Enter your data of the masses, mi & m2 in kg as related to the current, I, in Amper and time, t, in minutes in the table below: Table (2.1 ) MCu = Amount of Current (I) Time (t) (A) Charge (I × t) (Coulomb) mi × 10^(-3) (kg) m2 × 10^(-3) (kg) (m2 - mı) x 10^(-3) (kg) (min) 0.8 16 36.94 37.17 0.4 16 37.17 37.29 0.4 8 37.29 37.34 2. Use the table above to plot amount of charge (I x t) versus mass of the deposited copper MCu. add the slope on your graph using add trendline option. 3. What type of relationship do you see between Mcu and (I × t). 4. From your graph find the specific charge K, of Copper Ions by calculating the slope. 5. Calculate the charge carried by each Copper Ion in the solution. show calculations 6. Use the result above to calculate the Charge of the Electron " e ". How does it compare with standard value? show calculations
Enter your data of the masses, mi & m2 in kg as related to the current, I, in Amper and time, t, in minutes in the table below: Table (2.1 ) MCu = Amount of Current (I) Time (t) (A) Charge (I × t) (Coulomb) mi × 10^(-3) (kg) m2 × 10^(-3) (kg) (m2 - mı) x 10^(-3) (kg) (min) 0.8 16 36.94 37.17 0.4 16 37.17 37.29 0.4 8 37.29 37.34 2. Use the table above to plot amount of charge (I x t) versus mass of the deposited copper MCu. add the slope on your graph using add trendline option. 3. What type of relationship do you see between Mcu and (I × t). 4. From your graph find the specific charge K, of Copper Ions by calculating the slope. 5. Calculate the charge carried by each Copper Ion in the solution. show calculations 6. Use the result above to calculate the Charge of the Electron " e ". How does it compare with standard value? show calculations
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter17: Electrochemistry And Its Applications
Section17.8: Common Batteries
Problem 17.14E
Related questions
Question
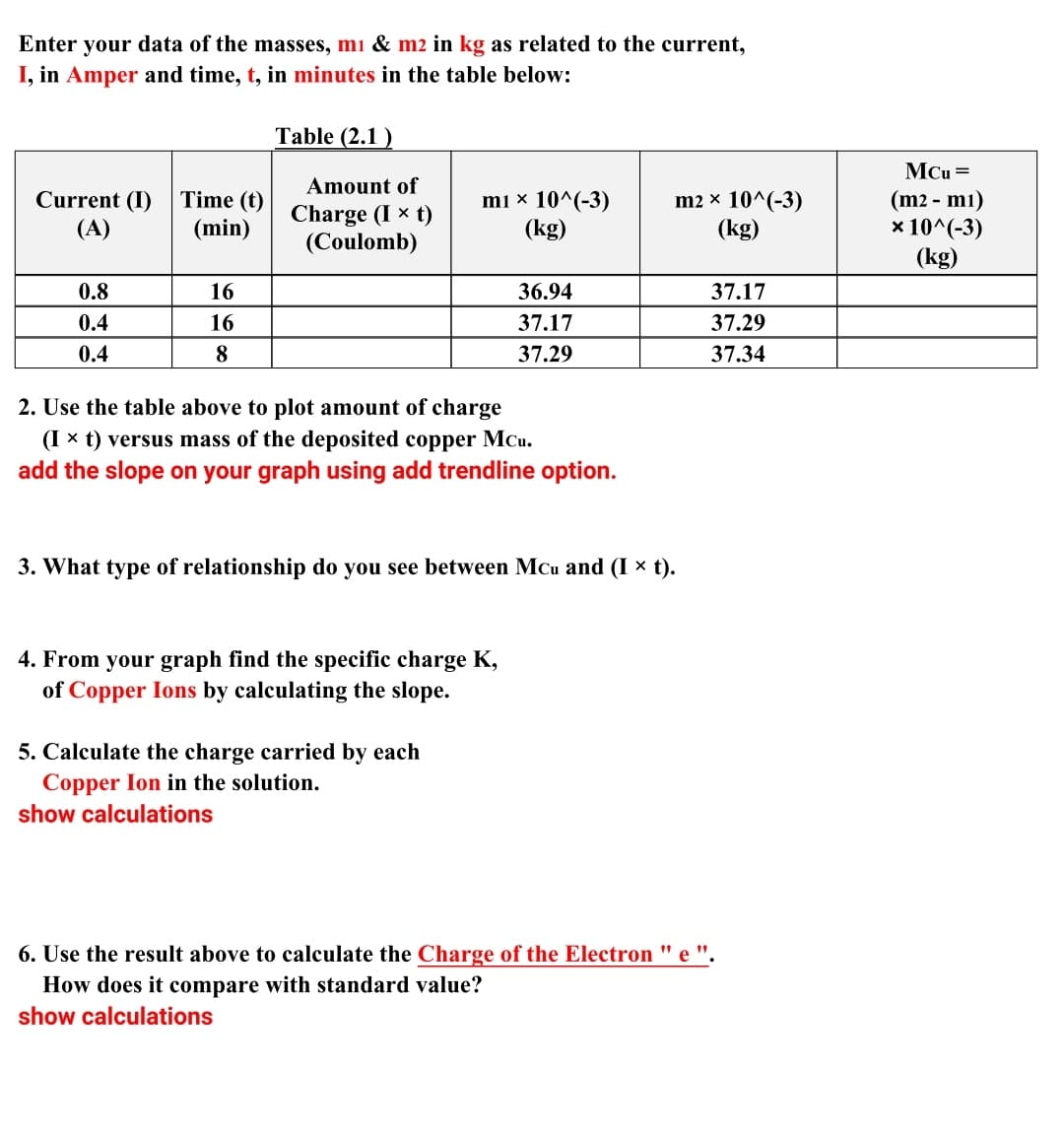
Transcribed Image Text:Enter your data of the masses, mi & m2 in kg as related to the current,
I, in Amper and time, t, in minutes in the table below:
Table (2.1 )
MCu =
Amount of
Current (I)
(A)
Time (t)
(min)
Charge (I x t)
(Coulomb)
mı × 10^(-3)
(kg)
m2 x 10^(-3)
(kg)
(m2 - mı)
x 10^(-3)
(kg)
0.8
16
36.94
37.17
0.4
16
37.17
37.29
0.4
8
37.29
37.34
2. Use the table above to plot amount of charge
(I x t) versus mass of the deposited copper MCu.
add the slope on your graph using add trendline option.
3. What type of relationship do you see between MCu and (I x t).
4. From your graph find the specific charge K,
of Copper Ions by calculating the slope.
5. Calculate the charge carried by each
Copper Ion in the solution.
show calculations
6. Use the result above to calculate the Charge of the Electron " e ".
How does it compare with standard value?
show calculations
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

