Data Table 1 Trial No. f (Hz)2 egment ength 33.3 5 33.S Data Analysis 1. Plot a graph of Frequency squared vs. Segments square 2. Determine the slope of the best-fit line on the Frequency squared vs. n2 graph. 3. Using the slope, length, and frequency, calculate the linear mass density of the string. (Hint: The slope is equal to). Solve for the linear mass density Calculate the percent difference between this value and the directly measured value and record it in the Lab Report, Table 3 4. Part 2: Variable Tension- keeping frequency and length constant In this variation, the mass per unit length, μ, the vibrating length, L are fixed. The tension, T, is varied to produce the normal modes of vibration. One must obtain a series of anti-nodes, n, by changing the tension on the string. It may not be possible to obtain the fundamental frequency. The mass may be too high for the driver to move the string. We can take our basic equation and solve for the tension. (12) 7125 kil A plot of T versus 1/n, allows comparison from the slope to L, f, or μ 94.
Data Table 1 Trial No. f (Hz)2 egment ength 33.3 5 33.S Data Analysis 1. Plot a graph of Frequency squared vs. Segments square 2. Determine the slope of the best-fit line on the Frequency squared vs. n2 graph. 3. Using the slope, length, and frequency, calculate the linear mass density of the string. (Hint: The slope is equal to). Solve for the linear mass density Calculate the percent difference between this value and the directly measured value and record it in the Lab Report, Table 3 4. Part 2: Variable Tension- keeping frequency and length constant In this variation, the mass per unit length, μ, the vibrating length, L are fixed. The tension, T, is varied to produce the normal modes of vibration. One must obtain a series of anti-nodes, n, by changing the tension on the string. It may not be possible to obtain the fundamental frequency. The mass may be too high for the driver to move the string. We can take our basic equation and solve for the tension. (12) 7125 kil A plot of T versus 1/n, allows comparison from the slope to L, f, or μ 94.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter16: Waves
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 27CQ: Many of the topics discussed in this chapter are useful beyond the topics of mechanical waves. It is...
Related questions
Question
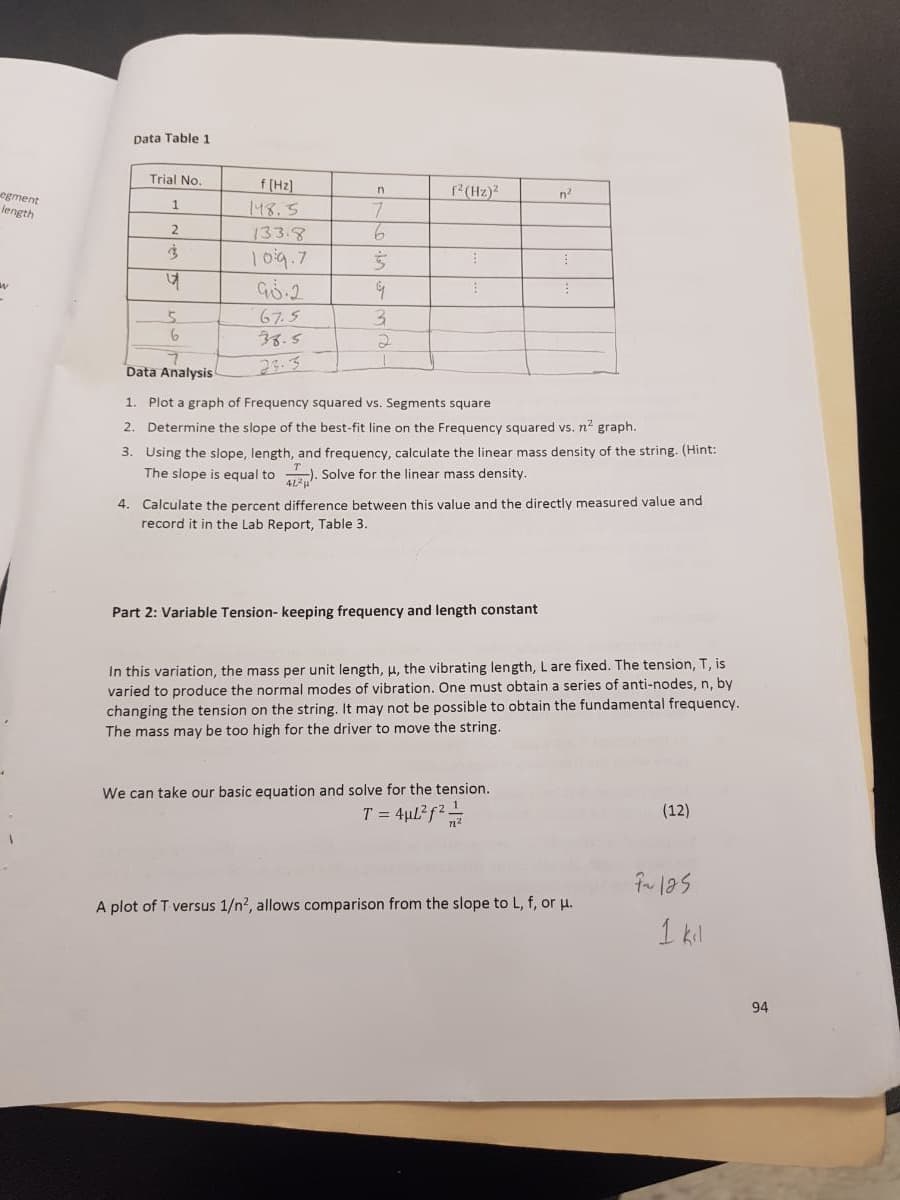
Transcribed Image Text:Data Table 1
Trial No.
f (Hz)2
egment
ength
33.3
5
33.S
Data Analysis
1. Plot a graph of Frequency squared vs. Segments square
2. Determine the slope of the best-fit line on the Frequency squared vs. n2 graph.
3. Using the slope, length, and frequency, calculate the linear mass density of the string. (Hint:
The slope is equal to). Solve for the linear mass density
Calculate the percent difference between this value and the directly measured value and
record it in the Lab Report, Table 3
4.
Part 2: Variable Tension- keeping frequency and length constant
In this variation, the mass per unit length, μ, the vibrating length, L are fixed. The tension, T, is
varied to produce the normal modes of vibration. One must obtain a series of anti-nodes, n, by
changing the tension on the string. It may not be possible to obtain the fundamental frequency.
The mass may be too high for the driver to move the string.
We can take our basic equation and solve for the tension.
(12)
7125
kil
A plot of T versus 1/n, allows comparison from the slope to L, f, or μ
94.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
