3. Consider a model where a consumer, Mehdi, is deciding how to allocate their 24 hours each day between work and leisure. The take-home wage they initially receive is w = 15, but following a rise in income tax, their take-home pay falls to w = 12. Following this change in the wage rate, Mehdi reallocates his time between work and leisure, as shown in the diagram below. Composite good 4 42 43 Time Constraint 24 Leisure (0-24)/ Work (24-0) Given this information, which of the following conclusions can we reach? (a) The substitution and income effects both cause Mehdi to take more leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good. (b) The substitution effect and income effects both cause Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good. (c) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, while the income effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is an inferior good. (d) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, while the income effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good. (e) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, while the income effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, meaning leisure is an inferior good.
3. Consider a model where a consumer, Mehdi, is deciding how to allocate their 24 hours each day between work and leisure. The take-home wage they initially receive is w = 15, but following a rise in income tax, their take-home pay falls to w = 12. Following this change in the wage rate, Mehdi reallocates his time between work and leisure, as shown in the diagram below. Composite good 4 42 43 Time Constraint 24 Leisure (0-24)/ Work (24-0) Given this information, which of the following conclusions can we reach? (a) The substitution and income effects both cause Mehdi to take more leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good. (b) The substitution effect and income effects both cause Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good. (c) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, while the income effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is an inferior good. (d) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, while the income effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good. (e) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, while the income effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, meaning leisure is an inferior good.
Chapter6: Demand Relationships Among Goods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.3P
Related questions
Question
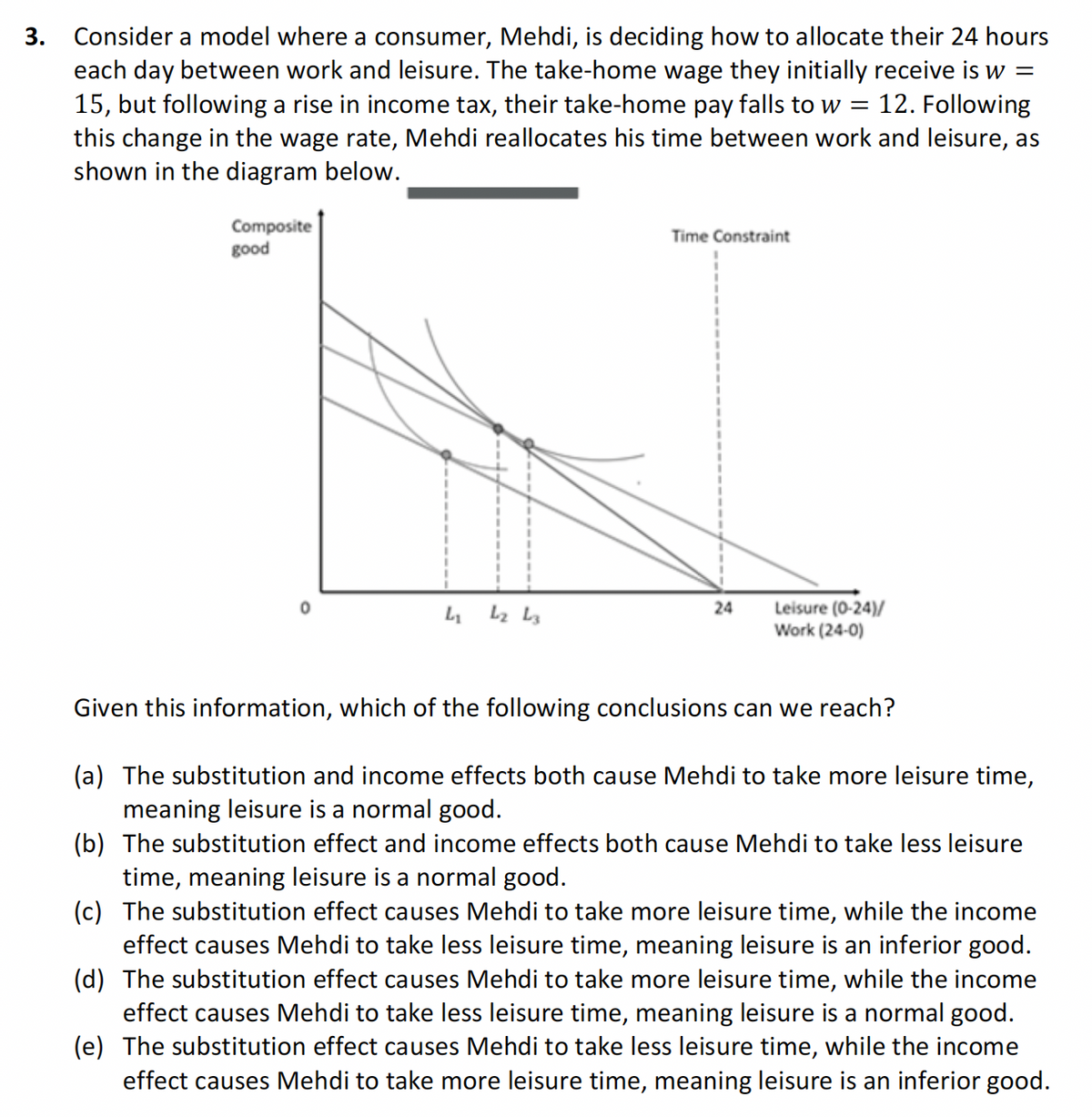
Transcribed Image Text:3.
Consider a model where a consumer, Mehdi, is deciding how to allocate their 24 hours
each day between work and leisure. The take-home wage they initially receive is w =
15, but following a rise in income tax, their take-home pay falls to w = 12. Following
this change in the wage rate, Mehdi reallocates his time between work and leisure, as
shown in the diagram below.
Composite
good
4
42 43
Time Constraint
24
Leisure (0-24)/
Work (24-0)
Given this information, which of the following conclusions can we reach?
(a) The substitution and income effects both cause Mehdi to take more leisure time,
meaning leisure is a normal good.
(b) The substitution effect and income effects both cause Mehdi to take less leisure
time, meaning leisure is a normal good.
(c) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, while the income
effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is an inferior good.
(d) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, while the income
effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, meaning leisure is a normal good.
(e) The substitution effect causes Mehdi to take less leisure time, while the income
effect causes Mehdi to take more leisure time, meaning leisure is an inferior good.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax