Equilibrium Constant 82 4) ½N2(g) + 02(g)= NO2(g) Kc 1.04 x 10-9 N2(g) + 202(g) N204(g) Kc =7.42 x 10-18 %3D Calculate Kc for each of the following. (a) 2NO2(g) = N2(g) + 202(g) (b) N2(g) + 202(g) = N2O4(g) PA at O002 16 mnundiliupo 0002 10 eft 00. Cci boouho ss sllo eolom 02.1 bae chHto estom 021 H Tondiliupe is inso H lo esfomem won (c) 2NO2(g) = N2O4(g) a li nao adt ai ol borsluoleg uor asulev od of qued blooerW ( ort nadw M000,0 bau o oldeid 2aw bo ov suiev ol enos walha g0)dgid 2aw bo oy eulev TUwens uoy nislg M00.210 oulsDsd in la6
Equilibrium Constant 82 4) ½N2(g) + 02(g)= NO2(g) Kc 1.04 x 10-9 N2(g) + 202(g) N204(g) Kc =7.42 x 10-18 %3D Calculate Kc for each of the following. (a) 2NO2(g) = N2(g) + 202(g) (b) N2(g) + 202(g) = N2O4(g) PA at O002 16 mnundiliupo 0002 10 eft 00. Cci boouho ss sllo eolom 02.1 bae chHto estom 021 H Tondiliupe is inso H lo esfomem won (c) 2NO2(g) = N2O4(g) a li nao adt ai ol borsluoleg uor asulev od of qued blooerW ( ort nadw M000,0 bau o oldeid 2aw bo ov suiev ol enos walha g0)dgid 2aw bo oy eulev TUwens uoy nislg M00.210 oulsDsd in la6
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Equilibrium Constant
82
4) ½N2(g) + 02(g)= NO2(g)
Kc 1.04 x 10-9
N2(g) + 202(g) N204(g)
Kc =7.42 x 10-18
%3D
Calculate Kc for each of the following.
(a) 2NO2(g) = N2(g) + 202(g)
(b) N2(g) + 202(g) = N2O4(g)
PA at O002 16 mnundiliupo
0002 10 eft 00. Cci boouho ss sllo eolom 02.1 bae chHto estom 021 H
Tondiliupe is inso H lo esfomem won
(c) 2NO2(g) = N2O4(g)
a li nao adt ai ol borsluoleg uor asulev od of qued blooerW (
ort nadw M000,0 bau o oldeid 2aw bo ov suiev ol enos walha
g0)dgid 2aw bo oy eulev
TUwens uoy nislg M00.210 oulsDsd in la6
Expert Solution
Concept Introductions :
The equilibrium constant of a reaction is calculated by the help of equilibrium concentrations of the components and their stoichiometric coefficients.
Given Data :
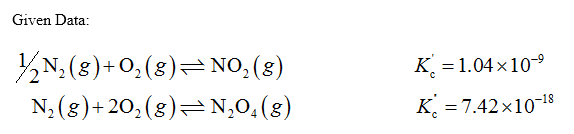
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 8 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY