Create CHART (C-omplaint, H-istory, A-ssessment, R-x - Drugs, T-reatment) documentation for the patient. 2. What is the discharge goal for the patient? Create discharge plan for the patient using METHOD. (M-edications, E-nvironment, T-reatment, H-ealth teaching, O-ut patient referral, D-iet) see photo for reference Thank you! :)
Create CHART (C-omplaint, H-istory, A-ssessment, R-x - Drugs, T-reatment) documentation for the patient. 2. What is the discharge goal for the patient? Create discharge plan for the patient using METHOD. (M-edications, E-nvironment, T-reatment, H-ealth teaching, O-ut patient referral, D-iet) see photo for reference Thank you! :)
Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billing and Reimbursement
14th Edition
ISBN:9781337679480
Author:GREEN
Publisher:GREEN
Chapter9: Cms Reimbursement Methodologies
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14R
Related questions
Question
100%
QUESTIONS. (see pictures for the case scenario and the CHART)
1. Create CHART (C-omplaint, H-istory, A-ssessment, R-x - Drugs, T-reatment) documentation for the patient.
2. What is the discharge goal for the patient? Create discharge plan for the patient using METHOD. (M-edications, E-nvironment, T-reatment, H-ealth teaching, O-ut patient referral, D-iet) see photo for reference
Thank you! :)

Transcribed Image Text:Discharge Goal:
Return to Home (self-care)
Return to Home but needs Assistance
Transfer to other Level of Institutional Care
Referral to Support Community Services'
Home Against Medical Advice
Discharge Plan
Date:
M
Time:
E
T
H
D
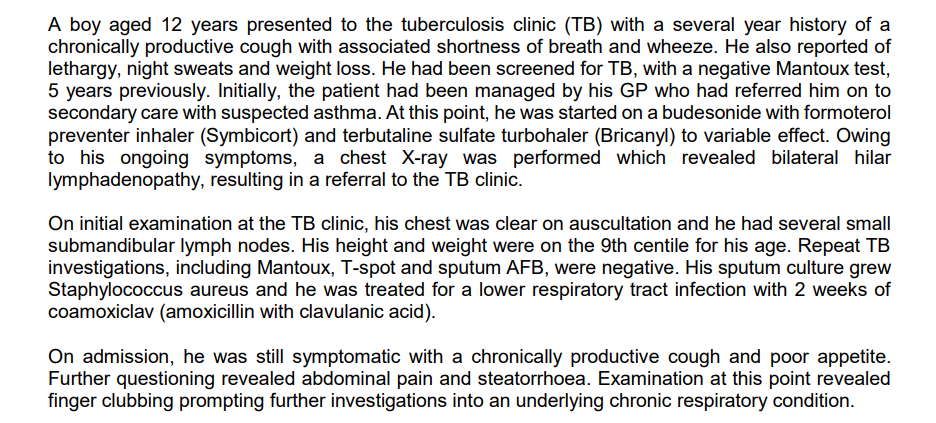
Transcribed Image Text:A boy aged 12 years presented to the tuberculosis clinic (TB) with a several year history of a
chronically productive cough with associated shortness of breath and wheeze. He also reported of
lethargy, night sweats and weight loss. He had been screened for TB, with a negative Mantoux test,
5 years previously. Initially, the patient had been managed by his GP who had referred him on to
secondary care with suspected asthma. At this point, he was started on a budesonide with formoterol
preventer inhaler (Symbicort) and terbutaline sulfate turbohaler (Bricanyl) to variable effect. Owing
to his ongoing symptoms, a chest X-ray was performed which revealed bilateral hilar
lymphadenopathy, resulting in a referral to the TB clinic.
On initial examination at the TB clinic, his chest was clear on auscultation and he had several small
submandibular lymph nodes. His height and weight were on the 9th centile for his age. Repeat TB
investigations, including Mantoux, T-spot and sputum AFB, were negative. His sputum culture grew
Staphylococcus aureus and he was treated for a lower respiratory tract infection with 2 weeks of
coamoxiclav (amoxicillin with clavulanic acid).
On admission, he was still symptomatic with a chronically productive cough and poor appetite.
Further questioning revealed abdominal pain and steatorrhoea. Examination at this point revealed
finger clubbing prompting further investigations into an underlying chronic respiratory condition.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin…
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337679480
Author:
GREEN
Publisher:
Cengage


Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin…
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337679480
Author:
GREEN
Publisher:
Cengage


Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning