Ed's Tires and Brakes has two locations, one on the northwest side of town and one on the southeast side of town. At both locations are pertformed routine tire repairs and rotations, as well as expensive brake repairs. This past week, 40% of the cars serviced at Ed's were serviced at the northwest location, while 60% of the cars were serviced at the southeast location. (No car was serviced at both locations.) Brake repairs were more typical at the northwest iocation than at the southeast location: 50% of the cars at the northwest location required brake repairs, while 25% of the cars at the southeast location required brake repairs. Let Ndenote the event that a randomly chosen car (taken to Ed's in the past week) was serviced at the northwest location and N denote the event that a randomly chosen car was serviced at the southeast location. Let B denote the event that a randomly chosen car required brake repairs and 3 denote the event that a randomly chosen car did not require brake repairs. F in the probabilites to complete the tree diagram below, and then answer the question that follows. Do not round any of your responses. (1f necessary, consult a ist of formulas,) (a) F in the missing probabilites. P(B IN) =O P (NnE) = 0 P(N) = 0.4 P(NnE) = 0 P(3 IN) = 0.5 P(BIN) = 0 25 P(NnB) = 0 P (N) = [] P(Nn 3) =0 P(3IN) = (0 (b) what is the probability that a randomly chosen car required brake repairs?
Ed's Tires and Brakes has two locations, one on the northwest side of town and one on the southeast side of town. At both locations are pertformed routine tire repairs and rotations, as well as expensive brake repairs. This past week, 40% of the cars serviced at Ed's were serviced at the northwest location, while 60% of the cars were serviced at the southeast location. (No car was serviced at both locations.) Brake repairs were more typical at the northwest iocation than at the southeast location: 50% of the cars at the northwest location required brake repairs, while 25% of the cars at the southeast location required brake repairs. Let Ndenote the event that a randomly chosen car (taken to Ed's in the past week) was serviced at the northwest location and N denote the event that a randomly chosen car was serviced at the southeast location. Let B denote the event that a randomly chosen car required brake repairs and 3 denote the event that a randomly chosen car did not require brake repairs. F in the probabilites to complete the tree diagram below, and then answer the question that follows. Do not round any of your responses. (1f necessary, consult a ist of formulas,) (a) F in the missing probabilites. P(B IN) =O P (NnE) = 0 P(N) = 0.4 P(NnE) = 0 P(3 IN) = 0.5 P(BIN) = 0 25 P(NnB) = 0 P (N) = [] P(Nn 3) =0 P(3IN) = (0 (b) what is the probability that a randomly chosen car required brake repairs?
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 28EQ
Related questions
Question
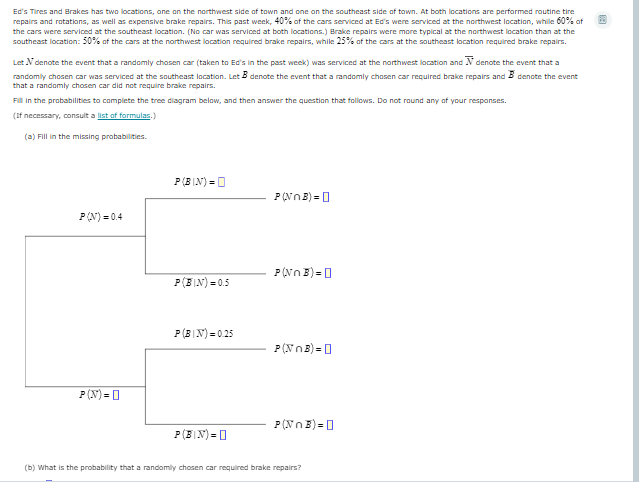
Transcribed Image Text:Ed's Tires and Brakes has two locations, one on the northwest side of town and one on the southeast side of town. At both locations are performed routine tire
repairs and rotations, as well as expensive brake repairs. This past week, 40% of the cars serviced at Ed's were serviced at the northwest location, while 60% of
the cars were serviced at the southeast location. (No car was serviced at both locations.) Brake repairs were more typical at the northwest location than at the
southeast location: 50% of the cars at the northwest location required brake repairs, while 25% of the cars at the southeast location required brake repairs.
Let N denote the event that a randomly chasen car (taken to Ed's in the past week) was serviced at the northwest location and N denote the event that a
randomly chosen car was serviced at the southeast location. Let B denote the event that a randomly chosen car required brake repairs and B denote the event
that a randomly chosen car did not require brake repairs.
Fill in the probabilities to complete the tree diagram below, and then answer the question that follows. Do not round any of your responses.
(If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
(a) Fill in the missing probabilities.
P(BIN) =0
P(NnB) = 0
P(N) = 0.4
P(Nn E) =0
P(BIN) = 0.5
P(BIN) = 025
P(NnB) = 0
P(N) = 0
P(NnE) =0
P(BIN) =0
(b) What is the probability that a randomly chosen car required brake repairs?
Expert Solution
Step 1
The conditional probability of happening of event when event already happened, can be expressed as, , further it can be given by the formula, . This can be modified as
where,
- denotes the probability of happening of both the events and simultaneously.
- denotes the probability of happening of event .
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill