Debra travels to Mexico and enjoys burritos and Coronas. The diagram at the right shows her utility-maximizing choices. a. If the budget line is line 1, describe why point A is Debra's utility-maximizing choice. (Select al that apply.) At point A, marginal rate of substitution is equal to the relative prices of the two goods. MUceronas Pcoronas MUurrtos Pouritos At point A, OC. At point A. MUCoronas Pceronas MUgumtos Pourtos line 1 D. At point A MUCoronas Pcoronas MUpumtos Peurtos Coronas b. What event can explain why the budget line moves to line 2? O A. An increase in the price of Coronas O B. A decrease in the price of burritos OC. An increase in the price of burritos D. A decrease in the price of Coronas c. What is the meaning of point B in the figure? Since points A and B share the same indifference curve the change from point A to point B represents the substitution effect when there is a decrease in the price of Coronas d. Suppose Coronas are a normal good for Debra. What does this restriction imply about the location of point C? Is this restriction satisfied in the diagram? O A. Point C would be on the same indifference curve as point A. This is not satisfied O B. Point C would correspond to a larger quantity of Coronas when compared to point A. This is satisfied. O C. Point C would correspond to a smaller quantity of Coronas when compared to point A. This is not satisfied. O D. Point C would be on the same budget line as point A. This is not satisfied
Debra travels to Mexico and enjoys burritos and Coronas. The diagram at the right shows her utility-maximizing choices. a. If the budget line is line 1, describe why point A is Debra's utility-maximizing choice. (Select al that apply.) At point A, marginal rate of substitution is equal to the relative prices of the two goods. MUceronas Pcoronas MUurrtos Pouritos At point A, OC. At point A. MUCoronas Pceronas MUgumtos Pourtos line 1 D. At point A MUCoronas Pcoronas MUpumtos Peurtos Coronas b. What event can explain why the budget line moves to line 2? O A. An increase in the price of Coronas O B. A decrease in the price of burritos OC. An increase in the price of burritos D. A decrease in the price of Coronas c. What is the meaning of point B in the figure? Since points A and B share the same indifference curve the change from point A to point B represents the substitution effect when there is a decrease in the price of Coronas d. Suppose Coronas are a normal good for Debra. What does this restriction imply about the location of point C? Is this restriction satisfied in the diagram? O A. Point C would be on the same indifference curve as point A. This is not satisfied O B. Point C would correspond to a larger quantity of Coronas when compared to point A. This is satisfied. O C. Point C would correspond to a smaller quantity of Coronas when compared to point A. This is not satisfied. O D. Point C would be on the same budget line as point A. This is not satisfied
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter21: The Theory Of Consumer Choice
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PA
Related questions
Question
7
Option (d) only
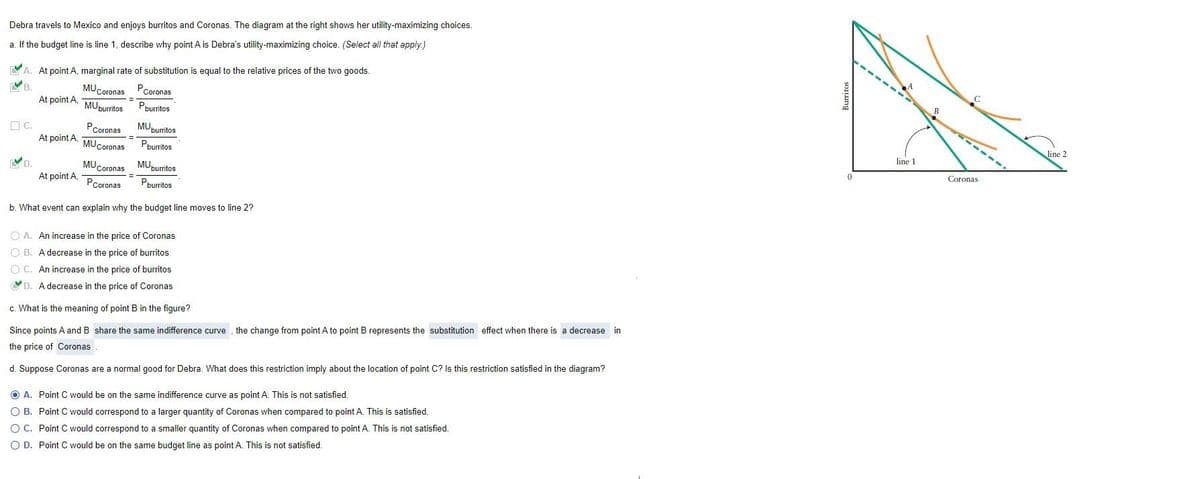
Transcribed Image Text:Debra travels to Mexico and enjoys burritos and Coronas. The diagram at the right shows her utility-maximizing choices.
a. If the budget line is line 1, describe why point A is Debra's utility-maximizing choice. (Select all that apply.)
A. At point A, marginal rate of substitution is equal to the relative prices of the two goods.
S B.
At point A,
MUCoronas Pcoronas
Pburritos
B
MUpurritos
MUpuritos
O C.
At point A
Pcoronas
line 2
MUCoronas
Pburritos
line 1
Coronas
YD.
MUCoronas
MUpurritos
At point A,
Pcoronas
Pburritos
b. What event can explain why the budget line moves to line 2?
O A. An increase in the price of Coronas
O B. A decrease in the price of burritos
O C. An increase in the price of burritos
YD. A decrease in the price of Coronas
c. What is the meaning of point B in the figure?
Since points A and B share the same indifference curve , the change from point A to point B represents the substitution effect when there is a decrease in
the price of Coronas
d. Suppose Coronas are a normal good for Debra. What does this restriction imply about the location of point C? Is this restriction satisfied in the diagram?
O A. Point C would be on the same indifference curve as point A. This is not satisfied.
O B. Point C would correspond to a larger quantity of Coronas when compared to point A. This is satisfied.
O C. Point C would correspond to a smaller quantity of Coronas when compared to point A. This is not satisfied.
O D. Point C would be on the same budget line as point A. This is not satisfied.
so11ung
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax