Current Attempt in Progress The figure shows a resistor of resistance R = 6.32 connected to an ideal battery of emf = 14.0 V by means of two copper wires. Each wire has length 22.0 cm and radius 2.30 mm. In dealing with such circuits in this chapter, we generally neglect the potential differences along the wires and the transfer of energy to thermal energy in them. Check the validity of this neglect for the circuit of the figure below. What is the potential difference across (a) the resistor and (b) each of the two sections of wire? At what rate is energy lost to thermal energy in (c) the resistor and (d) each section of wire? Wire 1 R Wire 2
Current Attempt in Progress The figure shows a resistor of resistance R = 6.32 connected to an ideal battery of emf = 14.0 V by means of two copper wires. Each wire has length 22.0 cm and radius 2.30 mm. In dealing with such circuits in this chapter, we generally neglect the potential differences along the wires and the transfer of energy to thermal energy in them. Check the validity of this neglect for the circuit of the figure below. What is the potential difference across (a) the resistor and (b) each of the two sections of wire? At what rate is energy lost to thermal energy in (c) the resistor and (d) each section of wire? Wire 1 R Wire 2
Chapter10: Direct-current Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 87AP: A 160F capacitor charged to 450 V is dischargedthrough a 31.2k resistor, (a) Find the time...
Related questions
Question
The figure shows a resistor of resistance R = 6.32 connected to an ideal battery of emf 8 = 14.0 V by means of two copper wires.
Each wire has length 22.0 cm and radius 2.30 mm. In dealing with such circuits in this chapter, we generally neglect the potential differences along the wires and the transfer of energy to thermal energy in them. Check the validity of this neglect for the circuit of the figure below. What is the potential difference across (a) the resistor and (b) each of the two sections of wire? At what rate is energy lost to thermal energy in (c) the resistor and (d) each section of wire?
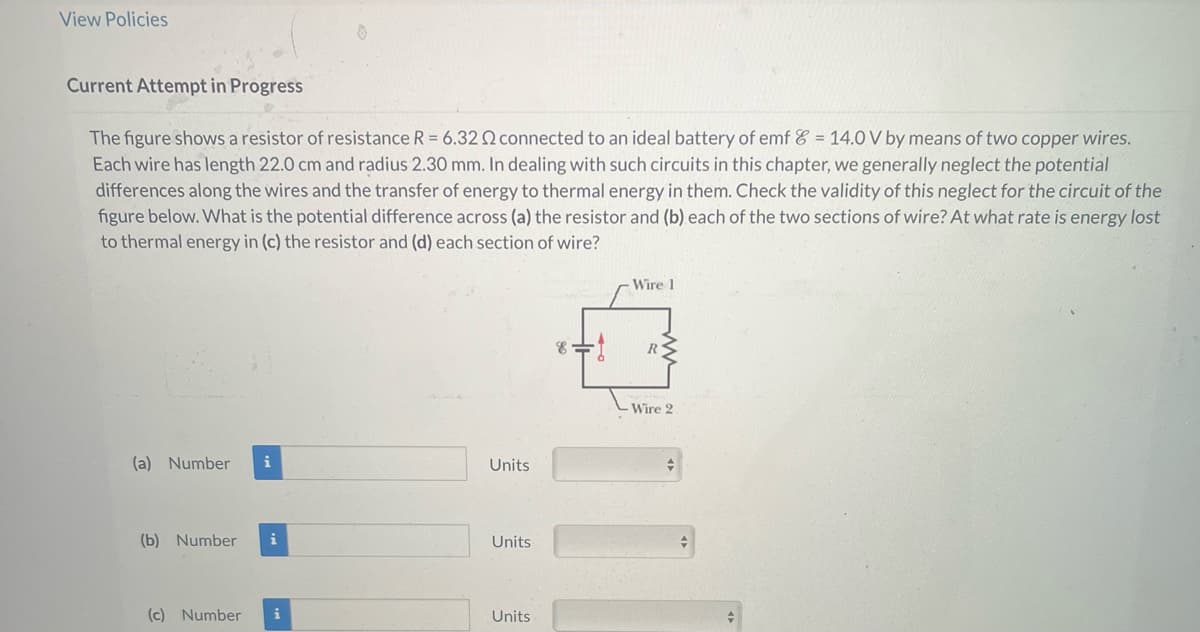
Transcribed Image Text:View Policies
Current Attempt in Progress
The figure shows a resistor of resistance R = 6.32 connected to an ideal battery of emf = 14.0 V by means of two copper wires.
Each wire has length 22.0 cm and radius 2.30 mm. In dealing with such circuits in this chapter, we generally neglect the potential
differences along the wires and the transfer of energy to thermal energy in them. Check the validity of this neglect for the circuit of the
figure below. What is the potential difference across (a) the resistor and (b) each of the two sections of wire? At what rate is energy lost
to thermal energy in (c) the resistor and (d) each section of wire?
Number i
(b) Number i
(c) Number i
Units
Units
Units
8=
Wire 1
R
-Wire 2
+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning