Factor-price differentials might persist in equilibrium because of A. compensating differentials where, for example, some jobs are cleaner than others. B. intrinsic differences where, for example, some jobs allow for independence and flexibility. C. intrinsic differences where, for example, the fertility of land can only be increased with costly fertilizers. D. compensating differentials where, for example, engineers must train to acquire adequate skills for employment.
Factor-price differentials might persist in equilibrium because of A. compensating differentials where, for example, some jobs are cleaner than others. B. intrinsic differences where, for example, some jobs allow for independence and flexibility. C. intrinsic differences where, for example, the fertility of land can only be increased with costly fertilizers. D. compensating differentials where, for example, engineers must train to acquire adequate skills for employment.
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Course List)
16th Edition
ISBN:9781305506725
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
ChapterST8: Earnings Differences Between Men And Women
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2CQ
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Factor-price differentials might persist in equilibrium because of
O A. compensating differentials where, for example, some jobs are cleaner than others.
B. intrinsic differences where, for example, some jobs allow for independence and flexibility.
C. intrinsic differences where, for example, the fertility of land can only be increased with costly fertilizers.
D. compensating differentials where, for example, engineers must train to acquire adequate skills for employment.
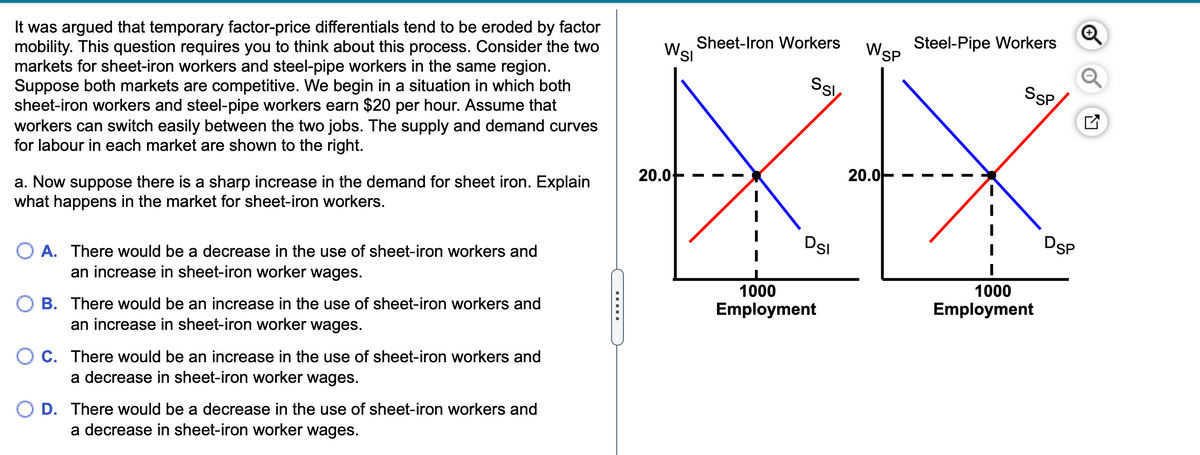
Transcribed Image Text:It was argued that temporary factor-price differentials tend to be eroded by factor
mobility. This question requires you to think about this process. Consider the two
markets for sheet-iron workers and steel-pipe workers in the same region.
Suppose both markets are competitive. We begin in a situation in which both
sheet-iron workers and steel-pipe workers earn $20 per hour. Assume that
workers can switch easily between the two jobs. The supply and demand curves
for labour in each market are shown to the right.
Steel-Pipe Workers
Wsp
Sheet-Iron Workers
Wsi
SsP
20.0-
20.0-
a. Now suppose there is a sharp increase in the demand for sheet iron. Explain
what happens in the market for sheet-iron workers.
DsI
DSP
O A. There would be a decrease in the use of sheet-iron workers and
an increase in sheet-iron worker wages.
1000
1000
B. There would be an increase in the use of sheet-iron workers and
Employment
Employment
an increase in sheet-iron worker wages.
O C. There would be an increase in the use of sheet-iron workers and
a decrease in sheet-iron worker wages.
D. There would be a decrease in the use of sheet-iron workers and
a decrease in sheet-iron worker wages.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


