Dmitri's pizza restaurant uses a combination of workers and ovens to produce pizzas. The total number of pizzas produced per hour is given by the function q = 4K0.510.5, where K is the number of ovens and L is the number of workers. Although the two inputs are relatively substitutable, the number of ovens is fixed in the short run, and therefore Dmitri is primarily interested in the marginal and average product of labor given his current number of ovens (16). Complete the following table using the production function given. Ovens Workers Pizzas Per Hour Average Productivity (K) (L) (9) (9/L) MPL 16 1 16 2 22.63 11.32 16 3 27.71 9.24 16 4 Given Dmitri's production function, he faces returns to scale. However, you can see that when one input is held constant, the as more and more workers are added. marginal productivity of workers
Dmitri's pizza restaurant uses a combination of workers and ovens to produce pizzas. The total number of pizzas produced per hour is given by the function q = 4K0.510.5, where K is the number of ovens and L is the number of workers. Although the two inputs are relatively substitutable, the number of ovens is fixed in the short run, and therefore Dmitri is primarily interested in the marginal and average product of labor given his current number of ovens (16). Complete the following table using the production function given. Ovens Workers Pizzas Per Hour Average Productivity (K) (L) (9) (9/L) MPL 16 1 16 2 22.63 11.32 16 3 27.71 9.24 16 4 Given Dmitri's production function, he faces returns to scale. However, you can see that when one input is held constant, the as more and more workers are added. marginal productivity of workers
Chapter22: Supply: The Costs Of Doing Business
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11E
Related questions
Question
A9
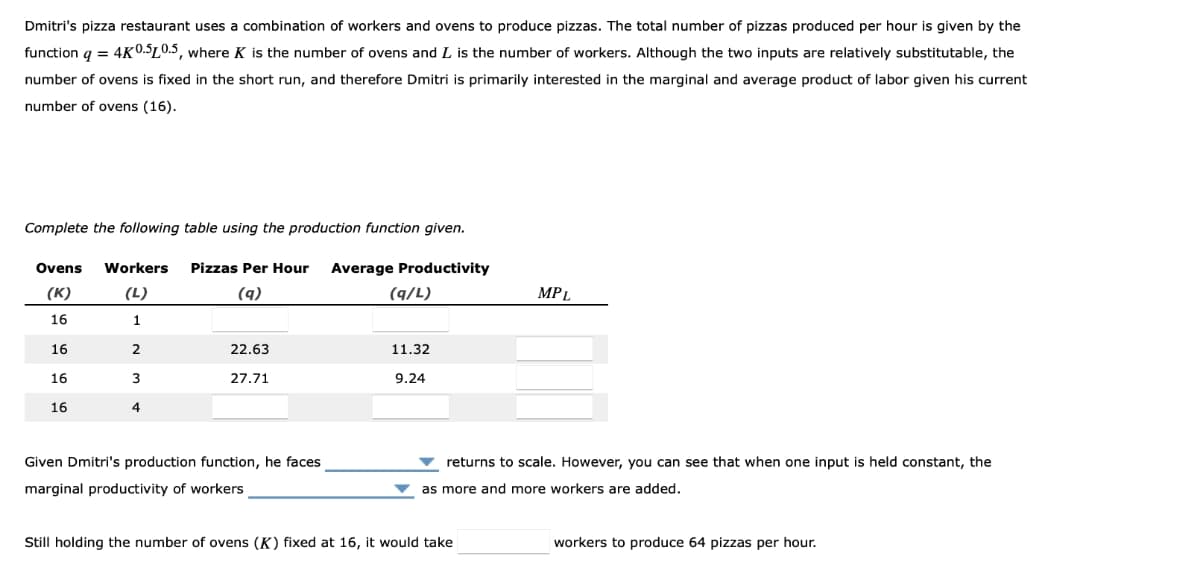
Transcribed Image Text:Dmitri's pizza restaurant uses a combination of workers and ovens to produce pizzas. The total number of pizzas produced per hour is given by the
function q = 4K0.510.5, where K is the number of ovens and I is the number of workers. Although the two inputs are relatively substitutable, the
number of ovens is fixed in the short run, and therefore Dmitri is primarily interested in the marginal and average product of labor given his current
number of ovens (16).
Complete the following table using the production function given.
Ovens Workers
Pizzas Per Hour Average Productivity
(K)
(L)
(9)
(9/L)
MPL
16
1
16
2
22.63
11.32
16
3
27.71
9.24
16
4
Given Dmitri's
tion, he faces
input is held constant, the
retu to scale. However, you can see that whe
as more and more workers are added.
marginal productivity of workers
Still holding the number of ovens (K) fixed at 16, it would take
workers to produce 64 pizzas per hour.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning