Describe how the structures of the following can be described in terms of the simple structures types of Table 3.4 but with complex ions: K2PtCl6, [Ni(H2O)][SiF6], CsCN
Describe how the structures of the following can be described in terms of the simple structures types of Table 3.4 but with complex ions: K2PtCl6, [Ni(H2O)][SiF6], CsCN
Chapter26: Molecular Absorption Spectrometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 26.15QAP
Related questions
Question
Describe how the structures of the following can be described in terms of the simple structures types of Table 3.4 but with complex ions: K2PtCl6, [Ni(H2O)][SiF6], CsCN
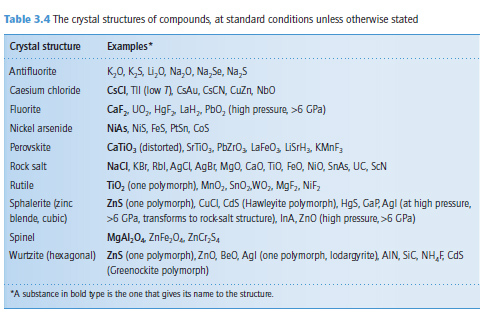
Transcribed Image Text:Table 3.4 The crystal structures of compounds, at standard conditions unless otherwise stated
Crystal structure
Examples*
Antifluorite
K,0, K,S, Li,0, Na,0, Na,Se, Na,5
Caesium chloride
CSCI, TII (low 7), CSAU, CSCN, Cuzn, Nbo
Caf, UO, HgF, LaH,, Pbo, (high pressure, >6 GPa)
NiAs, NIS, FeS, PtSn, Cos
Fluorite
Nickel arsenide
Perovskite
CaTiO, (distorted), STTIO,, PbZro, LaFe0, LisrH, KMNF;
NaCI, KBr, Rbl, AgCI, AgBr, Mg0, Cao, TIO, FeO, NiO, SnAs, UC, ScN
TiO (one polymorph), MnO, Sno, WO, MgF, NiF,
Rock salt
Rutile
Sphalerite (zinc
blende, cubic)
ZnS (one polymorph), CuCI, Cds (Hawleyite polymorph), HgS, CaP, Agl (at high pressure,
>6 GPa, transforms to rock salt structure), InA, Zno (high pressure, >6 GPa)
MgAI,0, ZnFe,0, ZnCr,S,
Spinel
Wurtzite (hexagonal) Zns (one polymorph), Zno, Be0, Agl (one polymorph, lodargyrite), AIN, SIC, NH,F, Cds
(Greenockite polymorph)
"A substance in bold type is the one that gives its name to the structure.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

