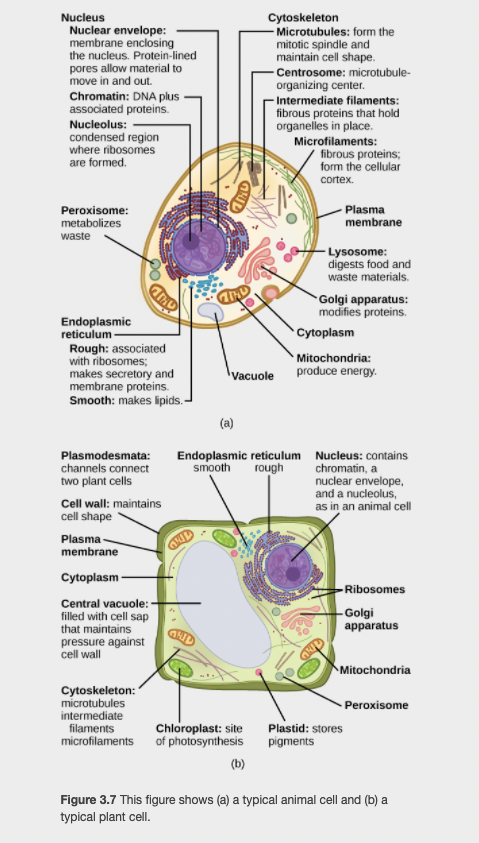
Cytoskeleton - Microtubules: form the mitotic spindle and maintain cell shape. Nucleus Nuclear envelope: membrane enclosing the nucleus. Protein-lined pores allow material to move in and out. Chromatin: DNA plus associated proteins. Centrosome: microtubule- organizing center. Intermediate filaments: fibrous proteins that hold organelles in place. Nucleolus: condensed region where ribosomes are formed. Microfilaments: fibrous proteins; form the cellular cortex. Peroxisome: metabolizes Plasma membrane waste Lysosome: digests food and waste materials. Golgi apparatus: modifies proteins. Endoplasmic reticulum - Rough: associated with ribosomes; makes secretory and membrane proteins. Smooth: makes lipids.- Cytoplasm Mitochondria: produce energy. \Vacuole (a) Plasmodesmata: channels connect Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus: contains chromatin, a nuclear envelope, and a nucleolus, as in an animal cell smooth rough two plant cells Cell wall: maintains cell shape Plasma - membrane GNID Cytoplasm - Ribosomes Central vacuole: - filled with cell sap that maintains -Golgi apparatus GNID pressure against cell wall Mitochondria Cytoskeleton:
Cell Structure
The knowledge and concept about the structure of the cells have changed constantly over the past years. Primarily the scientist defines the cells as a simple membranous sac with fluids and some particles. Researches have now revealed that the cell is the more complex and basic unit of life. There are different types of cells and they also differ in shape and structure. The basic three parts of a cell are cell membrane, cytoplasm, and organelle.
Plant Cell
The smallest functional unit of a living organism is known as the cell. It is composed of cytoplasm enclosed by an outer layer known as the cell membrane. A cell is classified as a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. A prokaryotic cell does not contain a nucleus, and the genetic material is freely suspended in the cell cytoplasm; for example, bacteria are composed of a prokaryotic cell. Whereas a eukaryotic cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles with a specific function, plants and animal cells are examples of eukaryotic cells.
Plant Cell Types
Plants are made up of a variety of cell types that include both living and dead cells. These cells provide them mechanical and structural support along with the growth of plants. Plant tissue is a group or collection of cells, which are similar in structure and work together to accomplish a specific function. Plant cells are most similar to animal cells, both being eukaryotic cells.
Provide a detailed description of the role of "Animal cell organelle #7/Plant cell organelle #15" in
cells.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps






