dy 3D f (x, у) — y sес х with y(0) — 2 dx
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
1. I have already solved for the analytical solution. Solve for the taylor expansion series. Use the guide.
ENCODE THE ANSWER.
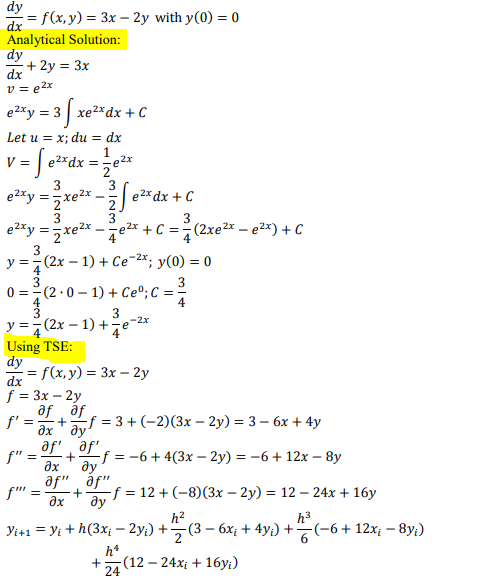
Transcribed Image Text:dy
= f(x,y) = 3x – 2y with y(0) = 0
dx
Analytical Solution:
dy
+ 2y = 3x
dx
v= e2x
e2xy = 3| xe2xdx + C
Let u = x; du = dx
= | e2*dx = ;e2x
etty = xe* - e*dx + C
V =
3
3
e 2x dx + C
2.
3
3
3.
e2*y =xe2x -e2* + C ==(2xe²x – e2x) + C
y =7(2x – 1) + Ce-2*; y(0) = 0
3
0 = (2.0 – 1) + Ce°;C = =
3
3
(2x – 1) +e-:
4
y = 7
Using TSE:
dy
= f(x, y) = 3x – 2y
dx
f = 3x – 2y
f' = ax" ay'
f = 3 + (-2)(3x – 2y) = 3 – 6x + 4y
+
f" =
of +Lf = -6+4(3x – 2y) = -6+12x – 8y
ax
ду
af" áf"
f" :
-f = 12 + (-8)(3x – 2y) = 12 – 24x + 16y
+
ax
ду
h3
h2
Yi+ı = yi + h(3x; – 2y;) +(3 – 6x; + 4y;) +(-6+ 12x; – 8y;)
h*
-(12 — 24х; + 16у)
24

Transcribed Image Text:dy
= f(x, y) = y sec x with y(0) = 2
dx
Analytical solution
dy
= y sec x
dx
dy
sec x dx
y
In y = In(sec x + tan x) + C
eln y = eln(secx+tan x)+C
eln y
= eln(secx+tan x)eC
y = C(sec x + tan x)
when x = 0, y = 2
2 = C(sec 0 + tan 0)
2 = C(1+ 0)
C = 2
General Solution:
y = 2(sec x + tan x)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

