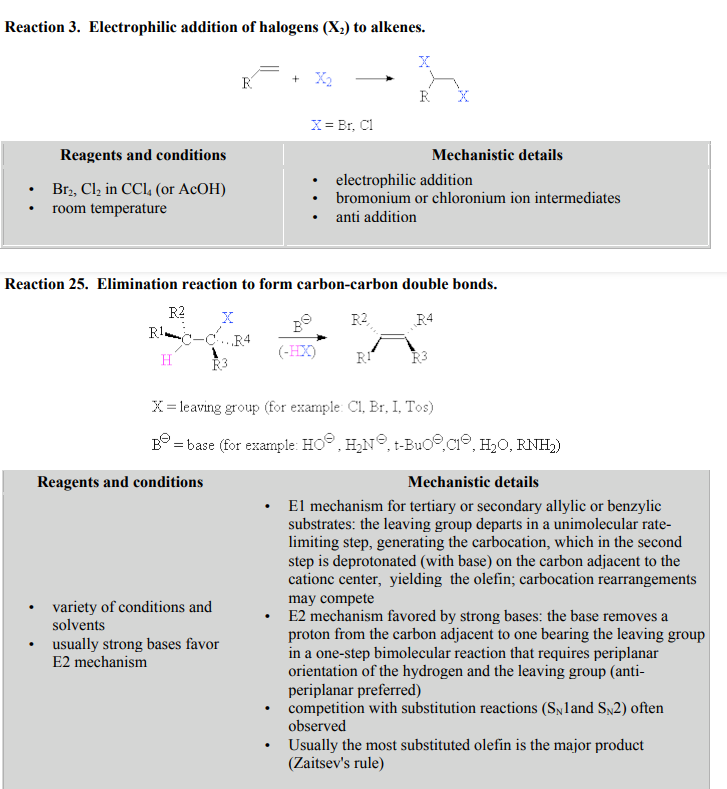
(E)-1-2- Diphenylethene reacts with Br 2 /CCI4 (see reaction) the reaction product is obtained (A) is a stereoisomer with 2 chiral optically inactive carbons that then reacts with KOH / ethanol (see reaction) that produces an intermediate (B) [C₁4H₁1 Brl that by continuing to react with KOH and heating to 190 degrees Celsius, compound (D) C14H10 is obtained a) Write the general reaction of this synthesis with the structures of the initial alkene of A, B and D b) Give the reaction mechanism to obtain A c) Indicate for the absolute configuration of each C* and the IUPAC name of the compound d) Give the IUPAC and common name of the obtained product D
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the organic compounds that are obtained in foods and living matters in the shape of sugars, cellulose, and starch. The general formula of carbohydrates is Cn(H2O)2. The ratio of H and O present in carbohydrates is identical to water.
Starch
Starch is a polysaccharide carbohydrate that belongs to the category of polysaccharide carbohydrates.
Mutarotation
The rotation of a particular structure of the chiral compound because of the epimerization is called mutarotation. It is the repercussion of the ring chain tautomerism. In terms of glucose, this can be defined as the modification in the equilibrium of the α- and β- glucose anomers upon its dissolution in the solvent water. This process is usually seen in the chemistry of carbohydrates.
L Sugar
A chemical compound that is represented with a molecular formula C6H12O6 is called L-(-) sugar. At the carbon’s 5th position, the hydroxyl group is placed to the compound’s left and therefore the sugar is represented as L(-)-sugar. It is capable of rotating the polarized light’s plane in the direction anticlockwise. L isomers are one of the 2 isomers formed by the configurational stereochemistry of the carbohydrates.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images






