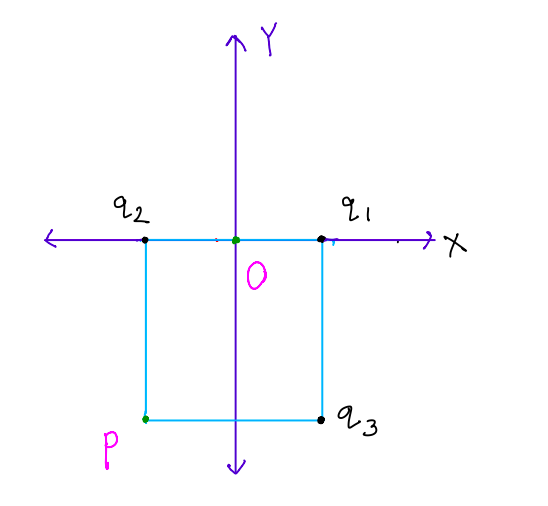
Suppose, We have a dipole where 3 charges q1=3e,q2=2e,q3=−5e are placed on the vertices of the square as shown in the figure given above. Side length of the square is 2nm.
a) Calculate the dipole moment of this dipole.
PartII
Now suppose, we have a continuous charge distribution D for which potential at any point (x,y) in the xy plane is given by, V(x,y)=3xy(mx+n), where V is in volt, coordinates x, y are in meter, m, n both are constant and m=1N/Cm2, n=1N/Cm.
c) Calculate the potential at point P due to continuous charge distribution D only.
d) Calculate the total electric potential at point P.
e) Calculate the net electric field field at point P. (Due to both dipole and continuous charge distribution D)
f)i. Calculate the coulomb force that is exerted on the proton placed at point P due to the net E field.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps


