Examine the following compounds, and answer questions 31-35. CH3-CH2-CH-CH, CH-CH-CH,-OH CH-CH2-OH CH-CH-OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-OH CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH, Он CH, CH.CH, II III IV V VI 31 Is 31
Examine the following compounds, and answer questions 31-35. CH3-CH2-CH-CH, CH-CH-CH,-OH CH-CH2-OH CH-CH-OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-OH CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH, Он CH, CH.CH, II III IV V VI 31 Is 31
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter10: Fuels, Organic Chemicals, And Polymers
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6QRT
Related questions
Question
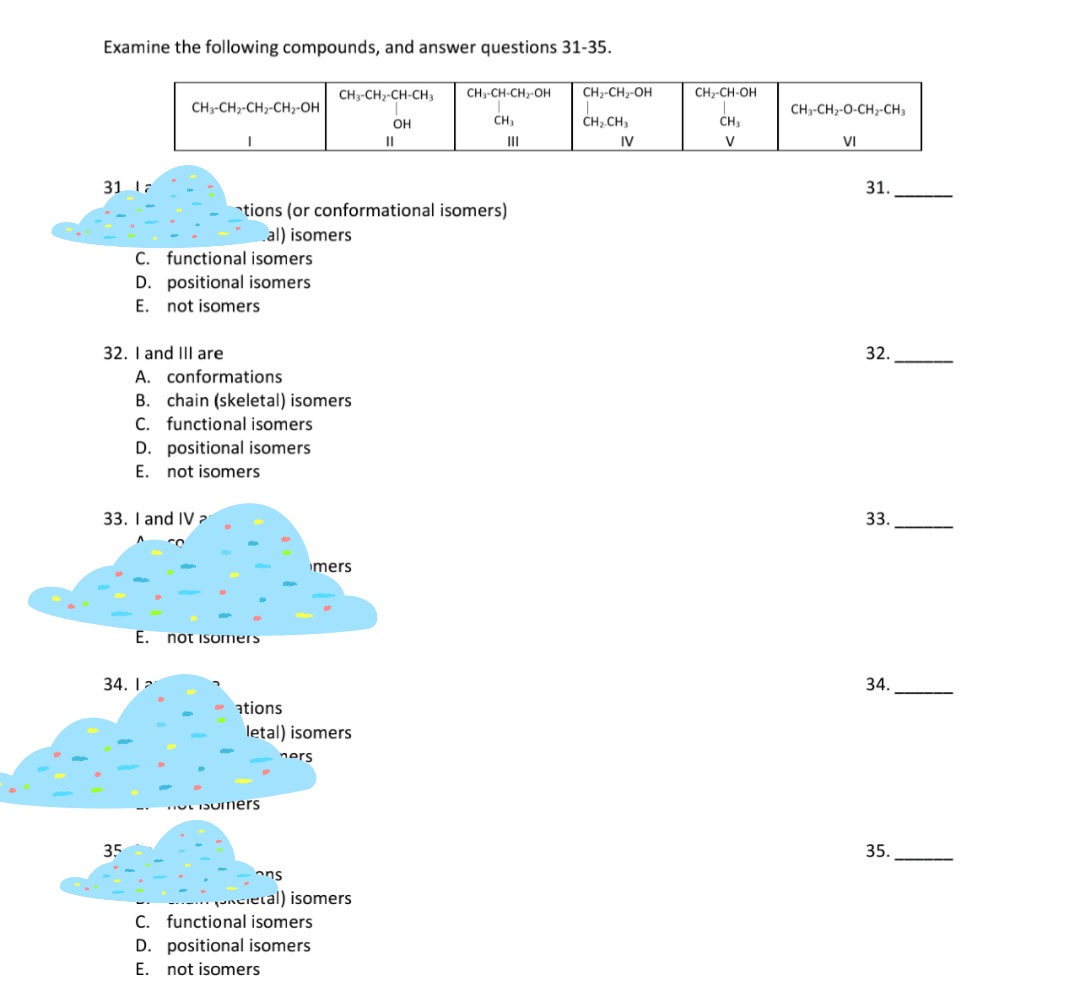
Transcribed Image Text:Examine the following compounds, and answer questions 31-35.
CH3-CH2-CH-CH,
CH-CH-CH,-OH
CH-CH2-OH
CH-CH-OH
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-OH
CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH,
Он
CH,
CH.CH,
II
III
IV
V
VI
31 Is
31
Expert Solution
Step 1
The isomers which have same chemical formula but different structures are called as structural isomers. The structural isomers can be broadly divided into following groups:
- Chain isomers: The structural isomers which show difference in the arrangement of the carbon atoms in the carbon skeletal are referred to as chain isomers. For example: Butane and 2-methylpropne are considered as chain isomers because they show difference in the arrangement of the methyl group in the skeletal.
- Positional isomers: The structural isomers which show difference in the position of the functional group in the structure are referred to as positional isomers. For example: 1-chlorobutne and 2-chloroutane are positional isomers.
- Functional isomers: The structural isomers which show difference in the type of the functional group present in their structure are referred to as functional isomers. For example: Acetone (ketone) and propanal (aldehyde) are the examples of functional isomers.
- Ring chain isomers: When the structural isomerism is exhibited by the ring, it is called as ring chain isomerism and the isomers are called as ring chain isomers. For example: Cyclobutane and 1-methylcyclopropane are the examples of ring chain isomers.
- Tautomerism
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning