Direct Materials and Direct Labor Variance Analysis Shasta Fixture Company manufactures faucets in a small manufacturing facility. The faucets are made from brass. Manufactu employees. Each employee presently provides 32 hours of labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows. Standard wage per hour $13.80 Standard labor time per unit 20 min. Standard number of Ibs. of brass 1.3 lbs. Standard price per Ib. of brass $9.75 Actual price per Ib. of brass $10.00 Actual Ibs. of brass used during the week 8,034 lbs. Number of units produced during the week 6,000 Actual wage per hour $14.21 Actual hours for the week (60 employees x 32 hours) 1,920 Required: a. Determine the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor. Round the cost per unit to two decimal places Direct materials standard cost per unit $4 13 X Direct labor standard cost per unit 4.6 V Total standard cost per unit 17.3 X b. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total materials cost variance. Rou answers to the nearest whole dollar. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an uhfavorable positive number. Direct Materials Price Variance 2,008.50 X Unfavorable Direct Materials Quantity Variance $ -2,281.5 x Unfavorable Total Direct Materials Cost Variance 4,290 X Unfavorable C. Determine the direct labor rate varlance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Round your answers nearest whole dollar. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a pos Direct Labor Rate Variance 787.2 X Unfavorable Direct Labor Time Variance %24 1,656 X Favorable Total Direct Labor Cost Variance 2,443.2 X Favorable Feedback Check My Work Unfavorable variances can be thought of as increasing costs (a debit) Favorable variances can be thought of as decreasing costs (a credit)
Direct Materials and Direct Labor Variance Analysis Shasta Fixture Company manufactures faucets in a small manufacturing facility. The faucets are made from brass. Manufactu employees. Each employee presently provides 32 hours of labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows. Standard wage per hour $13.80 Standard labor time per unit 20 min. Standard number of Ibs. of brass 1.3 lbs. Standard price per Ib. of brass $9.75 Actual price per Ib. of brass $10.00 Actual Ibs. of brass used during the week 8,034 lbs. Number of units produced during the week 6,000 Actual wage per hour $14.21 Actual hours for the week (60 employees x 32 hours) 1,920 Required: a. Determine the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor. Round the cost per unit to two decimal places Direct materials standard cost per unit $4 13 X Direct labor standard cost per unit 4.6 V Total standard cost per unit 17.3 X b. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total materials cost variance. Rou answers to the nearest whole dollar. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an uhfavorable positive number. Direct Materials Price Variance 2,008.50 X Unfavorable Direct Materials Quantity Variance $ -2,281.5 x Unfavorable Total Direct Materials Cost Variance 4,290 X Unfavorable C. Determine the direct labor rate varlance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Round your answers nearest whole dollar. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a pos Direct Labor Rate Variance 787.2 X Unfavorable Direct Labor Time Variance %24 1,656 X Favorable Total Direct Labor Cost Variance 2,443.2 X Favorable Feedback Check My Work Unfavorable variances can be thought of as increasing costs (a debit) Favorable variances can be thought of as decreasing costs (a credit)
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Chapter9: Evaluating Variances From Standard Costs
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PB: Direct materials and direct labor variance analysis Lenni Clothing Co. manufactures clothing in a...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Variance Analysis
In layman's terms, variance analysis is an analysis of a difference between planned and actual behavior. Variance analysis is mainly used by the companies to maintain a control over a business. After analyzing differences, companies find the reasons for the variance so that the necessary steps should be taken to correct that variance.
Standard Costing
The standard cost system is the expected cost per unit product manufactured and it helps in estimating the deviations and controlling them as well as fixing the selling price of the product. For example, it helps to plan the cost for the coming year on the various expenses.
Topic Video
Question
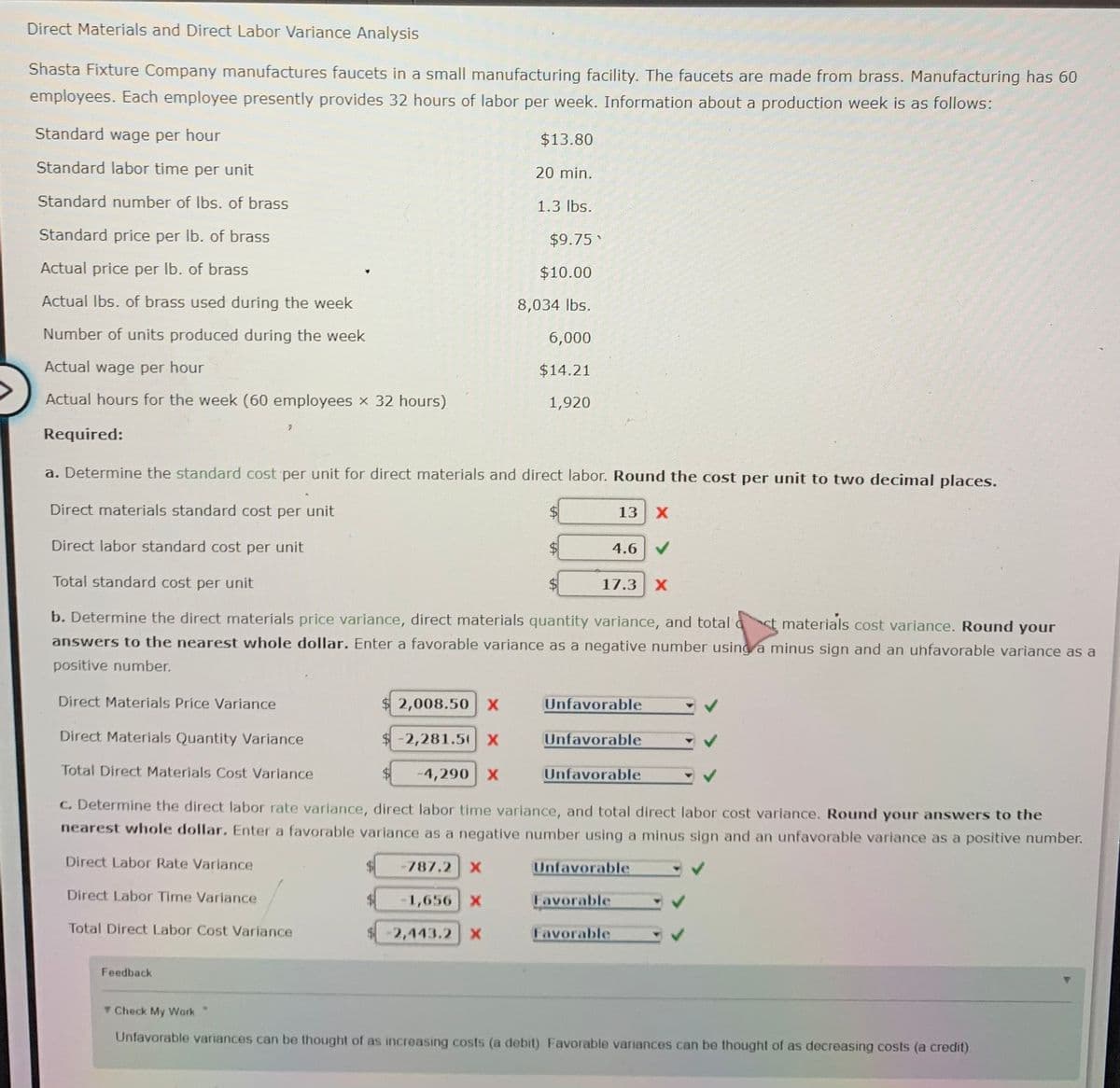
Transcribed Image Text:Direct Materials and Direct Labor Variance Analysis
Shasta Fixture Company manufactures faucets in a small manufacturing facility. The faucets are made from brass. Manufacturing has 60
employees. Each employee presently provides 32 hours of labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows:
Standard wage per hour
$13.80
Standard labor time per unit
20 min.
Standard number of Ibs. of brass
1.3 lbs.
Standard price per Ib. of brass
$9.75
Actual price per Ib. of brass
$10.00
Actual Ibs. of brass used during the week
8,034 lbs.
Number of units produced during the week
6,000
Actual wage per hour
$14.21
Actual hours for the week (60 employees x 32 hours)
1,920
Required:
a. Determine the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor. Round the cost per unit to two decimal places.
Direct materials standard cost per unit
13 X
Direct labor standard cost per unit
4.6 V
Total standard cost per unit
17.3 X
b. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total a
st materials cost variance. Round your
answers to the nearest whole dollar. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a
positive number.
Direct Materials Price Variance
2,008.50 X
Unfavorable
Direct Materials Quantity Variance
$-2,281.5X
Unfavorable
Total Direct Materials Cost Variance
-4,290 X
Unfavorable
C. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Round your answers to the
nearest whole dollar. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number.
Direct Labor Rate Variance
-787.2 X
Unfavorable
Direct Labor Time Variance
-1,656 X
Favorable
Total Direct Labor Cost Variance
2,443.2 X
Favorable
Feedback
Check My Work
Unfavorable variances can be thought of as increasing costs (a debit) Favorable variances can be thought of as decreasing costs (a credit).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning