drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.) Finally, use the red line (cross symbols) to un Phillips curve for this economy in 2021. FLATION RATE (Percent) Outcome A
drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.) Finally, use the red line (cross symbols) to un Phillips curve for this economy in 2021. FLATION RATE (Percent) Outcome A
Chapter10: Aggregate Demand And Supply
Section10.A: The Self Correcting Aggregate Demand And Supply Model
Problem 10SQ
Related questions
Question
1, outcome B/ outcome A
2, outcome A/ outcome B
3,
4, shift of/ movement along
5, a decrease/ an increase
6, an increase/ a decrease
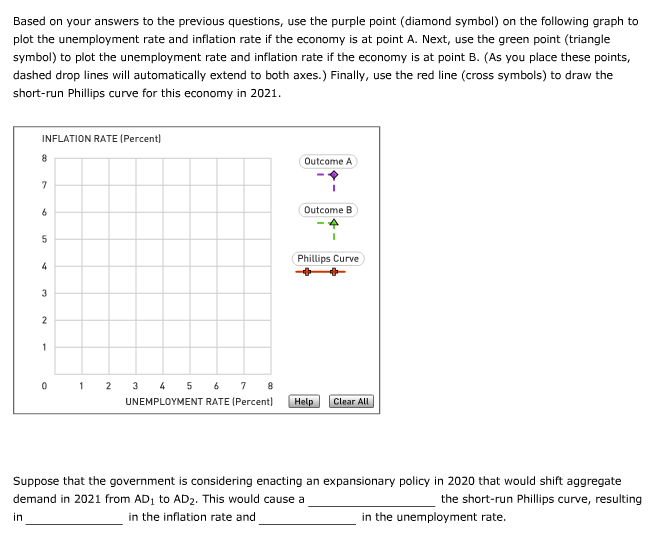
Transcribed Image Text:Based on your answers to the previous questions, use the purple point (diamond symbol) on the following graph to
plot the unemployment rate and inflation rate if the economy is at point A. Next, use the green point (triangle
symbol) to plot the unemployment rate and inflation rate if the economy is at point B. (As you place these points,
dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes.) Finally, use the red line (cross symbols) to draw the
short-run Phillips curve for this economy in 2021.
INFLATION RATE (Percent)
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
2
3 4 5 6 7
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)
8
Outcome A
Outcome B
Phillips Curve
Help
Clear All
Suppose that the government is considering enacting an expansionary policy in 2020 that would shift aggregate
demand in 2021 from AD₁ to AD₂. This would cause a
the short-run Phillips curve, resulting
in
in the inflation rate and
in the unemployment rate.
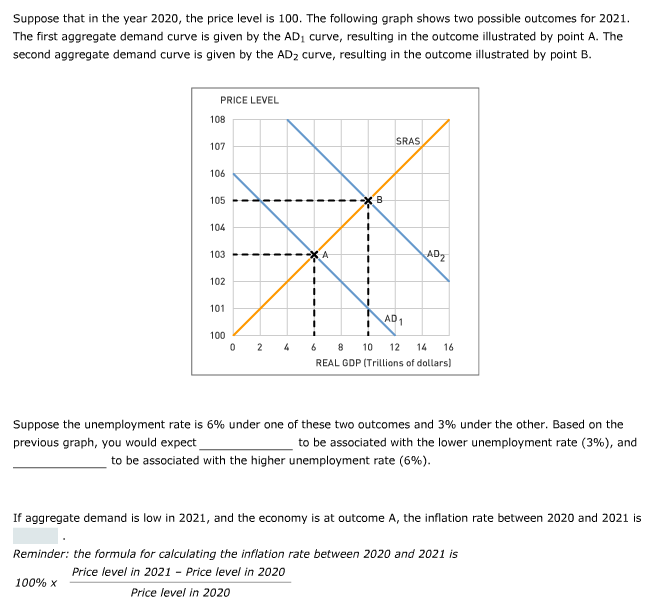
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that in the year 2020, the price level is 100. The following graph shows two possible outcomes for 2021.
The first aggregate demand curve is given by the AD₁ curve, resulting in the outcome illustrated by point A. The
second aggregate demand curve is given by the AD₂ curve, resulting in the outcome illustrated by point B.
PRICE LEVEL
108
107
100% X
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
0
I
2
4
A
I
B
SRAS
AD1
AD₂
6
8 10 12 14 16
REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars)
Suppose the unemployment rate is 6% under one of these two outcomes and 3% under the other. Based on the
previous graph, you would expect_
to be associated with the lower unemployment rate (3%), and
to be associated with the higher unemployment rate (6%).
If aggregate demand is low in 2021, and the economy is at outcome A, the inflation rate between 2020 and 2021 is
Reminder: the formula for calculating the inflation rate between 2020 and 2021 is
Price level in 2021 - Price level in 2020
Price level in 2020
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you





